|
β-zearalenol
β-Zearalenol is a nonsteroidal estrogen of the resorcylic acid lactone group related to mycoestrogens found in '' Fusarium spp''. It is the β epimer of α-zearalenol and along with α-zearalenol is a major metabolite of zearalenone formed mainly in the liver but also to a lesser extent in the intestines during first-pass metabolism. A relatively high proportion of α-zearalenol is formed from zearalenone compared to β-zearalenol in humans. β-Zearalenol is about the same or slightly less potent as an estrogen relative to zearalenone. See also * Taleranol (β-zearalanol) * Zeranol (α-zearalanol) * Zearalanone Zearalanone (ZAN) is a semi-synthetic mycoestrogen that is a derivative of zearalenone Zearalenone (ZEN), also known as RAL and F-2 mycotoxin, is a potent estrogenic metabolite produced by some ''Fusarium'' and ''Gibberella'' species. Specificall ... References {{DEFAULTSORT:Zearalenol, alpha- Lactones Mycoestrogens Mycotoxins Resorcinols ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zearalenone
Zearalenone (ZEN), also known as RAL and F-2 mycotoxin, is a potent estrogenic metabolite produced by some ''Fusarium'' and ''Gibberella'' species. Specifically, the ''Gibberella zeae ,'' the fungal species where zearalenone was initially detected, in its asexual/anamorph stage is known as ''Fusarium graminearum.'' Several ''Fusarium'' species produce toxic substances of considerable concern to livestock and poultry producers, namely deoxynivalenol, T-2 toxin, HT-2 toxin, diacetoxyscirpenol (DAS) and zearalenone. Particularly, ZEN is produced by ''Fusarium graminearum'', ''Fusarium culmorum'', '' Fusarium cerealis'', '' Fusarium equiseti'', ''Fusarium verticillioides'', and '' Fusarium incarnatum''. Zearalenone is the primary toxin that binds to estrogen receptors, causing infertility, abortion or other breeding problems, especially in swine. Often, ZEN is detected together with deoxynivalenol in contaminated samples and its toxicity needs to be considered in combination with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
α-zearalenol
α-Zearalenol is a nonsteroidal estrogen of the resorcylic acid lactone group related to mycoestrogens found in '' Fusarium spp''. It is the α epimer of β-zearalenol and along with β-zearalenol is a major metabolite of zearalenone formed mainly in the liver but also to a lesser extent in the intestines during first-pass metabolism. A relatively low proportion of β-zearalenol is formed from zearalenone compared to α-zearalenol in humans. α-Zearalenol is about 3- to 4-fold more potent as an estrogen relative to zearalenone. See also * Taleranol (β-zearalanol) * Zeranol (α-zearalanol) * Zearalanone Zearalanone (ZAN) is a semi-synthetic mycoestrogen that is a derivative of zearalenone Zearalenone (ZEN), also known as RAL and F-2 mycotoxin, is a potent estrogenic metabolite produced by some ''Fusarium'' and ''Gibberella'' species. Specificall ... References {{DEFAULTSORT:Zearalenol, alpha- Lactones Mycoestrogens Mycotoxins Resorcinols ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resorcylic Acid Lactone
Resorcylic acid lactones are a group of estrogenic compounds. They are lactones of resorcylic acid. Examples include the mycoestrogens (and synthetic analogues) zearalenone, zearalanone, zeranol (α-zearalanol), taleranol (β-zearalanol), α-zearalenol, and β-zearalenol β-Zearalenol is a nonsteroidal estrogen of the resorcylic acid lactone group related to mycoestrogens found in '' Fusarium spp''. It is the β epimer of α-zearalenol and along with α-zearalenol is a major metabolite of zearalenone formed main .... References Dihydroxybenzoic acids Lactones Mycoestrogens {{Chemistry-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mycoestrogen
Mycoestrogens are xenoestrogens produced by fungi. They are sometimes referred to as mycotoxins. Among important mycoestrogens are zearalenone, zearalenol and zearalanol. Although all of these can be produced by various ''Fusarium'' species, zearalenol and zearalanol may also be produced endogenously in ruminants that have ingested zearalenone. Alpha-zearalanol is also produced semisynthetically, for veterinary use; such use is prohibited in the European Union. Mechanism of action Mycoestrogens act as agonists of the estrogen receptors, ERα and ERβ. Sources Mycoestrogens are produced by various strains of fungi, many of which fall under the genus ''Fusarium''. ''Fusarium'' fungi are filamentous fungi that are found in the soil and are associated with plants and some crops, especially cereals. Zearalenone is mainly produced by ''F. graminearum'' and ''F. culmorum'' strains, which inhabit different areas depending on temperature and humidity. ''F. graminearum'' prefers to inha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mycoestrogens
Mycoestrogens are xenoestrogens produced by fungi. They are sometimes referred to as mycotoxins. Among important mycoestrogens are zearalenone, zearalenol and zearalanol. Although all of these can be produced by various ''Fusarium'' species, zearalenol and zearalanol may also be produced endogenously in ruminants that have ingested zearalenone. Alpha-zearalanol is also produced semisynthetically, for veterinary use; such use is prohibited in the European Union. Mechanism of action Mycoestrogens act as agonists of the estrogen receptors, ERα and ERβ. Sources Mycoestrogens are produced by various strains of fungi, many of which fall under the genus ''Fusarium''. ''Fusarium'' fungi are filamentous fungi that are found in the soil and are associated with plants and some crops, especially cereals. Zearalenone is mainly produced by ''F. graminearum'' and ''F. culmorum'' strains, which inhabit different areas depending on temperature and humidity. ''F. graminearum'' prefers to inha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zearalanone
Zearalanone (ZAN) is a semi-synthetic mycoestrogen that is a derivative of zearalenone (ZEN). Zearalanone is extracted from medical herbs and edible herbs alone with other substance called aflatoxins in the same time by a specific immunoaffinity column. Zearalanone has six analog. They are ZEN, zearalanone, α-zeralanol, β-zeralanol, α-zearalenol, and β-zearalenol. See also * α-Zearalenol * β-Zearalenol * Taleranol * Zeranol Zeranol (, , ) (brand names Frideron, Ralabol, Ralgro, Ralone, Zerano; developmental code names MK-188, P-1496), or zearanol, also known as α-zearalanol or simply zearalanol, is a synthetic nonsteroidal estrogen of the resorcylic acid lactone R ... References Estrogens Lactones Resorcinols {{biochem-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nonsteroidal
A nonsteroidal compound is a drug that is not a steroid nor a steroid derivative. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are distinguished from corticosteroids as a class of anti-inflammatory agents. List of nonsteroidal steroid receptor modulators Examples include the following: * Estrogens: benzestrol, bifluranol, estrobin (DBE), diethylstilbestrol (stilbestrol), dienestrol, erteberel, fosfestrol, hexestrol (dihydroxystilbestrol), methallenestril, methestrol, methestrol dipropionate, paroxypropione, prinaberel, and triphenylethylene, as well as many xenoestrogens * : acolbifene, afimoxifene, arzoxifene, bazedoxifene, broparestrol, chlorotrianisene, clomifene, clomifenoxide, cyclofenil, droloxifene, enclomifene, endoxifen, ethamoxytriphetol, fispemifene, idoxifene, lasofoxifene, levormeloxifene, miproxifene, nafoxidine, nitromifene, ormeloxifene, ospemifene, panomifene, pipendoxifene, raloxifene, tamoxifen, toremifene, trioxifene, zindoxifene, zuclomifene * An ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taleranol
Taleranol (International Nonproprietary Name, INN, United States Adopted Name, USAN) (developmental code name P-1560), or teranol, also known as β-zearalanol, is a synthetic compound, synthetic, nonsteroidal estrogen of the resorcylic acid lactone group related to mycoestrogens found in ''Fusarium, Fusarium spp'' which was never marketed. It is the β epimer of zeranol (α-zearalanol) and is a major metabolite of zeranol but with less biological activity. See also * α-Zearalenol * β-Zearalenol * Zearalanone * Zearalenone References Lactones Mycoestrogens Mycotoxins Resorcinols {{genito-urinary-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
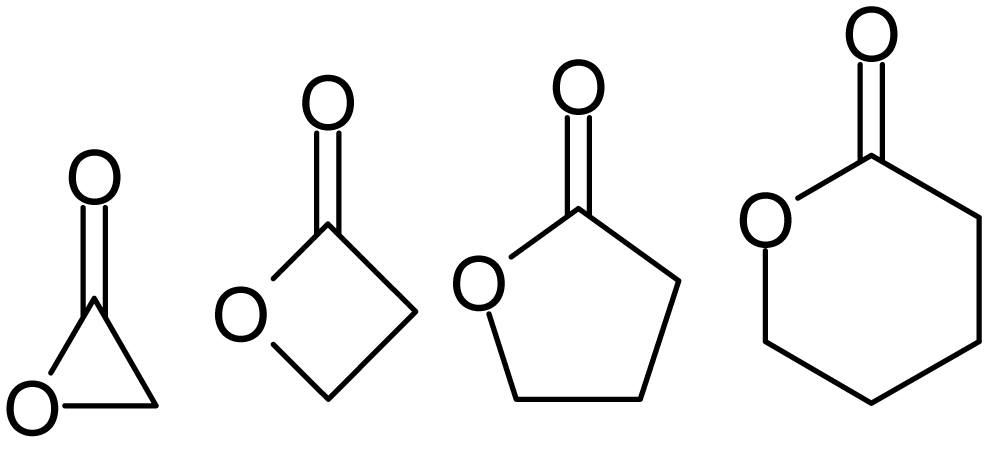
Lactones
Lactones are cyclic carboxylic esters, containing a 1-oxacycloalkan-2-one structure (), or analogues having unsaturation or heteroatoms replacing one or more carbon atoms of the ring. Lactones are formed by intramolecular esterification of the corresponding hydroxycarboxylic acids, which takes place spontaneously when the ring that is formed is five- or six-membered. Lactones with three- or four-membered rings (α-lactones and β-lactones) are very reactive, making their isolation difficult. Special methods are normally required for the laboratory synthesis of small-ring lactones as well as those that contain rings larger than six-membered. Nomenclature Lactones are usually named according to the precursor acid molecule (''aceto'' = 2 carbon atoms, ''propio'' = 3, ''butyro'' = 4, ''valero'' = 5, ''capro'' = 6, etc.), with a ''-lactone'' suffix and a Greek letter prefix that specifies the number of carbon atoms in the heterocycle — that is, the distance between the relevant -OH ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zeranol
Zeranol (, , ) (brand names Frideron, Ralabol, Ralgro, Ralone, Zerano; developmental code names MK-188, P-1496), or zearanol, also known as α-zearalanol or simply zearalanol, is a synthetic nonsteroidal estrogen of the resorcylic acid lactone group related to mycoestrogens found in fungi in the ''Fusarium'' genus and is used mainly as an anabolic agent in veterinary medicine. Zeranol is approved for use as a growth promoter in livestock, including beef cattle, under the brand name Ralgro (by Merck Animal Health) in the United States. In Canada, it is approved for use in beef cattle only. Its application is not approved for use in the European Union. However, it is marketed under the brand name Ralone in Spain. Although zeranol may increase cancer cell proliferation in already existing breast cancer, dietary exposure from the use of zeranol-containing implants in cattle is insignificant. Zeranol may be found as a contaminant in fungus-infected crops. It is 3 to 4 times more pote ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liver
The liver is a major Organ (anatomy), organ only found in vertebrates which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of proteins and biochemicals necessary for digestion and growth. In humans, it is located in the quadrant (anatomy), right upper quadrant of the abdomen, below the thoracic diaphragm, diaphragm. Its other roles in metabolism include the regulation of Glycogen, glycogen storage, decomposition of red blood cells, and the production of hormones. The liver is an accessory digestive organ that produces bile, an alkaline fluid containing cholesterol and bile acids, which helps the fatty acid degradation, breakdown of fat. The gallbladder, a small pouch that sits just under the liver, stores bile produced by the liver which is later moved to the small intestine to complete digestion. The liver's highly specialized biological tissue, tissue, consisting mostly of hepatocytes, regulates a w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First-pass Metabolism
The first pass effect (also known as first-pass metabolism or presystemic metabolism) is a phenomenon of drug metabolism whereby the concentration of a drug, specifically when administered orally, is greatly reduced before it reaches the systemic circulation. It is the fraction of drug lost during the process of absorption which is generally related to the liver and gut wall. Notable drugs that experience a significant first-pass effect are buprenorphine, chlorpromazine, cimetidine, diazepam, ethanol (drinking alcohol), imipramine, insulin, lidocaine, midazolam, morphine, pethidine, propranolol, and tetrahydrocannabinol (THC). First pass metabolism may occur in the liver (for propranolol, lidocaine, clomethiazole, and NTG) or in the gut (for benzylpenicillin and insulin). After a drug is swallowed, it is absorbed by the digestive system and enters the hepatic portal system. It is carried through the portal vein into the liver before it reaches the rest of the body. The liver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |