|
Myelencephalon
The myelencephalon or afterbrain is the most posterior region of the embryonic hindbrain, from which the medulla oblongata develops. Development Neural tube to myelencephalon During fetal development, divisions of the neural tube that give rise to the hindbrain (rhombencephalon) and the other primary vesicles (forebrain and midbrain) occur at just 28 days after conception. With the exception of the midbrain, these primary vesicles undergo further differentiation at 5 weeks after conception to form the myelencephalon and the other secondary vesicles. Myelencephalon to medulla Final shape differentiation of the myelencephalon into the medulla oblongata can be observed at 20 weeks gestation.Carlson, Neil R. Foundations of Behavioral Neuroscience.63-65 Medulla oblongata The medulla oblongata is part of the brain stem that serves as the connection of the spinal cord to the brain. It is situated between the pons and the spinal cord. Function The medulla oblongata ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medulla Oblongata
The medulla oblongata or simply medulla is a long stem-like structure which makes up the lower part of the brainstem. It is anterior and partially inferior to the cerebellum. It is a cone-shaped neuronal mass responsible for autonomic (involuntary) functions, ranging from vomiting to sneezing. The medulla contains the cardiac, respiratory, vomiting and vasomotor centers, and therefore deals with the autonomic functions of breathing, heart rate and blood pressure as well as the sleep–wake cycle. During embryonic development, the medulla oblongata develops from the myelencephalon. The myelencephalon is a secondary vesicle which forms during the maturation of the rhombencephalon, also referred to as the hindbrain. The bulb is an archaic term for the medulla oblongata. In modern clinical usage, the word bulbar (as in bulbar palsy) is retained for terms that relate to the medulla oblongata, particularly in reference to medical conditions. The word bulbar can refer to the nerves ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
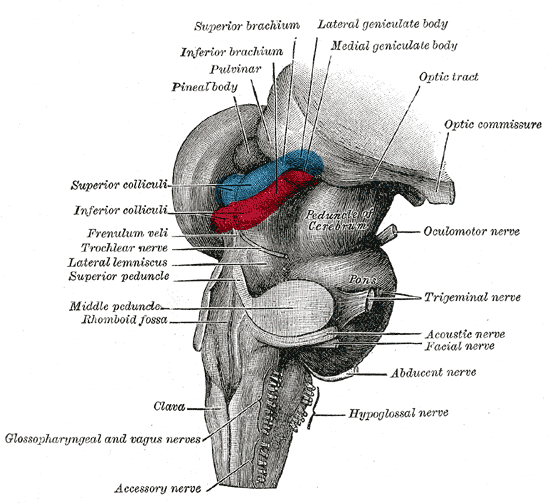
Brainstem
The brainstem (or brain stem) is the posterior stalk-like part of the brain that connects the cerebrum with the spinal cord. In the human brain the brainstem is composed of the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata. The midbrain is continuous with the thalamus of the diencephalon through the tentorial notch, and sometimes the diencephalon is included in the brainstem. The brainstem is very small, making up around only 2.6 percent of the brain's total weight. It has the critical roles of regulating cardiac, and respiratory function, helping to control heart rate and breathing rate. It also provides the main motor and sensory nerve supply to the face and neck via the cranial nerves. Ten pairs of cranial nerves come from the brainstem. Other roles include the regulation of the central nervous system and the body's sleep cycle. It is also of prime importance in the conveyance of motor and sensory pathways from the rest of the brain to the body, and from the body back to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhombencephalon
The hindbrain or rhombencephalon or lower brain is a developmental categorization of portions of the central nervous system in vertebrates. It includes the medulla, pons, and cerebellum. Together they support vital bodily processes. Metencephalon Rhombomeres Rh3-Rh1 form the metencephalon. The metencephalon is composed of the pons and the cerebellum; it contains: * a portion of the fourth (IV) ventricle, * the trigeminal nerve (CN V), * abducens nerve (CN VI), * facial nerve (CN VII), * and a portion of the vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII). Myelencephalon Rhombomeres Rh8-Rh4 form the myelencephalon. The myelencephalon forms the medulla oblongata in the adult brain; it contains: * a portion of the fourth ventricle, * the glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX), * vagus nerve (CN X), * accessory nerve (CN XI), * hypoglossal nerve (CN XII), * and a portion of the vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII). Evolution The hindbrain is homologous to a part of the arthropod brain known as the sub-oes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hindbrain
The hindbrain or rhombencephalon or lower brain is a developmental categorization of portions of the central nervous system in vertebrates. It includes the medulla, pons, and cerebellum. Together they support vital bodily processes. Metencephalon Rhombomeres Rh3-Rh1 form the metencephalon. The metencephalon is composed of the pons and the cerebellum; it contains: * a portion of the fourth (IV) ventricle, * the trigeminal nerve (CN V), * abducens nerve (CN VI), * facial nerve (CN VII), * and a portion of the vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII). Myelencephalon Rhombomeres Rh8-Rh4 form the myelencephalon. The myelencephalon forms the medulla oblongata in the adult brain; it contains: * a portion of the fourth ventricle, * the glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX), * vagus nerve (CN X), * accessory nerve (CN XI), * hypoglossal nerve (CN XII), * and a portion of the vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII). Evolution The hindbrain is homologous to a part of the arthropod brain known as the sub- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hindbrain
The hindbrain or rhombencephalon or lower brain is a developmental categorization of portions of the central nervous system in vertebrates. It includes the medulla, pons, and cerebellum. Together they support vital bodily processes. Metencephalon Rhombomeres Rh3-Rh1 form the metencephalon. The metencephalon is composed of the pons and the cerebellum; it contains: * a portion of the fourth (IV) ventricle, * the trigeminal nerve (CN V), * abducens nerve (CN VI), * facial nerve (CN VII), * and a portion of the vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII). Myelencephalon Rhombomeres Rh8-Rh4 form the myelencephalon. The myelencephalon forms the medulla oblongata in the adult brain; it contains: * a portion of the fourth ventricle, * the glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX), * vagus nerve (CN X), * accessory nerve (CN XI), * hypoglossal nerve (CN XII), * and a portion of the vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII). Evolution The hindbrain is homologous to a part of the arthropod brain known as the sub- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neural Tube
In the developing chordate (including vertebrates), the neural tube is the embryonic precursor to the central nervous system, which is made up of the brain and spinal cord. The neural groove gradually deepens as the neural fold become elevated, and ultimately the folds meet and coalesce in the middle line and convert the groove into the closed neural tube. In humans, neural tube closure usually occurs by the fourth week of pregnancy (the 28th day after conception). The ectodermal wall of the tube forms the rudiment of the nervous system. The centre of the tube is the ''neural canal''.It is an important structure for the development of fetus's brain and spine Development The neural tube develops in two ways: primary neurulation and secondary neurulation. Primary neurulation divides the ectoderm into three cell types: * The internally located neural tube * The externally located epidermis * The neural crest cells, which develop in the region between the neural tube and epider ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forebrain
In the anatomy of the brain of vertebrates, the forebrain or prosencephalon is the Anatomical terms of location#Directional terms, rostral (forward-most) portion of the brain. The forebrain (prosencephalon), the midbrain (mesencephalon), and hindbrain (rhombencephalon) are the three Brain vesicle, primary brain vesicles during the early development of the nervous system. The forebrain controls body temperature, reproductive functions, eating, sleeping, and the display of emotions. At the five-vesicle stage, the forebrain separates into the diencephalon (thalamus, hypothalamus, subthalamus, and epithalamus) and the telencephalon which develops into the cerebrum. The cerebrum consists of the cerebral cortex, underlying white matter, and the basal ganglia. In humans, by 5 weeks in utero it is visible as a single portion toward the front of the fetus. At 8 weeks in utero, the forebrain splits into the left and right cerebral hemispheres. When the embryonic forebrain fails to divide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diencephalon
The diencephalon (or interbrain) is a division of the forebrain (embryonic ''prosencephalon''). It is situated between the telencephalon and the midbrain (embryonic ''mesencephalon''). The diencephalon has also been known as the 'tweenbrain in older literature. It consists of structures that are on either side of the third ventricle, including the thalamus, the hypothalamus, the epithalamus and the subthalamus. The diencephalon is one of the main vesicles of the brain formed during embryogenesis. During the third week of development a neural tube is created from the ectoderm, one of the three primary germ layers. The tube forms three main vesicles during the third week of development: the prosencephalon, the mesencephalon and the rhombencephalon. The prosencephalon gradually divides into the telencephalon and the diencephalon. Structure The diencephalon consists of the following structures: *Thalamus *Hypothalamus including the posterior pituitary *Epithalamus which consists of: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Midbrain
The midbrain or mesencephalon is the forward-most portion of the brainstem and is associated with vision, hearing, motor control, sleep and wakefulness, arousal (alertness), and temperature regulation. The name comes from the Greek ''mesos'', "middle", and ''enkephalos'', "brain". Structure The principal regions of the midbrain are the tectum, the cerebral aqueduct, tegmentum, and the cerebral peduncles. Rostrally the midbrain adjoins the diencephalon (thalamus, hypothalamus, etc.), while caudally it adjoins the hindbrain (pons, medulla and cerebellum). In the rostral direction, the midbrain noticeably splays laterally. Sectioning of the midbrain is usually performed axially, at one of two levels – that of the superior colliculi, or that of the inferior colliculi. One common technique for remembering the structures of the midbrain involves visualizing these cross-sections (especially at the level of the superior colliculi) as the upside-down face of a be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Midbrain
The midbrain or mesencephalon is the forward-most portion of the brainstem and is associated with vision, hearing, motor control, sleep and wakefulness, arousal (alertness), and temperature regulation. The name comes from the Greek ''mesos'', "middle", and ''enkephalos'', "brain". Structure The principal regions of the midbrain are the tectum, the cerebral aqueduct, tegmentum, and the cerebral peduncles. Rostrally the midbrain adjoins the diencephalon (thalamus, hypothalamus, etc.), while caudally it adjoins the hindbrain (pons, medulla and cerebellum). In the rostral direction, the midbrain noticeably splays laterally. Sectioning of the midbrain is usually performed axially, at one of two levels – that of the superior colliculi, or that of the inferior colliculi. One common technique for remembering the structures of the midbrain involves visualizing these cross-sections (especially at the level of the superior colliculi) as the upside-down face of a be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1302 Brain Vesicle DevN
Thirteen or 13 may refer to: * 13 (number), the natural number following 12 and preceding 14 * One of the years 13 BC, AD 13, 1913, 2013 Music * 13AD (band), an Indian classic and hard rock band Albums * ''13'' (Black Sabbath album), 2013 * ''13'' (Blur album), 1999 * ''13'' (Borgeous album), 2016 * ''13'' (Brian Setzer album), 2006 * ''13'' (Die Ärzte album), 1998 * ''13'' (The Doors album), 1970 * ''13'' (Havoc album), 2013 * ''13'' (HLAH album), 1993 * ''13'' (Indochine album), 2017 * ''13'' (Marta Savić album), 2011 * ''13'' (Norman Westberg album), 2015 * ''13'' (Ozark Mountain Daredevils album), 1997 * ''13'' (Six Feet Under album), 2005 * ''13'' (Suicidal Tendencies album), 2013 * ''13'' (Solace album), 2003 * ''13'' (Second Coming album), 2003 * ''13'' (Ces Cru EP), 2012 * ''13'' (Denzel Curry EP), 2017 * ''Thirteen'' (CJ & The Satellites album), 2007 * ''Thirteen'' (Emmylou Harris album), 1986 * ''Thirteen'' (Harem Scarem album), 2014 * ''Thirt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pons
The pons (from Latin , "bridge") is part of the brainstem that in humans and other bipeds lies inferior to the midbrain, superior to the medulla oblongata and anterior to the cerebellum. The pons is also called the pons Varolii ("bridge of Varolius"), after the Italian anatomist and surgeon Costanzo Varolio (1543–75). This region of the brainstem includes neural pathways and tracts that conduct signals from the brain down to the cerebellum and medulla, and tracts that carry the sensory signals up into the thalamus.Saladin Kenneth S.(2007) Anatomy & physiology the unity of form and function. Dubuque, IA: McGraw-Hill Structure The pons is in the brainstem situated between the midbrain and the medulla oblongata, and in front of the cerebellum. A separating groove between the pons and the medulla is the inferior pontine sulcus. The superior pontine sulcus separates the pons from the midbrain. The pons can be broadly divided into two parts: the basilar part of the pons (ventral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |