|
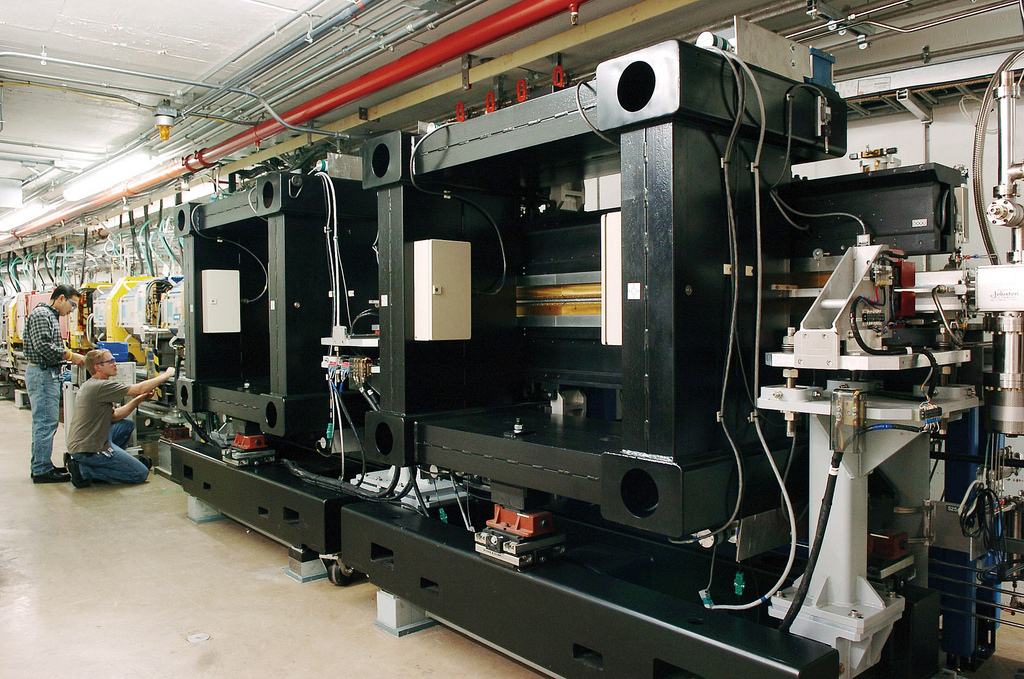
Wiggler (synchrotron)
A wiggler is an insertion device in a synchrotron. It is a series of magnets designed to periodically laterally deflect ('wiggle') a beam of charged particles (invariably electrons or positrons) inside a storage ring of a synchrotron. These deflections create a change in acceleration which in turn produces emission of broad synchrotron radiation tangent to the curve, much like that of a bending magnet, but the intensity is higher due to the contribution of many magnetic dipoles in the wiggler. Furthermore, as the wavelength (λ) is decreased this means the frequency (ƒ) has increased. This increase of frequency is directly proportional to energy, hence, the wiggler creates a wavelength of light with a larger energy. A wiggler has a broader spectrum of radiation than an undulator. Typically the magnets in a wiggler are arranged in a Halbach array. The design shown above is usually known as a Halbach wiggler. History The first suggestion of a wiggler magnet to produce s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australian Synchrotron
ANSTO's Australian Synchrotron is a 3 GeV national synchrotron radiation facility located in Clayton, in the south-eastern suburbs of Melbourne, Victoria, which opened in 2007. ANSTO's Australian Synchrotron is a light source facility (in contrast to a collider), which uses particle accelerators to produce a beam of high energy electrons that are boosted to nearly the speed of light and directed into a storage ring where they circulate for many hours or even days at a time. As the path of these electrons are deflected in the storage ring by either bending magnets or insertion devices, they emit synchrotron light. The light is channelled to experimental endstations containing specialised equipment, enabling a range of research applications including high resolution imagery that is not possible under normal laboratory conditions. ANSTO's Australian Synchrotron supports the research needs of Australia's major universities and research centres, and businesses ranging from small-to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physics Today
''Physics Today'' is the membership magazine of the American Institute of Physics. First published in May 1948, it is issued on a monthly schedule, and is provided to the members of ten physics societies, including the American Physical Society. It is also available to non-members as a paid annual subscription. The magazine informs readers about important developments in overview articles written by experts, shorter review articles written internally by staff, and also discusses issues and events of importance to the science community in politics, education, and other fields. The magazine provides a historical resource of events associated with physics. For example it discussed debunking the physics of the Star Wars program of the 1980s, and the state of physics in China and the Soviet Union during the 1950s and 1970s. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2017 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic jour ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stanford Synchrotron Radiation Lightsource
The Stanford Synchrotron Radiation Lightsource (formerly Stanford Synchrotron Radiation Laboratory), a division of SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory, is operated by Stanford University for the Department of Energy. SSRL is a National User Facility which provides synchrotron radiation, a name given to electromagnetic radiation in the x-ray, ultraviolet, visible and infrared realms produced by electrons circulating in a storage ring (Stanford Positron Electron Asymmetric Ring - SPEAR) at nearly the speed of light. The extremely bright light that is produced can be used to investigate various forms of matter ranging from objects of atomic and molecular size to man-made materials with unusual properties. The obtained information and knowledge is of great value to society, with impact in areas such as the environment, future technologies, health, biology, basic research, and education. SSRL provides experimental facilities to some 2,000 academic and industrial scientists working in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Betatron
A betatron is a type of cyclic particle accelerator. It is essentially a transformer with a torus-shaped vacuum tube as its secondary coil. An alternating current in the primary coils accelerates electrons in the vacuum around a circular path. The betatron was the first machine capable of producing electron beams at energies higher than could be achieved with a simple electron gun, and the first circular accelerator in which particles orbited at a constant radius. The concept of the betatron had been proposed as early as 1922 by Joseph Slepian. Through the 1920s and 30s a number of theoretical problems related to the device were considered by scientists including Rolf Wideroe, Ernest Walton, and Max Steenbeck. The first working betatron was constructed by Donald Kerst at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign in 1940. History After the discovery in the 1800s of Faraday's law of induction, which showed that an electromotive force could be generated by a changing mag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harvard University
Harvard University is a private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Founded in 1636 as Harvard College and named for its first benefactor, the Puritan clergyman John Harvard, it is the oldest institution of higher learning in the United States and one of the most prestigious and highly ranked universities in the world. The university is composed of ten academic faculties plus Harvard Radcliffe Institute. The Faculty of Arts and Sciences offers study in a wide range of undergraduate and graduate academic disciplines, and other faculties offer only graduate degrees, including professional degrees. Harvard has three main campuses: the Cambridge campus centered on Harvard Yard; an adjoining campus immediately across Charles River in the Allston neighborhood of Boston; and the medical campus in Boston's Longwood Medical Area. Harvard's endowment is valued at $50.9 billion, making it the wealthiest academic institution in the world. Endow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halbach Array
A Halbach array is a special arrangement of permanent magnets that augments the magnetic field on one side of the array while cancelling the field to near zero on the other side. This is achieved by having a spatially rotating pattern of magnetisation. The rotating pattern of permanent magnets (on the front face; on the left, up, right, down) can be continued indefinitely and have the same effect. The effect of this arrangement is roughly similar to many horseshoe magnets placed adjacent to each other, with similar poles touching. The principle was first invented by James (Jim) M. Winey of Magnepan in 1970, for the ideal case of continuously rotating magnetization, induced by a one-sided stripe-shaped coil. The effect was also discovered by John C. Mallinson in 1973, and these "one-sided flux" structures were initially described by him as a "curiosity", although at the time he recognized from this discovery the potential for significant improvements in magnetic tape techno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Undulator
An undulator is an insertion device from high-energy physics and usually part of a larger installation, a synchrotron storage ring, or it may be a component of a free electron laser. It consists of a periodic structure of dipole magnets. These can be permanent magnets or superconducting magnets. The static magnetic field alternates along the length of the undulator with a wavelength \lambda_u. Electrons traversing the periodic magnet structure are forced to undergo oscillations and thus to radiate energy. The radiation produced in an undulator is very intense and concentrated in narrow energy bands in the spectrum. It is also collimated on the orbit plane of the electrons. This radiation is guided through beamlines for experiments in various scientific areas. The undulator strength parameter is: :K=\frac, where ''e'' is the electron charge, ''B'' is the magnetic field, ''\lambda_u'' is the spatial period of the undulator magnets, ''m_'' is the electron rest mass, and ''c'' is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Dipoles
In electromagnetism, a magnetic dipole is the limit of either a closed loop of electric current or a pair of poles as the size of the source is reduced to zero while keeping the magnetic moment constant. It is a magnetic analogue of the electric dipole, but the analogy is not perfect. In particular, a true magnetic monopole, the magnetic analogue of an electric charge, has never been observed in nature. However, magnetic monopole quasiparticles have been observed as emergent properties of certain condensed matter systems. Moreover, one form of magnetic dipole moment is associated with a fundamental quantum property—the spin of elementary particles. Because magnetic monopoles do not exist, the magnetic field at a large distance from any static magnetic source looks like the field of a dipole with the same dipole moment. For higher-order sources (e.g. quadrupoles) with no dipole moment, their field decays towards zero with distance faster than a dipole field does. External mag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insertion Device
An insertion device (ID) is a component in modern synchrotron light sources, so called because they are "inserted" into accelerator tracks. They are periodic magnetic structures that stimulate highly brilliant, forward-directed synchrotron radiation emission by forcing a stored charged particle beam to perform wiggles, or undulations, as they pass through the device. This motion is caused by the Lorentz force, and it is from this oscillatory motion that we get the names for the two classes of device, which are known as wigglers and undulators. As well as creating a brighter light, some insertion devices enable tuning of the light so that different frequencies can be generated for different applications. History The theory behind undulators was developed by Vitaly Ginzburg in the USSR. However it was Motz and his team who in 1953 installed the first undulator in a linac at Stanford, using it to generate millimetre wave radiation through to visible light. It was not until the 1970s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
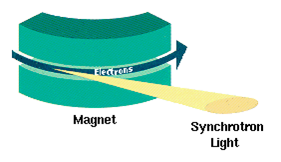
Bending Magnet
A dipole magnet is the simplest type of magnet. It has two poles, one north and one south. Its magnetic field lines form simple closed loops which emerge from the north pole, re-enter at the south pole, then pass through the body of the magnet. The simplest example of a dipole magnet is a ''bar magnet''. Bar Magnet" hyperphysics; http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/magnetic/elemag.html/ref> Dipole magnets in accelerators In particle accelerators, a dipole magnet is the electromagnet used to create a homogeneous magnetic field over some distance. Particle motion in that field will be circular in a plane perpendicular to the field and collinear to the direction of particle motion and free in the direction orthogonal to it. Thus, a particle injected into a dipole magnet will travel on a circular or helical trajectory. By adding several dipole sections on the same plane, the bending radial effect of the beam increases. In accelerator physics, dipole magnets are used to re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synchrotron Radiation
Synchrotron radiation (also known as magnetobremsstrahlung radiation) is the electromagnetic radiation emitted when relativistic charged particles are subject to an acceleration perpendicular to their velocity (). It is produced artificially in some types of particle accelerators, or naturally by fast electrons moving through magnetic fields. The radiation produced in this way has a characteristic polarization and the frequencies generated can range over a large portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. Synchrotron radiation is similar to bremsstrahlung radiation, which is emitted by a charged particle when the acceleration is parallel to the direction of motion. The general term for radiation emitted by particles in a magnetic field is ''gyromagnetic radiation'', for which synchrotron radiation is the ultra-relativistic special case. Radiation emitted by charged particles moving non-relativistically in a magnetic field is called cyclotron emission. For particles in the mild ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |