|
Weldability
The weldability, also known as joinability,. of a material refers to its ability to be welded. Many metals and thermoplastics can be welded, but some are easier to weld than others (see Rheological weldability). A material's weldability is used to determine the welding process and to compare the final weld quality to other materials. Weldability is often hard to define quantitatively, so most standards define it qualitatively. For instance the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) defines weldability in ISO standard 581-1980 as: "Metallic material is considered to be susceptible to welding to an established extent with given processes and for given purposes when welding provides metal integrity by a corresponding technological process for welded parts to meet technical requirements as to their own qualities as well as to their influence on a structure they form." Other welding organizations define it similarly. Steels For steel there are three major failure modes by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rheological Weldability
Rheological weldability (RW) of thermoplastics considers the materials flow characteristics in determining the weldability of the given material. The process of welding thermal plastics requires three general steps, first is surface preparation. The second step is the application of heat and pressure to create intimate contact between the components being joined and initiate inter-molecular diffusion across the joint and the third step is cooling. RW can be used to determine the effectiveness of the second step of the process for given materials. Rheology Rheology is the study of material flow as well as how a material deforms under an applied force. Rheological properties are typically applied to Non-Newtonian fluids but can also be applied to soft solids such as thermoplastics at elevated temperatures experienced during the welding process. The material properties associated with the rheological behavior include viscosity, elasticity, plasticity, viscoelasticity, and the mater ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equivalent Carbon Content
The equivalent carbon content concept is used on ferrous materials, typically steel and cast iron, to determine various properties of the alloy when more than just carbon is used as an alloyant, which is typical. The idea is to convert the percentage of alloying elements other than carbon to the equivalent carbon percentage, because the iron-carbon phases are better understood than other iron-alloy phases. Most commonly this concept is used in welding, but it is also used when heat treating and casting cast iron. Steel In welding, equivalent carbon content (C.E) is used to understand how the different alloying elements affect hardness of the steel being welded. This is then directly related to hydrogen-induced cold cracking, which is the most common weld defect for steel, thus it is most commonly used to determine weldability. Higher concentrations of carbon and other alloying elements such as manganese, chromium, silicon, molybdenum, vanadium, copper, and nickel tend to increase ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
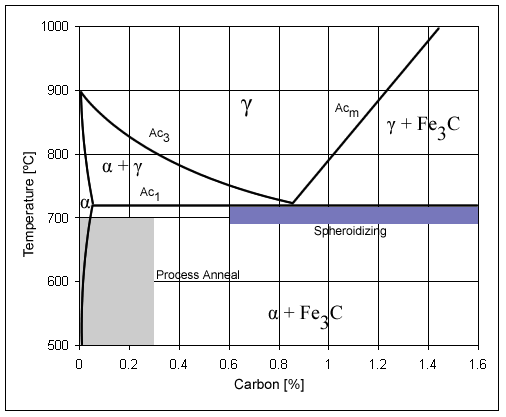
Plain Carbon Steel
Carbon steel is a steel with carbon content from about 0.05 up to 2.1 percent by weight. The definition of carbon steel from the American Iron and Steel Institute (AISI) states: * no minimum content is specified or required for chromium, cobalt, molybdenum, nickel, niobium, titanium, tungsten, vanadium, zirconium, or any other element to be added to obtain a desired alloying effect; * the specified minimum for copper does not exceed 0.40%; * or the maximum content specified for any of the following elements does not exceed the percentages noted: manganese 1.65%; silicon 0.60%; copper 0.60%. The term ''carbon steel'' may also be used in reference to steel which is not stainless steel; in this use carbon steel may include alloy steels. High carbon steel has many different uses such as milling machines, cutting tools (such as chisels) and high strength wires. These applications require a much finer microstructure, which improves the toughness. Carbon steel is a popular metal choic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stainless Steel
Stainless steel is an alloy of iron that is resistant to rusting and corrosion. It contains at least 11% chromium and may contain elements such as carbon, other nonmetals and metals to obtain other desired properties. Stainless steel's corrosion resistance, resistance to corrosion results from the chromium, which forms a Passivation (chemistry), passive film that can protect the material and self-healing material, self-heal in the presence of oxygen. The alloy's properties, such as luster and resistance to corrosion, are useful in many applications. Stainless steel can be rolled into Sheet metal, sheets, plates, bars, wire, and tubing. These can be used in cookware, cutlery, surgical instruments, major appliances, vehicles, construction material in large buildings, industrial equipment (e.g., in paper mills, chemical plants, water treatment), and storage tanks and tankers for chemicals and food products. The biological cleanability of stainless steel is superior to both alumi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Welding
Welding is a fabrication (metal), fabrication process that joins materials, usually metals or thermoplastics, by using high heat to melt the parts together and allowing them to cool, causing Fusion welding, fusion. Welding is distinct from lower temperature techniques such as brazing and soldering, which do not melting, melt the base metal (parent metal). In addition to melting the base metal, a filler material is typically added to the joint to form a pool of molten material (the weld pool) that cools to form a joint that, based on weld configuration (butt, full penetration, fillet, etc.), can be stronger than the base material. Pressure may also be used in conjunction with heat or by itself to produce a weld. Welding also requires a form of shield to protect the filler metals or melted metals from being contaminated or Oxidation, oxidized. Many different energy sources can be used for welding, including a gas flame (chemical), an electric arc (electrical), a laser, an electron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cold Cracking
In metalworking, a welding defect is any flaw that compromises the usefulness of a weldment. There is a great variety of welding defects. Welding imperfections are classified according to ISO 6520, while their acceptable limits are specified in ISO 5817 and ISO 10042. Major causes According to the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), causes of welding defects can be broken down as follows: 41% poor process conditions, 32% operator error, 12% wrong technique, 10% incorrect consumables and 5% bad weld grooves. Hydrogen embrittlement Residual stresses The magnitude of stress that can be formed from welding can be roughly calculated using: :E \alpha \Delta T Where E is Young's modulus, α is the coefficient of thermal expansion, and ΔT is the temperature change. For steel this calculates out to be approximately . Types Cracks Defects related to fracture. Arc strikes An Arc Strike is a discontinuity resulting from an arc, consisting of any localized remelted met ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hardenability
The hardenability of a metal alloy is the depth to which a material is hardened after putting it through a heat treatment process. It should not be confused with hardness, which is a measure of a sample's resistance to indentation or scratching. It is an important property for welding, since it is inversely proportional to weldability, that is, the ease of welding a material. When a hot steel work-piece is quenched, the area in contact with the water immediately cools and its temperature equilibrates with the quenching medium. The inner depths of the material however, do not cool so rapidly, and in work-pieces that are large, the cooling rate may be slow enough to allow the austenite to transform fully into a structure other than martensite or bainite. This results in a work-piece that does not have the same crystal structure throughout its entire depth; with a softer core and harder "shell". The softer core is some combination of ferrite and cementite, such as pearlite. The har ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High-strength Low-alloy Steel
High-strength low-alloy steel (HSLA) is a type of alloy steel that provides better mechanical properties or greater resistance to corrosion than carbon steel. HSLA steels vary from other steels in that they are not made to meet a specific chemical composition but rather specific mechanical properties. They have a carbon content between 0.05 and 0.25% to retain formability and weldability. Other alloying elements include up to 2.0% manganese and small quantities of copper, nickel, niobium, nitrogen, vanadium, chromium, molybdenum, titanium, calcium, rare-earth elements, or zirconium. Copper, titanium, vanadium, and niobium are added for strengthening purposes. These elements are intended to alter the microstructure of carbon steels, which is usually a ferrite-pearlite aggregate, to produce a very fine dispersion of alloy carbides in an almost pure ferrite matrix. This eliminates the toughness-reducing effect of a pearlitic volume fraction yet maintains and increases the material's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steel
Steel is an alloy made up of iron with added carbon to improve its strength and fracture resistance compared to other forms of iron. Many other elements may be present or added. Stainless steels that are corrosion- and oxidation-resistant typically need an additional 11% chromium. Because of its high tensile strength and low cost, steel is used in buildings, infrastructure, tools, ships, trains, cars, machines, electrical appliances, weapons, and rockets. Iron is the base metal of steel. Depending on the temperature, it can take two crystalline forms (allotropic forms): body-centred cubic and face-centred cubic. The interaction of the allotropes of iron with the alloying elements, primarily carbon, gives steel and cast iron their range of unique properties. In pure iron, the crystal structure has relatively little resistance to the iron atoms slipping past one another, and so pure iron is quite ductile, or soft and easily formed. In steel, small amounts of carbon, other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nickel
Nickel is a chemical element with symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel is a hard and ductile transition metal. Pure nickel is chemically reactive but large pieces are slow to react with air under standard conditions because a passivation layer of nickel oxide forms on the surface that prevents further corrosion. Even so, pure native nickel is found in Earth's crust only in tiny amounts, usually in ultramafic rocks, and in the interiors of larger nickel–iron meteorites that were not exposed to oxygen when outside Earth's atmosphere. Meteoric nickel is found in combination with iron, a reflection of the origin of those elements as major end products of supernova nucleosynthesis. An iron–nickel mixture is thought to compose Earth's outer and inner cores. Use of nickel (as natural meteoric nickel–iron alloy) has been traced as far back as 3500 BCE. Nickel was first isolated and classified as an e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dross
Dross is a mass of solid impurities floating on a molten metal or dispersed in the metal, such as in wrought iron. It forms on the surface of low- melting-point metals such as tin, lead, zinc or aluminium or alloys by oxidation of the metal. For higher melting point metals and alloys such as steel and silver, oxidized impurities melt and float making them easy to pour off. With wrought iron, hammering and later rolling remove some dross. With tin and lead the dross can be removed by adding sodium hydroxide pellets, which dissolve the oxides and form a slag. If floating, dross can also be skimmed off. Dross, as a solid, is distinguished from slag, which is a liquid. Dross product is not entirely waste material; for example, aluminium dross can be recycled and is also used in secondary steelmaking for slag deoxidation. Etymology and usage The term ''dross'' derives from the Old English word ''dros'', meaning the scum produced when smelting metals (extracting them from their ore ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxide
An oxide () is a chemical compound that contains at least one oxygen atom and one other element in its chemical formula. "Oxide" itself is the dianion of oxygen, an O2– (molecular) ion. with oxygen in the oxidation state of −2. Most of the Earth's crust consists of oxides. Even materials considered pure elements often develop an oxide coating. For example, aluminium foil develops a thin skin of Al2O3 (called a passivation layer) that protects the foil from further corrosion.Greenwood, N. N.; & Earnshaw, A. (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd Edn.), Oxford:Butterworth-Heinemann. . Stoichiometry (the measurable relationship between reactants and chemical equations of a equation or reaction) Oxides are extraordinarily diverse in terms of stoichiometries and in terms of the structures of each stoichiometry. Most elements form oxides of more than one stoichiometry. A well known example is carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide.Greenwood, N. N.; & Earnshaw, A. (1997). Chemistry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |