Mantra of Light on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
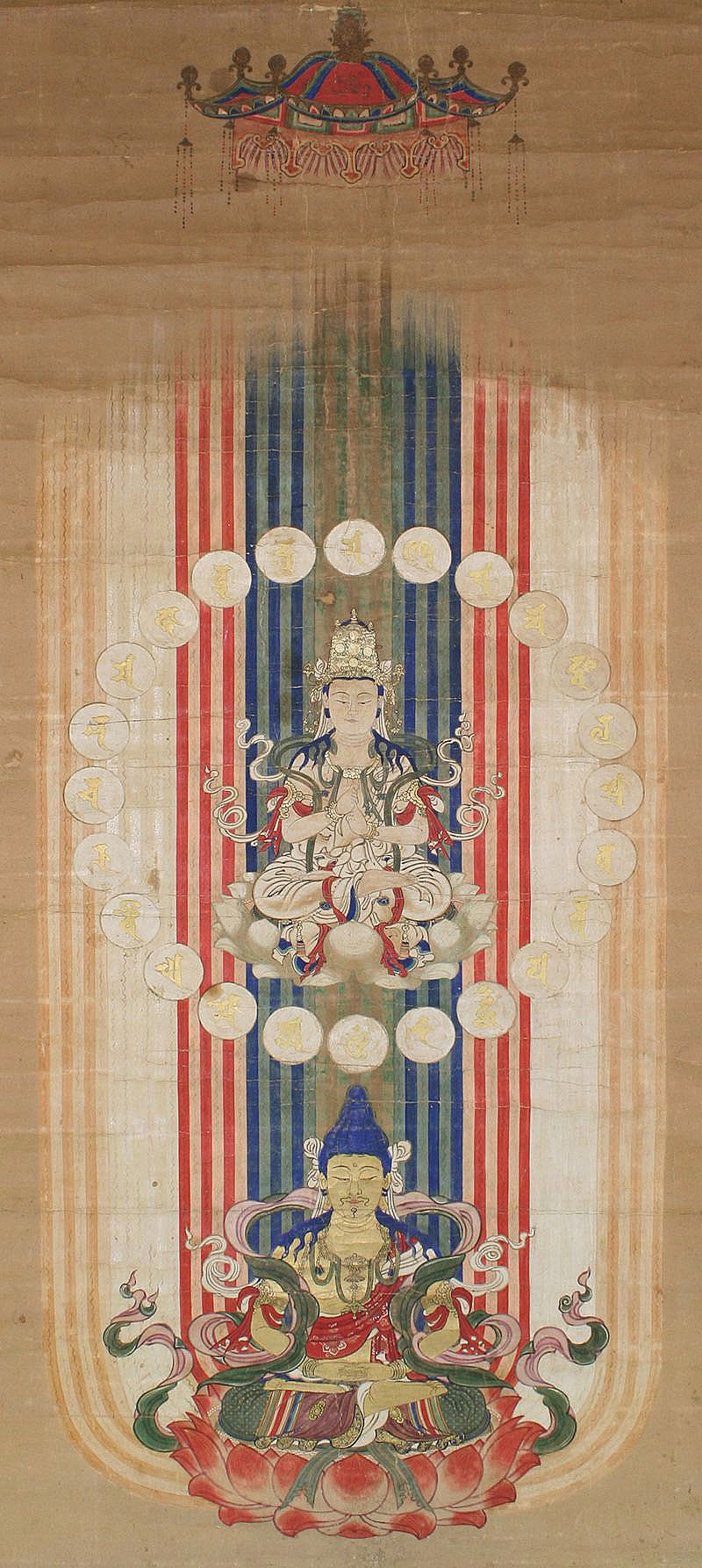 The Mantra of Light, also called the ''Mantra of the Unfailing Rope Snare'', is an important
The Mantra of Light, also called the ''Mantra of the Unfailing Rope Snare'', is an important
 The Mantra of Light, also called the ''Mantra of the Unfailing Rope Snare'', is an important
The Mantra of Light, also called the ''Mantra of the Unfailing Rope Snare'', is an important mantra
A mantra (Pali: ''manta'') or mantram (मन्त्रम्) is a sacred utterance, a numinous sound, a syllable, word or phonemes, or group of words in Sanskrit, Pali and other languages believed by practitioners to have religious, ma ...
of the Shingon
file:Koyasan (Mount Koya) monks.jpg, Shingon monks at Mount Koya
is one of the major schools of Buddhism in Japan and one of the few surviving Vajrayana lineages in East Asia, originally spread from India to China through traveling monks suc ...
and Kegon
The Huayan or Flower Garland school of Buddhism (, from sa, अवतंसक, Avataṃsaka) is a tradition of Mahayana Buddhist philosophy that first flourished in China during the Tang dynasty (618-907). The Huayan worldview is based primar ...
sects of Buddhism, but is not emphasized in other Vajrayana
Vajrayāna ( sa, वज्रयान, "thunderbolt vehicle", "diamond vehicle", or "indestructible vehicle"), along with Mantrayāna, Guhyamantrayāna, Tantrayāna, Secret Mantra, Tantric Buddhism, and Esoteric Buddhism, are names referring t ...
sects of Buddhism. It is taken from the ''Amoghapāśa-kalparāja-sūtra'' (Chinese translation Taisho ed. no. 1092) or ''Sutra of the Mantra of the Unfailing Rope Snare of the Buddha Vairocana's Great Baptism'' and is associated with the deity Amoghapāśa (Unfailing Rope), a form of Avalokiteshvara''.''
The mantra is the following:
* Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had diffused there from the northwest in the late ...
:Roman Script: Oṃ Amogha Vairocana Mahāmudrā Maṇipadma Jvalapravartāya Hūṃ
:Devanagari
Devanagari ( ; , , Sanskrit pronunciation: ), also called Nagari (),Kathleen Kuiper (2010), The Culture of India, New York: The Rosen Publishing Group, , page 83 is a left-to-right abugida (a type of segmental Writing systems#Segmental syste ...
: ॐ अमोघ वैरोचन महामुद्रा मणिपद्म ज्वल प्रवर्ताय हूँ
: Siddhaṃ:
:
*Japanese
Japanese may refer to:
* Something from or related to Japan, an island country in East Asia
* Japanese language, spoken mainly in Japan
* Japanese people, the ethnic group that identifies with Japan through ancestry or culture
** Japanese diaspor ...
: おん あぼきゃ べいろしゃのう まかぼだら まに はんどま じんばら はらばりたや うん Om abogya beiroshanō makabodara mani handoma jinbara harabari tayaun
*Korean
Korean may refer to:
People and culture
* Koreans, ethnic group originating in the Korean Peninsula
* Korean cuisine
* Korean culture
* Korean language
**Korean alphabet, known as Hangul or Chosŏn'gŭl
**Korean dialects and the Jeju language
** ...
: 옴 아모가 바이로차나 마하무드라 마니 파드마 즈바라 프라바릍타야 훔 om amoga bairochana mahamudeura mani padeuma jeubara peurabareutaya hum
*Vietnamese
Vietnamese may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Vietnam, a country in Southeast Asia
** A citizen of Vietnam. See Demographics of Vietnam.
* Vietnamese people, or Kinh people, a Southeast Asian ethnic group native to Vietnam
** Overse ...
: Án (Ông/Úm) A ma cát Hoài lô giai nã Ma cáp mẫu đức la Ma ni bá đức ma Cập phạp la Bát la phạp nhĩ đả nha Hồng
*Kanji
are the logographic Chinese characters taken from the Chinese family of scripts, Chinese script and used in the writing of Japanese language, Japanese. They were made a major part of the Japanese writing system during the time of Old Japanese ...
and Chinese script
Chinese characters () are logograms developed for the writing of Chinese. In addition, they have been adapted to write other East Asian languages, and remain a key component of the Japanese writing system where they are known as ''kanji' ...
: 唵 阿謨伽 尾盧左曩 摩訶母捺囉 麽抳 鉢納麽 入嚩攞 鉢囉韈哆野 吽 Ǎn ā mó jiā wěi lú zuǒ nǎng mó hē mǔ nà luō me nǐ bō nà me rù mó luó bō luō wà duō yě hōng
:Tibetan
Tibetan may mean:
* of, from, or related to Tibet
* Tibetan people, an ethnic group
* Tibetan language:
** Classical Tibetan, the classical language used also as a contemporary written standard
** Standard Tibetan, the most widely used spoken dial ...
: ཨོཾ་ཨ་མོ་གྷ་བཻ་རོ་ཙ་ན་མ་ཧཱ་མུ་དྲཱ་མ་ཎི་པདྨ་ཛྭ་ལ་པྲ་ཝརྟཱ་ཡ་ཧཱུྃ
The translation of this mantra, according to Professor Mark Unno, is roughly:
Another translation according to the Dharmachakra Translation Committee is: “Oṁ, amogha jewel-lotus of the splendorous great mudrā! Blaze! Set in motion! Hūṁ!”Initially, the mantra received little mention in East Asian Buddhist texts, and although Kukai brought the sutra to Japan in the 9th century, there are no records that he ever utilized it in tantric practices. Records show gradually increasing use in the
Heian Period
The is the last division of classical Japanese history, running from 794 to 1185. It followed the Nara period, beginning when the 50th emperor, Emperor Kanmu, moved the capital of Japan to Heian-kyō (modern Kyoto). means "peace" in Japanese. ...
, until the 13th century when it was popularized in medieval Japanese Buddhism
Buddhism has been practiced in Japan since about the 6th century CE. Japanese Buddhism () created many new Buddhist schools, and some schools are original to Japan and some are derived from Chinese Buddhist schools. Japanese Buddhism has had a ...
by Myōe
(February 21, 1173 – February 11, 1232) was a Japanese Buddhist monk active during the Kamakura period who also went by the name ''Kōben'' ( ja, 高弁). He was a contemporary of Jōkei and Hōnen.
Biography
Myōe was born in what is no ...
, and later by Shingon
file:Koyasan (Mount Koya) monks.jpg, Shingon monks at Mount Koya
is one of the major schools of Buddhism in Japan and one of the few surviving Vajrayana lineages in East Asia, originally spread from India to China through traveling monks suc ...
monks Eison
(1201–1290) was a Japanese Buddhist monk who founded the Shingon Risshu sect.
Eison entered religious training when he was eleven years old, studying initially at Daigo-ji and later at Kongōbu-ji. At the age of 34, while at Saidai-ji, he made ...
and Ninshō
was a Japanese Shingon Risshu priest during the Kamakura period. His was instrumental in reviving Ritsu Buddhism during this period, as well as establishing facilities to care for invalids. He was criticized by his contemporary Nichiren.
He is ...
in their ministries. Both the Mantra and the nembutsu
Nianfo (, Japanese: , , vi, niệm Phật) is a term commonly seen in Pure Land Buddhism. In the context of Pure Land practice, it generally refers to the repetition of the name of Amitābha. It is a translation of Sanskrit '' '' (or, "recolle ...
were often incorporated by medieval Buddhists at one time or another, often in the same service. A common practice for the Mantra of Light was to sprinkle pure sand, blessed with this mantra, on the body of a deceased person or their tomb, based on teachings expounded in the Sutra. The belief was that a person who had accumulated much bad karma, and possible rebirth in Hell
In religion and folklore, hell is a location in the afterlife in which evil souls are subjected to punitive suffering, most often through torture, as eternal punishment after death. Religions with a linear divine history often depict hell ...
would be immediately freed and allowed a favorable rebirth into the Pure Land
A pure land is the celestial realm of a buddha or bodhisattva in Mahayana Buddhism. The term "pure land" is particular to East Asian Buddhism () and related traditions; in Sanskrit the equivalent concept is called a buddha-field (Sanskrit ). Th ...
of Amitabha Buddha. This practice is known as in Japanese.
References