|
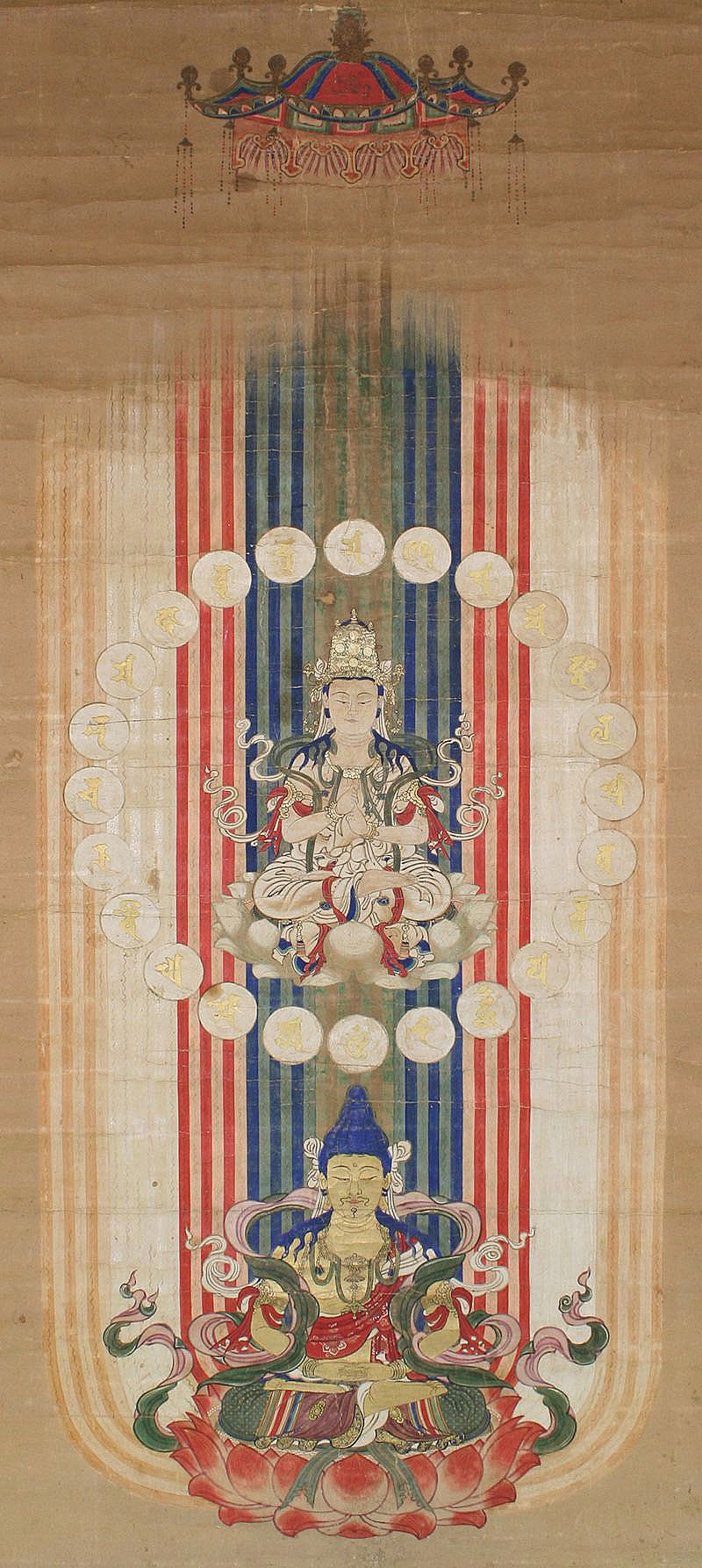
ŇĆjŇć
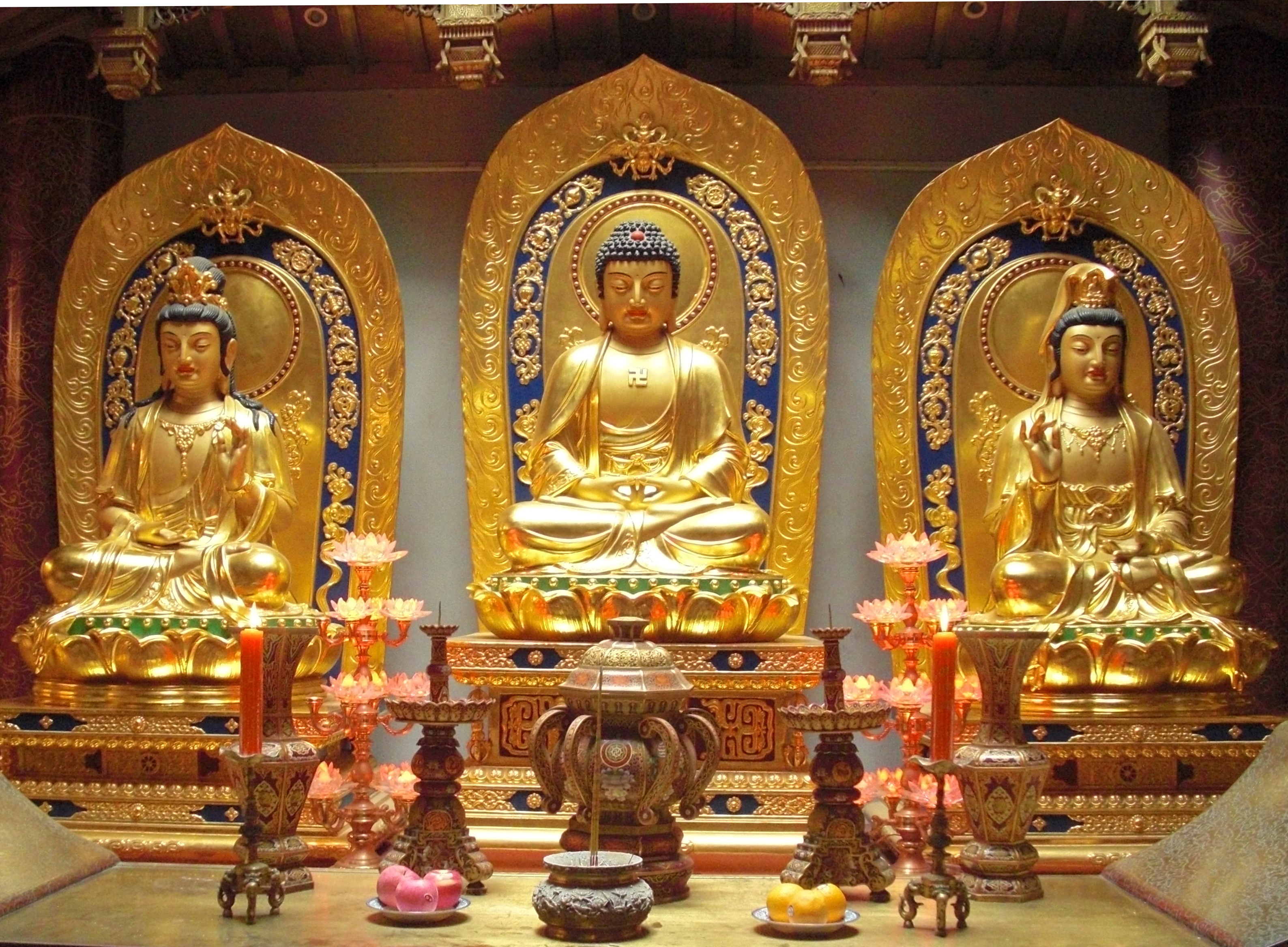
The term ŇĆjŇć ( ja, ŚĺÄÁĒü) is a term in Japanese Buddhism for rebirth in the Pure Land of Amitabha Buddha. Sometimes the term is expressed as . The subject of how to obtain birth in the Pure Land remained an important question throughout Japanese Buddhist history even until today. The Nara Schools The early Nara Buddhism schools provided different opinions as to how to obtain rebirth in the Pure Land, though in some cases, such as the HossŇć school taught that icchantikas (people who committed the Five Grave Acts) could not obtain rebirth ever. Other schools taught that while accessible to all, the rituals involved were difficult, or that rebirth was not desirable. Tendai and Shingon Early sects, particularly the Tendai and Shingon sects relied on esoteric texts, or interpretations of the Contemplation Sutra to develop rituals and visualizations of rebirth in the Pure Land. Genshin, a Tendai monk, wrote the ''ŇĆjŇćyŇćshŇę'' in which he described the horrors of Hell i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genshin
, also known as , was the most influential of a number of scholar-monks of the Buddhist Tendai sect active during the tenth and eleventh centuries in Japan. Genshin, who was trained in both esoteric and exoteric teachings, wrote a number of treatises pertaining to the increasingly popular Pure Land Buddhism from a Tendai viewpoint, but his magnum opus, the , had considerable influence on later Pure Land teachers such as Honen and Shinran. In spite of growing political tensions within the Tendai religious hierarchy, and despite being one of the two leading disciples of the controversial Ryogen, 18th head of the Enryakuji Temple, Genshin and a small group of fellow monks maintained a secluded community at Yokawa on Mount Hiei solely devoted toward rebirth in the Pure Land, while staying largely neutral in the conflict. He was one of the thinkers who maintained that the nembutsu ritual, which was said to induce a vision of Amida, was an important hermeneutic principle in the Bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ŇĆjŇćyŇćshŇę
The was an influential medieval Buddhist text composed in 985 by the Japanese Buddhist monk Genshin. Three volumes in length and in kanbun prose, the text is a comprehensive analysis of Buddhist practices related to rebirth in the Pure Land of Amida Buddha, drawing upon earlier Buddhist texts from China, and sutras such as the Contemplation Sutra. Genshin advocated a collection of mutually supportive practices, such as sutra recitation, centered around visual meditation of Amitabha Buddha where later Pure Land sects favored an approach that relied on exclusive recitation of the verbal ''nembutsu''. The text is also well known for its graphic descriptions of the Hell realms, and sufferings one might endure for harmful acts committed in this life. Its influence can be seen in Japanese Buddhist paintings and other, later, texts. The founder of JŇćdo ShinshŇę Buddhism, Shinran, wrote an influential commentary on the ''ŇĆjŇćyŇćshŇę'' titled, "Notes on Essentials of Rebirth", while ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pure Land Buddhism
Pure Land Buddhism (; ja, śĶĄŚúüšĽŹśēô, translit=JŇćdo bukkyŇć; , also referred to as Amidism in English,) is a broad branch of Mahayana Buddhism focused on achieving rebirth in a Buddha's Buddha-field or Pure Land. It is one of the most widely practiced traditions of Buddhism in East Asia. According to Charles B. Jones "Pure Land is the dominant form of Buddhism in China, Japan and Korea."Jones, Charles B. (2021). ''Pure Land: History, Tradition, and Practice'', p. xii. Shambhala Publications, . In Chinese Buddhism, the tradition is sometimes called a zŇćng (school) in an institutional sense, but historically it was most commonly described as a "dharma-gate" (f«ém√©n ś≥ēťĖÄ), referring to a method of Buddhist practice. In Japanese Buddhism, the term more commonly refers to specific institutions.Jones, Charles B. (2019) ''Chinese Pure Land Buddhism, Understanding a Tradition of Practice,'' pp. 10-12. University of Hawai‚Äėi Press / Honolulu. In Tibetan Buddhism, prayers an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tendai
, also known as the Tendai Lotus School (Ś§©ŚŹįś≥ēŤŹĮŚģó ''Tendai hokke shŇę,'' sometimes just "''hokke shŇę''") is a MahńĀyńĀna Buddhist tradition (with significant esoteric elements) officially established in Japan in 806 by the Japanese monk SaichŇć ( posthumously known as DengyŇć Daishi). The Tendai school, which has been based on Mount Hiei since its inception, rose to prominence during the Heian period (794-1185). It gradually eclipsed the powerful ''HossŇć'' school and competed with the rival Shingon school to become the most influential sect at the Imperial court. By the Kamakura period (1185-1333), Tendai had become one of the dominant forms of Japanese Buddhism, with numerous temples and vast landholdings. During the Kamakura period, various monks left Tendai (seeing it as corrupt) to establish their own "new" or "Kamakura" Buddhist schools such as JŇćdo-shŇę, Nichiren-shŇę and SŇćtŇć Zen. The destruction of the head temple of Enryaku-ji by Oda Nobunaga in 1571, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hell In Buddhism
Naraka ( sa, ŗ§®ŗ§įŗ§ē; pi, ūĎĶūĎÄļūĎÄ≠ūĎĨ Niraya) is a term in Buddhist cosmology usually referred to in English as "hell" (or "hell realm") or "purgatory". The Narakas of Buddhism are closely related to ''Diyu'', the hell in Chinese mythology. A Naraka differs from the hell of Christianity in two respects: firstly, beings are not sent to Naraka as the result of a Damnation, divine judgment or punishment; and secondly, the length of a being's stay in a Naraka is not eternal, though it is usually incomprehensibly long, from hundreds of millions to sextillions (1021) of years. A being is born into a Naraka as a direct result of its accumulated actions (Karma in Buddhism, karma) and resides there for a finite period of time until that karma has achieved its full result. After its karma is used up, it will be reborn in one of the higher worlds as the result of karma that had not yet ripened. In the Upajjhatthana Sutta#DevadŇęta Sutta (MN 130 & AN 3.35), Devaduta Sutta, the 13 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kamakura Period
The is a period of Japanese history that marks the governance by the Kamakura shogunate, officially established in 1192 in Kamakura by the first ''shŇćgun'' Minamoto no Yoritomo after the conclusion of the Genpei War, which saw the struggle between the Taira and Minamoto clans. The period is known for the emergence of the samurai, the warrior caste, and for the establishment of feudalism in Japan. During the early Kamakura period, the shogunate continued warfare against the Northern Fujiwara which was only defeated in 1189. Then, the authority to the Kamakura rulers waned in the 1190s and power was transferred to the powerful HŇćjŇć clan in the early 13th century with the head of the clan as regent (Shikken) under the shogun which became a powerless figurehead. The later Kamakura period saw the invasions of the Mongols in 1274 and again in 1281. To reduce the amount of chaos, the HŇćjŇć rulers decided to decentralize power by allowing two imperial lines ‚Äď Northern and Southern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mantra Of Light
The Mantra of Light, also called the ''Mantra of the Unfailing Rope Snare'', is an important mantra of the Shingon and Kegon sects of Buddhism, but is not emphasized in other Vajrayana sects of Buddhism. It is taken from the ''AmoghapńĀŇõa-kalparńĀja-sŇętra'' (Chinese translation Taisho ed. no. 1092) or ''Sutra of the Mantra of the Unfailing Rope Snare of the Buddha Vairocana's Great Baptism'' and is associated with the deity AmoghapńĀŇõa (Unfailing Rope), a form of Avalokiteshvara''.'' The mantra is the following: * Sanskrit :Roman Script: OŠĻÉ Amogha Vairocana MahńĀmudrńĀ MaŠĻáipadma JvalapravartńĀya HŇęŠĻÉ :Devanagari: ŗ•ź ŗ§Öŗ§ģŗ•čŗ§ė ŗ§Ķŗ•ąŗ§įŗ•čŗ§öŗ§® ŗ§ģŗ§Ļŗ§ĺŗ§ģŗ•Āŗ§¶ŗ•ćŗ§įŗ§ĺ ŗ§ģŗ§£ŗ§Ņŗ§™ŗ§¶ŗ•ćŗ§ģ ŗ§úŗ•ćŗ§Ķŗ§≤ ŗ§™ŗ•ćŗ§įŗ§Ķŗ§įŗ•ćŗ§§ŗ§ĺŗ§Į ŗ§Ļŗ•āŗ§Ā : SiddhaŠĻÉ: : *Japanese: „Āä„āď „Āā„Āľ„Āć„āÉ „ĀĻ„ĀĄ„āć„Āó„āÉ„Āģ„ĀÜ „Āĺ„Āč„Āľ„Ā†„āČ „Āĺ„Āę „ĀĮ„āď„Ā©„Āĺ „Āė„āď„Āį„āČ „ĀĮ„āČ„Āį„āä„Āü„āĄ „ĀÜ„āď Om abogya beiroshanŇć makabodara mani handoma jinbara harabari tayaun *Korean: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Icchantika
In Mahayana Buddhism the ''icchantika'' is a deluded being who can never attain enlightenment (Buddhahood). Description According to some Mahayana Buddhist scriptures, the ''icchantika'' is the most base and spiritually deluded of all types of being. The term implies being given over to total hedonism and greed. In the Tathagatagarbha sutras, some of which pay particular attention to the ''icchantikas'', the term is frequently used of those persons who do not believe in the Buddha, his eternal Selfhood and his Dharma (Truth) or in karma; who seriously transgress against the Buddhist moral codes and vinaya; and who speak disparagingly and dismissively of the reality of the immortal Buddha-nature (''Buddha-dhatu'') or Tathagatagarbha present within all beings. The two shortest versions of the Mahayana Mahaparinirvana Sutra - one translated by Fa-xian, and the other a middle-length Tibetan version of the sutra - indicate that the ''icchantika'' has so totally severed all his/her root ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HŇćnen
was the religious reformer and founder of the first independent branch of Japanese Pure Land Buddhism called . He is also considered the Seventh JŇćdo ShinshŇę Patriarch. HŇćnen became a Tendai initiate at an early age, but grew disaffected and sought an approach to Buddhism that anyone could follow, even during the perceived Three Ages of Buddhism, Age of Dharma Decline. After discovering the writings of the Chinese Buddhist Shandao, he undertook the teaching of rebirth in the pure land of AmitńĀbha through nianfo or "recitation of the Buddha's name". HŇćnen gathered a wide array of followers and critics. Emperor Tsuchimikado exiled HŇćnen and his followers in 1207 after an incident regarding two of his disciples in addition to persuasion by influential Buddhist communities. HŇćnen was eventually pardoned and allowed to return to Kyoto, where he stayed for a short time before his death. Biography Early life HŇćnen was born to a prominent family in the city of Kume in Mim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
JŇćdo ShinshŇę
, also known as Shin Buddhism or True Pure Land Buddhism, is a school of Pure Land Buddhism. It was founded by the former Tendai Japanese monk Shinran. Shin Buddhism is the most widely practiced branch of Buddhism in Japan. History Shinran (founder) Shinran (1173‚Äď1263) lived during the late Heian to early Kamakura period (1185‚Äď1333), a time of turmoil for Japan when the emperor was stripped of political power by the ''shŇćguns''. Shinran's family had a high rank at the Imperial court in Kyoto, but given the times, many aristocratic families were sending sons off to be Buddhist monks instead of having them participate in the Imperial government. When Shinran was nine (1181), he was sent by his uncle to Mount Hiei, where he was ordained as a ŇõrńĀmaŠĻáera in the Tendai sect. Over time, Shinran became disillusioned with how Buddhism was practiced, foreseeing a decline in the potency and practicality of the teachings espoused. Shinran left his role as a ''dosŇć'' ("practice ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |