|
Xenobiology
Xenobiology (XB) is a subfield of synthetic biology, the study of synthesizing and manipulating biological devices and systems. The name "xenobiology" derives from the Greek word ''xenos'', which means "stranger, alien". Xenobiology is a form of biology that is not (yet) familiar to science and is not found in nature. In practice, it describes novel biological systems and biochemistries that differ from the canonical DNA–RNA-20 amino acid system (see central dogma of molecular biology). For example, instead of DNA or RNA, XB explores nucleic acid analogues, termed xeno nucleic acid (XNA) as information carriers. It also focuses on an expanded genetic code and the incorporation of non-proteinogenic amino acids into proteins. Difference between xeno-, exo-, and astro-biology "Astro" means "star" and "exo" means "outside". Both exo- and astrobiology deal with the search for naturally evolved life in the Universe, mostly on other planets in the circumstellar habitable zone. (The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astrobiology
Astrobiology, and the related field of exobiology, is an interdisciplinary scientific field that studies the origins, early evolution, distribution, and future of life in the universe. Astrobiology is the multidisciplinary field that investigates the deterministic conditions and contingent events with which life arises, distributes, and evolves in the universe. Astrobiology makes use of molecular biology, biophysics, biochemistry, chemistry, astronomy, physical cosmology, exoplanetology, geology, paleontology, and ichnology to investigate the possibility of life on other worlds and help recognize biospheres that might be different from that on Earth. The origin and early evolution of life is an inseparable part of the discipline of astrobiology. Astrobiology concerns itself with interpretation of existing scientific data, and although speculation is entertained to give context, astrobiology concerns itself primarily with hypotheses that fit firmly into existing scienti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleic Acid Analogues
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are Analog (chemistry), analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research. Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases. An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as peptide nucleic acid, PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix). Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries. Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synthetic Biology
Synthetic biology (SynBio) is a multidisciplinary area of research that seeks to create new biological parts, devices, and systems, or to redesign systems that are already found in nature. It is a branch of science that encompasses a broad range of methodologies from various disciplines, such as biotechnology, biomaterials, material science/engineering, genetic engineering, molecular biology, molecular engineering, systems biology, membrane science, biophysics, chemical and biological engineering, electrical and computer engineering, control engineering and evolutionary biology. Due to more powerful genetic engineering capabilities and decreased DNA synthesis and sequencing costs, the field of synthetic biology is rapidly growing. In 2016, more than 350 companies across 40 countries were actively engaged in synthetic biology applications; all these companies had an estimated net worth of $3.9 billion in the global market. Definition Synthetic biology currently has no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synthetic Biological Circuit
Synthetic biological circuits are an application of synthetic biology where biological parts inside a cell are designed to perform logical functions mimicking those observed in electronic circuits. The applications range from simply inducing production to adding a measurable element, like GFP, to an existing natural biological circuit, to implementing completely new systems of many parts. The goal of synthetic biology is to generate an array of tunable and characterized parts, or modules, with which any desirable synthetic biological circuit can be easily designed and implemented. These circuits can serve as a method to modify cellular functions, create cellular responses to environmental conditions, or influence cellular development. By implementing rational, controllable logic elements in cellular systems, researchers can use living systems as engineered "biological machines" to perform a vast range of useful functions. History The first natural gene circuit studied in detail ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foldamer
In chemistry, a foldamer is a discrete chain molecule (oligomer) that folds into a conformationally ordered state in solution. They are artificial molecules that mimic the ability of proteins, nucleic acids, and polysaccharides to fold into well-defined conformations, such as α-helices and β-sheets. The structure of a foldamer is stabilized by noncovalent interactions between nonadjacent monomers. Foldamers are studied with the main goal of designing large molecules with predictable structures. The study of foldamers is related to the themes of molecular self-assembly, molecular recognition, and host–guest chemistry. Design Foldamers can vary in size, but they are defined by the presence of noncovalent, nonadjacent interactions. This definition excludes molecules like poly(isocyanates) (commonly known as (polyurethane)) and poly(prolines) as they fold into helices reliably due to ''adjacent'' covalent interactions., Foldamers have a dynamic folding reaction nfolde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Expanded Genetic Code
An expanded genetic code is an artificially modified genetic code in which one or more specific codons have been re-allocated to encode an amino acid that is not among the 22 common naturally-encoded proteinogenic amino acids. The key prerequisites to expand the genetic code are: * the non-standard amino acid to encode, * an unused codon to adopt, * a tRNA that recognises this codon, and * a tRNA synthetase that recognises only that tRNA and only the non-standard amino acid. Expanding the genetic code is an area of research of synthetic biology, an applied biological discipline whose goal is to engineer living systems for useful purposes. The genetic code expansion enriches the repertoire of useful tools available to science. In May 2019, researchers, in a milestone effort, reported the creation of a new synthetic (possibly artificial) form of viable life, a variant of the bacteria ''Escherichia coli'', by reducing the natural number of 64 codons in the bacterial genome to 61 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
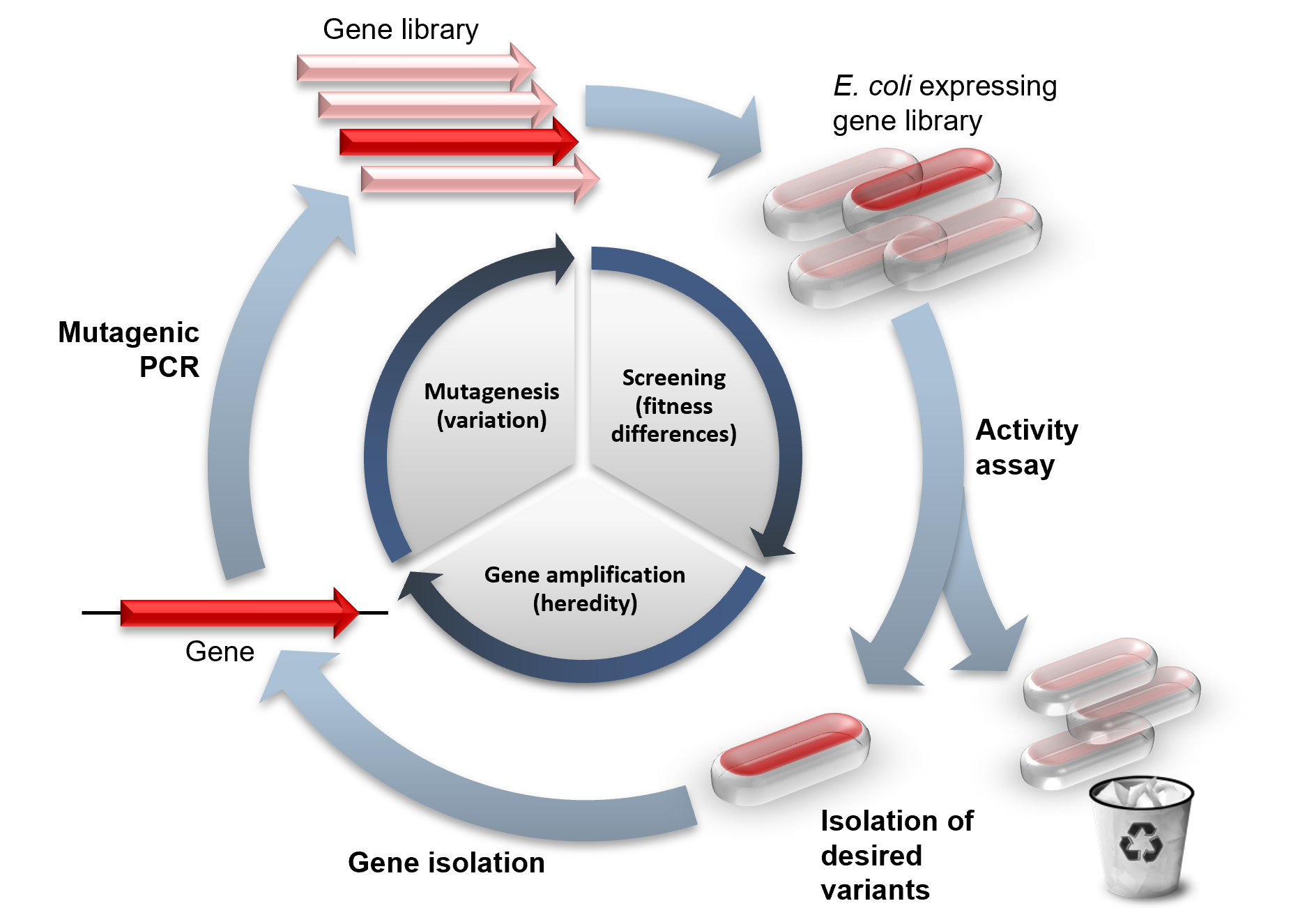
Directed Evolution
Directed evolution (DE) is a method used in protein engineering that mimics the process of natural selection to steer proteins or nucleic acids toward a user-defined goal. It consists of subjecting a gene to iterative rounds of mutagenesis (creating a library of variants), selection (expressing those variants and isolating members with the desired function) and amplification (generating a template for the next round). It can be performed ''in vivo'' (in living organisms), or ''in vitro'' (in cells or free in solution). Directed evolution is used both for protein engineering as an alternative to rationally designing modified proteins, as well as for experimental evolution studies of fundamental evolutionary principles in a controlled, laboratory environment. History Directed evolution has its origins in the 1960s with the evolution of RNA molecules in the " Spiegelman's Monster" experiment. The concept was extended to protein evolution via evolution of bacteria under select ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Body Plan
A body plan, ( ), or ground plan is a set of morphological features common to many members of a phylum of animals. The vertebrates share one body plan, while invertebrates have many. This term, usually applied to animals, envisages a "blueprint" encompassing aspects such as symmetry, layers, segmentation, nerve, limb, and gut disposition. Evolutionary developmental biology seeks to explain the origins of diverse body plans. Body plans have historically been considered to have evolved in a flash in the Ediacaran biota; filling the Cambrian explosion with the results, and a more nuanced understanding of animal evolution suggests gradual development of body plans throughout the early Palaeozoic. Recent studies in animals and plants started to investigate whether evolutionary constraints on body plan structures can explain the presence of developmental constraints during embryogenesis such as the phenomenon referred to as phylotypic stage. History Among the pioneering zool ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biological Dark Matter
Biological dark matter is an informal term for unclassified or poorly understood genetic material. This genetic material may refer to genetic material produced by unclassified microorganisms. By extension, biological dark matter may also refer to the un-isolated microorganism whose existence can only be inferred from the genetic material that they produce. Some of the genetic material may not fall under the three existing domains of life: Bacteria, Archaea and Eukaryota; thus, it has been suggested that a possible fourth domain of life may yet be discovered, * although other explanations are also probable. Alternatively, the genetic material may refer to non-coding DNA (so-called "junk DNA") and non-coding RNA produced by known organisms. Genomic dark matter Much of the genomic dark matter is thought to originate from ancient transposable elements and from other low-complexity repetitive elements. Uncategorized genetic material is found in humans and many other species. * Thei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auxotrophy
Auxotrophy ( grc, αὐξάνω "to increase"; ''τροφή'' "nourishment") is the inability of an organism to synthesize a particular organic compound required for its growth (as defined by IUPAC). An auxotroph is an organism that displays this characteristic; ''auxotrophic'' is the corresponding adjective. Auxotrophy is the opposite of prototrophy, which is characterized by the ability to synthesize all the compounds needed for growth. Prototrophic cells (also referred to as the 'wild type') are self sufficient producers of all required metabolites (e.g. amino acids, lipids, cofactors), while auxotrophs require to be on medium with the metabolite that they cannot produce. For example saying a cell is methionine auxotrophic means that it would need to be on a medium containing methionine or else it would not be able to replicate. In this example this is because it is unable to produce its own methionine (methionine auxotroph). However, a prototroph or a methionine prototrophic c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Escherichia Coli
''Escherichia coli'' (),Wells, J. C. (2000) Longman Pronunciation Dictionary. Harlow ngland Pearson Education Ltd. also known as ''E. coli'' (), is a Gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacterium of the genus '' Escherichia'' that is commonly found in the lower intestine of warm-blooded organisms. Most ''E. coli'' strains are harmless, but some serotypes ( EPEC, ETEC etc.) can cause serious food poisoning in their hosts, and are occasionally responsible for food contamination incidents that prompt product recalls. Most strains do not cause disease in humans and are part of the normal microbiota of the gut; such strains are harmless or even beneficial to humans (although these strains tend to be less studied than the pathogenic ones). For example, some strains of ''E. coli'' benefit their hosts by producing vitamin K2 or by preventing the colonization of the intestine by pathogenic bacteria. These mutually beneficial relationships between ''E. co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
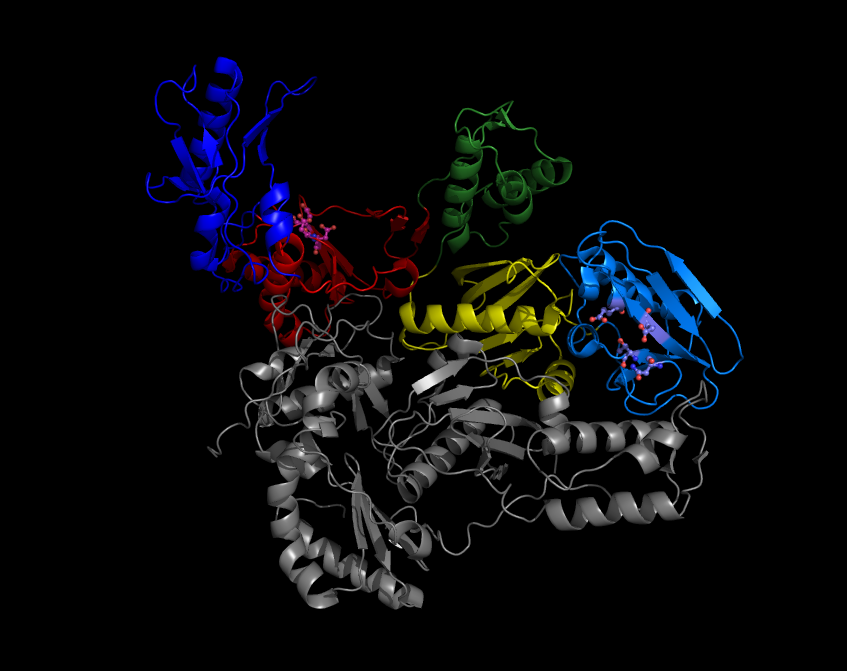
Reverse Transcriptase
A reverse transcriptase (RT) is an enzyme used to generate complementary DNA (cDNA) from an RNA template, a process termed reverse transcription. Reverse transcriptases are used by viruses such as HIV and hepatitis B to replicate their genomes, by retrotransposon mobile genetic elements to proliferate within the host genome, and by eukaryotic cells to extend the telomeres at the ends of their linear chromosomes. Contrary to a widely held belief, the process does not violate the flows of genetic information as described by the classical central dogma, as transfers of information from RNA to DNA are explicitly held possible. Retroviral RT has three sequential biochemical activities: RNA-dependent DNA polymerase activity, ribonuclease H (RNase H), and DNA-dependent DNA polymerase activity. Collectively, these activities enable the enzyme to convert single-stranded RNA into double-stranded cDNA. In retroviruses and retrotransposons, this cDNA can then integrate into the host geno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |