|
Water Blue
Water blue, also known as aniline blue, Acid blue 22, Soluble Blue 3M, Marine Blue V, or C.I. 42755, is a chemical compound used as a stain in histology. Water blue stains collagen blue in tissue sections. It is soluble in water and slightly soluble in ethanol. Water blue is also available in mixture with methyl blue, under the names Aniline Blue WS, Aniline blue, China blue, or Soluble blue. It can be used in the Mallory's trichrome stain of connective tissue and Gömöri trichrome stain of muscle tissue. It is used in differential staining Differential staining is a staining process which uses more than one chemical stain. Using multiple stains can better differentiate between different microorganisms or structures/cellular components of a single organism. Differential staining is u .... See also * RAL 5021 Water blue References {{Reflist Triarylmethane dyes Staining dyes Benzenesulfonates Organic sodium salts Anilines Acid dyes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Compound
A chemical compound is a chemical substance composed of many identical molecules (or molecular entities) containing atoms from more than one chemical element held together by chemical bonds. A molecule consisting of atoms of only one element is therefore not a compound. A compound can be transformed into a different substance by a chemical reaction, which may involve interactions with other substances. In this process, bonds between atoms may be broken and/or new bonds formed. There are four major types of compounds, distinguished by how the constituent atoms are bonded together. Molecular compounds are held together by covalent bonds; ionic compounds are held together by ionic bonds; intermetallic compounds are held together by metallic bonds; coordination complexes are held together by coordinate covalent bonds. Non-stoichiometric compounds form a disputed marginal case. A chemical formula specifies the number of atoms of each element in a compound molecule, using the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gömöri Trichrome Stain
Gömöri trichrome stain is a histological stain used on muscle tissue. It can be used to test for certain forms of mitochondrial myopathy. It is named for George Gömöri George Gomori may refer to: * György Gömöri (1904–1957), Hungarian-American physician and histochemist * George Gomori (born 1934), Hungarian-born poet, writer and academic {{hndis, Gomori, George ..., who developed it in 1950.GOMORI, G. - A rapid one-step trichrome stain. Am. J. Clin. Path. 20: 661-664, 1950. References External links Staining 1950 introductions {{pathology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Sodium Salts
Organic may refer to: * Organic, of or relating to an organism, a living entity * Organic, of or relating to an anatomical organ Chemistry * Organic matter, matter that has come from a once-living organism, is capable of decay or is the product of decay, or is composed of organic compounds * Organic compound, a compound that contains carbon ** Organic chemistry, chemistry involving organic compounds Farming, certification and products * Organic farming, agriculture conducted according to certain standards, especially the use of stated methods of fertilization and pest control * Organic certification, accreditation process for producers of organically-farmed products * Organic horticulture, the science and art of growing fruits, vegetables, flowers, or ornamental plants by following the essential principles of organic agriculture * Organic products, "organics": ** Organic food, food produced from organic farming methods and often certified organic according to organic farming stan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Staining Dyes
Staining is a technique used to enhance contrast in samples, generally at the microscopic level. Stains and dyes are frequently used in histology (microscopic study of biological tissues), in cytology (microscopic study of cells), and in the medical fields of histopathology, hematology, and cytopathology that focus on the study and diagnoses of diseases at the microscopic level. Stains may be used to define biological tissues (highlighting, for example, muscle fibers or connective tissue), cell populations (classifying different blood cells), or organelles within individual cells. In biochemistry, it involves adding a class-specific ( DNA, proteins, lipids, carbohydrates) dye to a substrate to qualify or quantify the presence of a specific compound. Staining and fluorescent tagging can serve similar purposes. Biological staining is also used to mark cells in flow cytometry, and to flag proteins or nucleic acids in gel electrophoresis. Light microscopes are used for viewing st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RAL 5021 Water Blue
The following is a list of RAL Classic colours from the RAL colour standard. The visual samples are approximate and informative only. RAL Classic Yellow and beige Orange Red Violet Blue Green Grey Brown White and black Overview Below is a list of RAL Classic colours from the RAL colour standard. Alongside every colour, the corresponding values are given for: * hexadecimal triplet for the sRGB colour space, approximating the given RAL colour * sRGB value * Grey value calculated from (0.2126 × red) + (0.7152 × green) + (0.0722 × blue) * CIE L*a*b* values * sRGB value expressed as hue, saturation and lightness (HSL) * device-independent CMYK The CMYK color model (also known as process color, or four color) is a subtractive color model, based on the CMY color model, used in color printing, and is also used to describe the printing process itself. The abbreviation ''CMYK'' refers ... value: cyan, magenta, yellow, black or key * LRV, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
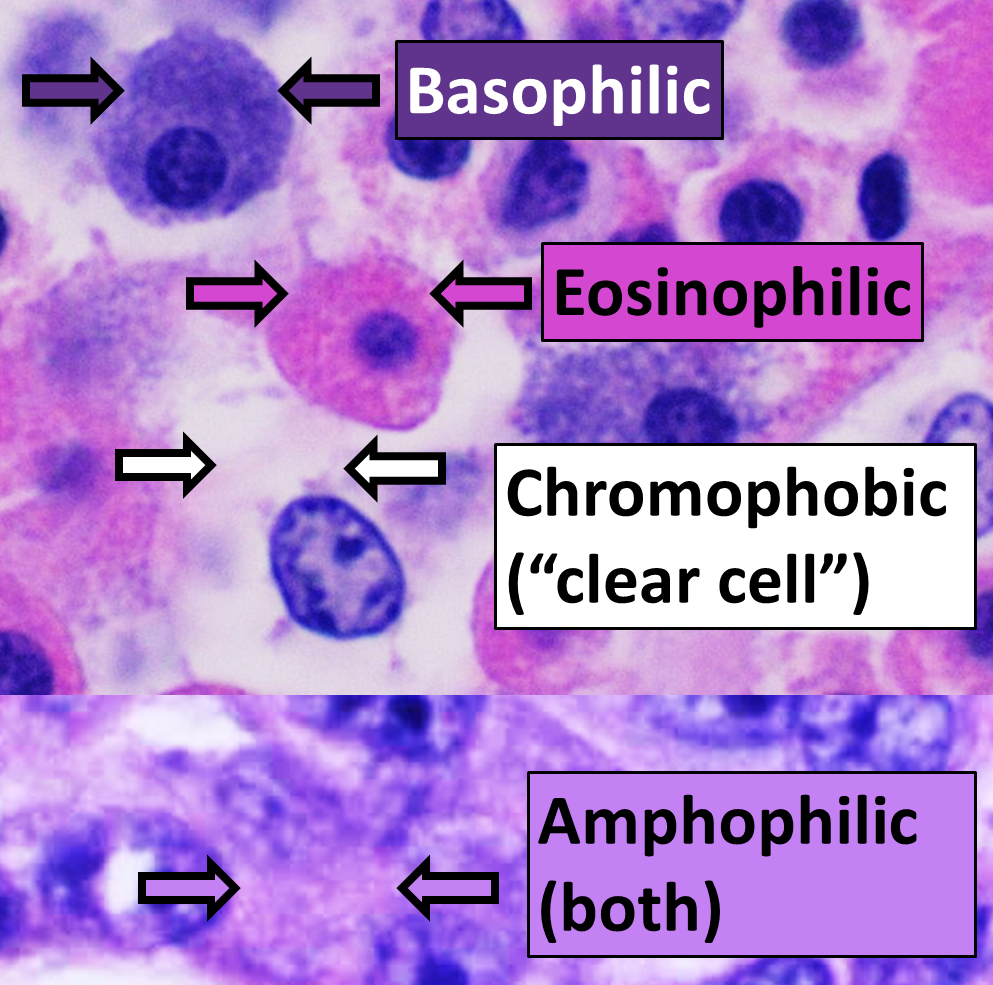
Differential Staining
Differential staining is a staining process which uses more than one chemical staining, stain. Using multiple stains can better differentiate between different microorganisms or structures/cellular components of a single organism. Differential staining is used to detect abnormalities in the proportion of different white blood cells in the blood. The process or results are called a WBC differential. This test is useful because many diseases alter the proportion of certain white blood cells. By analyzing these differences in combination with a clinical exam and other lab tests, medical professionals can diagnose disease. One commonly recognizable use of differential staining is the Gram stain. Gram staining uses two dyes: Crystal violet and Fuchsin or Safranin (the counterstain) to differentiate between Gram-positive bacteria (large Peptidoglycan layer on outer surface of cell) and Gram-negative bacteria. Acid-fast stains are also differential stains. Further reading *http://ww ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Connective Tissue
Connective tissue is one of the four primary types of animal tissue, along with epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. It develops from the mesenchyme derived from the mesoderm the middle embryonic germ layer. Connective tissue is found in between other tissues everywhere in the body, including the nervous system. The three meninges, membranes that envelop the brain and spinal cord are composed of connective tissue. Most types of connective tissue consists of three main components: elastic and collagen fibers, ground substance, and cells. Blood, and lymph are classed as specialized fluid connective tissues that do not contain fiber. All are immersed in the body water. The cells of connective tissue include fibroblasts, adipocytes, macrophages, mast cells and leucocytes. The term "connective tissue" (in German, ''Bindegewebe'') was introduced in 1830 by Johannes Peter Müller. The tissue was already recognized as a distinct class in the 18th century. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Staining (biology)
Staining is a technique used to enhance contrast in samples, generally at the microscopic level. Stains and dyes are frequently used in histology (microscopic study of biological tissues), in cytology (microscopic study of cells), and in the medical fields of histopathology, hematology, and cytopathology that focus on the study and diagnoses of diseases at the microscopic level. Stains may be used to define biological tissues (highlighting, for example, muscle fibers or connective tissue), cell populations (classifying different blood cells), or organelles within individual cells. In biochemistry, it involves adding a class-specific ( DNA, proteins, lipids, carbohydrates) dye to a substrate to qualify or quantify the presence of a specific compound. Staining and fluorescent tagging can serve similar purposes. Biological staining is also used to mark cells in flow cytometry, and to flag proteins or nucleic acids in gel electrophoresis. Light microscopes are used for viewing st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mallory's Trichrome Stain
Mallory's trichrome stain also called Mallory's Triple Stain is a stain utilized in histology to aid in revealing different macromolecules that make up the cell. It uses the three stains: aniline blue, acid fuchsin, and orange G. As a result, this staining technique can reveal collagen, ordinary cytoplasm, and red blood cells. It is used in examining the collagen of connective tissue. For tissues that are not directly acidic or basic, it can be difficult to use only one stain to reveal the necessary structures of interest. A combination of the three different stains in precise amounts applied in the correct order reveals the details selectively. This is the result of more than just electrostatic interactions of stain with the tissue and the stain not being washed out after each step. Collectively the stains complement one another. The staining technique was first published in 1900 by Frank Burr Mallory, then a histologist at Harvard University Medical School. Many variants of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aniline Blue WS
Aniline Blue WS, also called aniline blue, diphenylamine blue, China blue, or Soluble blue, is a mixture of methyl blue and water blue. It may also be either one of them. It is a soluble dye used as a biological dye, in fluorescence microscopy, appearing a yellow-green colour after excitation with violet light. It is a mixture of the trisulfonates of triphenyl rosaniline and of diphenyl rosaniline. Aniline blue or its constituents are used to stain collagen, as the fibre stain in Masson's trichrome, as well as to reveal callose structures in plant tissues. It can be used in the Mallory's connective tissue stain and Gömöri trichrome stain. It is used in differential staining Differential staining is a staining process which uses more than one chemical stain. Using multiple stains can better differentiate between different microorganisms or structures/cellular components of a single organism. Differential staining is u .... References {{DEFAULTSORT:Aniline Blue Ws Stai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |