|
Vesicle (embryology)
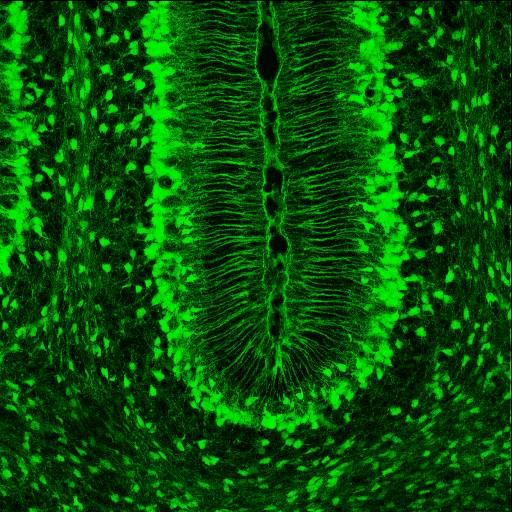
Brain vesicles are the bulge-like features of the early development of the neural tube in vertebrates. Vesicle formation begins shortly after anterior neural tube closure at about embryonic day 9.0 in the mouse and the fourth and fifth gestational week in human development. In zebrafish and chicken embryos, brain vesicles form by about 24 hours and 48 hours post-conception, respectively. Initially there are three primary brain vesicles: prosencephalon, mesencephalon, and rhombencephalon. These develop into five secondary brain vesicles – the prosencephalon is subdivided into the telencephalon and diencephalon, and the rhombencephalon into the metencephalon and myelencephalon. During these early vesicle stages, the walls of the neural tube contain neural stem cells in a region called the neuroepithelium or ventricular zone. These neural stem cells divide rapidly, driving growth of the early brain, but later, these stem cells begin to generate neurons through the process of neur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1302 Brain Vesicle DevN
Thirteen or 13 may refer to: * 13 (number), the natural number following 12 and preceding 14 * One of the years 13 BC, AD 13, 1913, 2013 Music * 13AD (band), an Indian classic and hard rock band Albums * ''13'' (Black Sabbath album), 2013 * ''13'' (Blur album), 1999 * ''13'' (Borgeous album), 2016 * ''13'' (Brian Setzer album), 2006 * ''13'' (Die Ärzte album), 1998 * ''13'' (The Doors album), 1970 * ''13'' (Havoc album), 2013 * ''13'' (HLAH album), 1993 * ''13'' (Indochine album), 2017 * ''13'' (Marta Savić album), 2011 * ''13'' (Norman Westberg album), 2015 * ''13'' (Ozark Mountain Daredevils album), 1997 * ''13'' (Six Feet Under album), 2005 * ''13'' (Suicidal Tendencies album), 2013 * ''13'' (Solace album), 2003 * ''13'' (Second Coming album), 2003 * ''13'' (Ces Cru EP), 2012 * ''13'' (Denzel Curry EP), 2017 * ''Thirteen'' (CJ & The Satellites album), 2007 * ''Thirteen'' (Emmylou Harris album), 1986 * ''Thirteen'' (Harem Scarem album), 2014 * ''Thirt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuroepithelium
Neuroepithelial cells, or neuroectodermal cells, form the wall of the closed neural tube in early embryonic development. The neuroepithelial cells span the thickness of the tube's wall, connecting with the pial surface and with the ventricular or lumenal surface. They are joined at the lumen of the tube by junctional complexes, where they form a pseudostratified layer of epithelium called neuroepithelium. Neuroepithelial cells are the stem cells of the central nervous system, known as neural stem cells, and generate the intermediate progenitor cells known as radial glial cells, that differentiate into neurons and glia in the process of neurogenesis. Embryonic neural development Brain development During the third week of embryonic growth the brain begins to develop in the early fetus in a process called morphogenesis. Neuroepithelial cells of the ectoderm begin multiplying rapidly and fold in forming the neural plate, which invaginates during the fourth week of embryonic growth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurogenesis
Neurogenesis is the process by which nervous system cells, the neurons, are produced by neural stem cells (NSCs). It occurs in all species of animals except the porifera (sponges) and placozoans. Types of NSCs include neuroepithelial cells (NECs), radial glial cells (RGCs), basal progenitors (BPs), intermediate neuronal precursors (INPs), subventricular zone astrocytes, and subgranular zone radial astrocytes, among others. Neurogenesis is most active during embryonic development and is responsible for producing all the various types of neurons of the organism, but it continues throughout adult life in a variety of organisms. Once born, neurons do not divide (see mitosis), and many will live the lifespan of the animal. Neurogenesis in mammals Developmental neurogenesis During embryonic development, the mammalian central nervous system (CNS; brain and spinal cord) is derived from the neural tube, which contains NSCs that will later generate neurons. However, neurogenesis does ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radial Glial Cell
Radial glial cells, or radial glial progenitor cells (RGPs), are bipolar-shaped progenitor cells that are responsible for producing all of the neurons in the cerebral cortex. RGPs also produce certain lineages of glia, including astrocytes and oligodendrocytes. Their cell bodies (somata) reside in the embryonic ventricular zone, which lies next to the developing ventricular system. During development, newborn neurons use radial glia as scaffolds, traveling along the radial glial fibers in order to reach their final destinations. Despite the various possible fates of the radial glial population, it has been demonstrated through clonal analysis that most radial glia have restricted, unipotent or multipotent, fates. Radial glia can be found during the neurogenic phase in all vertebrates (studied to date). The term "radial glia" refers to the morphological characteristics of these cells that were first observed: namely, their radial processes and their similarity to astrocytes, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stem Cell
In multicellular organisms, stem cells are undifferentiated or partially differentiated cells that can differentiate into various types of cells and proliferate indefinitely to produce more of the same stem cell. They are the earliest type of cell in a cell lineage. They are found in both embryonic and adult organisms, but they have slightly different properties in each. They are usually distinguished from progenitor cells, which cannot divide indefinitely, and precursor or blast cells, which are usually committed to differentiating into one cell type. In mammals, roughly 50–150 cells make up the inner cell mass during the blastocyst stage of embryonic development, around days 5–14. These have stem-cell capability. ''In vivo'', they eventually differentiate into all of the body's cell types (making them pluripotent). This process starts with the differentiation into the three germ layers – the ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm – at the gastrulation stage. However ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neural Stem Cell
Neural stem cells (NSCs) are self-renewing, multipotent cells that firstly generate the radial glial progenitor cells that generate the neurons and glia of the nervous system of all animals during embryonic development. Some neural progenitor stem cells persist in highly restricted regions in the adult vertebrate brain and continue to produce neurons throughout life. Differences in the size of the central nervous system are among the most important distinctions between the species and thus mutations in the genes that regulate the size of the neural stem cell compartment are among the most important drivers of vertebrate evolution. Stem cells are characterized by their capacity to differentiate into multiple cell types. They undergo symmetric or asymmetric cell division into two daughter cells. In symmetric cell division, both daughter cells are also stem cells. In asymmetric division, a stem cell produces one stem cell and one specialized cell. NSCs primarily differentiate i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurogenesis
Neurogenesis is the process by which nervous system cells, the neurons, are produced by neural stem cells (NSCs). It occurs in all species of animals except the porifera (sponges) and placozoans. Types of NSCs include neuroepithelial cells (NECs), radial glial cells (RGCs), basal progenitors (BPs), intermediate neuronal precursors (INPs), subventricular zone astrocytes, and subgranular zone radial astrocytes, among others. Neurogenesis is most active during embryonic development and is responsible for producing all the various types of neurons of the organism, but it continues throughout adult life in a variety of organisms. Once born, neurons do not divide (see mitosis), and many will live the lifespan of the animal. Neurogenesis in mammals Developmental neurogenesis During embryonic development, the mammalian central nervous system (CNS; brain and spinal cord) is derived from the neural tube, which contains NSCs that will later generate neurons. However, neurogenesis does ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuron
A neuron, neurone, or nerve cell is an electrically excitable cell that communicates with other cells via specialized connections called synapses. The neuron is the main component of nervous tissue in all animals except sponges and placozoa. Non-animals like plants and fungi do not have nerve cells. Neurons are typically classified into three types based on their function. Sensory neurons respond to stimuli such as touch, sound, or light that affect the cells of the sensory organs, and they send signals to the spinal cord or brain. Motor neurons receive signals from the brain and spinal cord to control everything from muscle contractions to glandular output. Interneurons connect neurons to other neurons within the same region of the brain or spinal cord. When multiple neurons are connected together, they form what is called a neural circuit. A typical neuron consists of a cell body (soma), dendrites, and a single axon. The soma is a compact structure, and the axon and dend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ventricular Zone
In vertebrates, the ventricular zone (VZ) is a transient embryonic layer of tissue containing neural stem cells, principally radial glial cells, of the central nervous system (CNS). The VZ is so named because it lines the ventricular system, which contains cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). The embryonic ventricular system contains growth factors and other nutrients needed for the proper function of neural stem cells. Neurogenesis, or the generation of neurons, occurs in the VZ during embryonic and fetal development as a function of the Notch pathway, and the newborn neurons must migrate substantial distances to their final destination in the developing brain or spinal cord where they will establish neural circuits. A secondary proliferative zone, the subventricular zone (SVZ), lies adjacent to the VZ. In the embryonic cerebral cortex, the SVZ contains intermediate neuronal progenitors that continue to divide into post-mitotic neurons. Through the process of neurogenesis, the parent n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neural Stem Cells
Neural stem cells (NSCs) are self-renewing, multipotent cells that firstly generate the radial glial progenitor cells that generate the neurons and glia of the nervous system of all animals during embryonic development. Some neural progenitor stem cells persist in highly restricted regions in the adult vertebrate brain and continue to produce neurons throughout life. Differences in the size of the central nervous system are among the most important distinctions between the species and thus mutations in the genes that regulate the size of the neural stem cell compartment are among the most important drivers of vertebrate evolution. Stem cells are characterized by their capacity to differentiate into multiple cell types. They undergo symmetric or asymmetric cell division into two daughter cells. In symmetric cell division, both daughter cells are also stem cells. In asymmetric division, a stem cell produces one stem cell and one specialized cell. NSCs primarily differentiate i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Embryogenesis
An embryo is an initial stage of development of a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male sperm cell. The resulting fusion of these two cells produces a single-celled zygote that undergoes many cell divisions that produce cells known as blastomeres. The blastomeres are arranged as a solid ball that when reaching a certain size, called a morula, takes in fluid to create a cavity called a blastocoel. The structure is then termed a blastula, or a blastocyst in mammals. The mammalian blastocyst hatches before implantating into the endometrial lining of the womb. Once implanted the embryo will continue its development through the next stages of gastrulation, neurulation, and organogenesis. Gastrulation is the formation of the three germ layers that will form all of the different parts of the body. Neurulation forms the nervous sys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myelencephalon
The myelencephalon or afterbrain is the most posterior region of the embryonic hindbrain, from which the medulla oblongata develops. Development Neural tube to myelencephalon During fetal development, divisions of the neural tube that give rise to the hindbrain (rhombencephalon) and the other primary vesicles (forebrain and midbrain) occur at just 28 days after conception. With the exception of the midbrain, these primary vesicles undergo further differentiation at 5 weeks after conception to form the myelencephalon and the other secondary vesicles. Myelencephalon to medulla Final shape differentiation of the myelencephalon into the medulla oblongata can be observed at 20 weeks gestation.Carlson, Neil R. Foundations of Behavioral Neuroscience.63-65 Medulla oblongata The medulla oblongata is part of the brain stem that serves as the connection of the spinal cord to the brain. It is situated between the pons and the spinal cord. Function The medulla oblongata ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |