|
Vajrolī
''Vajroli mudra'' (Sanskrit: वज्रोली मुद्रा ''vajrolī mudrā''), the Vajroli Seal, is a practice in Hatha yoga which requires the yogin to preserve his semen, either by learning not to release it, or if released by drawing it up through his urethra from the vagina of "a woman devoted to the practice of yoga". The mudra was described as "obscene" by the translator Rai Bahadur Srisa Chandra Vasu, and as "obscure and repugnant" by another translator, Hans-Ulrich Rieker. The mudra is rarely practised in modern times. It was covered in the 1900s by the American sexologist Ida C. Craddock, the resulting legal proceedings against her leading to her imprisonment and suicide. The explorer Theos Bernard learnt and illustrated the posture associated with the mudra. The pioneer of modern yoga, Krishnamacharya, gives impractical instructions for the mudra, demonstrating in Norman Sjoman's opinion that he had never tried the practice. Context Hatha yoga is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had diffused there from the northwest in the late Bronze Age. Sanskrit is the sacred language of Hinduism, the language of classical Hindu philosophy, and of historical texts of Buddhism and Jainism. It was a link language in ancient and medieval South Asia, and upon transmission of Hindu and Buddhist culture to Southeast Asia, East Asia and Central Asia in the early medieval era, it became a language of religion and high culture, and of the political elites in some of these regions. As a result, Sanskrit had a lasting impact on the languages of South Asia, Southeast Asia and East Asia, especially in their formal and learned vocabularies. Sanskrit generally connotes several Old Indo-Aryan language varieties. The most archaic of these is the Vedic Sanskrit found in the Rig Veda, a colle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
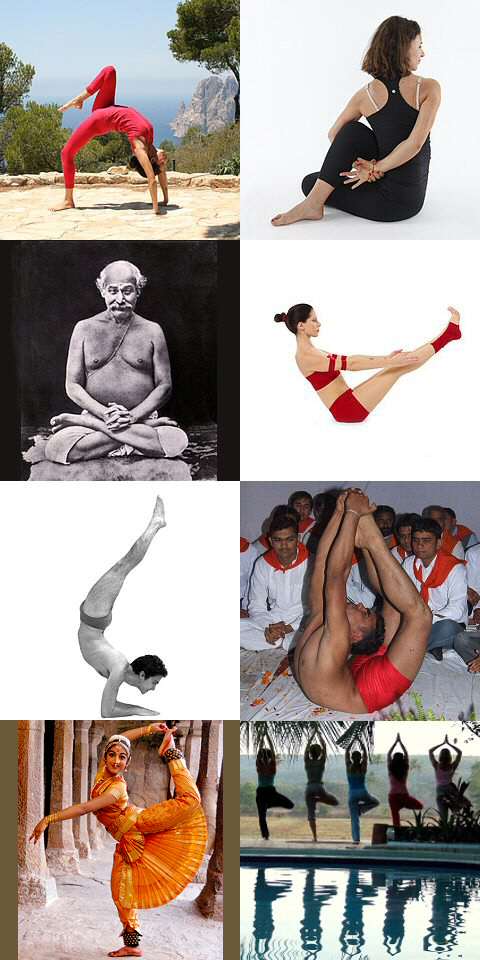
Asana
An asana is a body posture, originally and still a general term for a sitting meditation pose,Verse 46, chapter II, "Patanjali Yoga sutras" by Swami Prabhavananda, published by the Sri Ramakrishna Math p. 111 and later extended in hatha yoga and modern yoga as exercise, to any type of position, adding reclining, standing, inverted, twisting, and balancing poses. The ''Yoga Sutras of Patanjali'' define "asana" as " position thatis steady and comfortable". Patanjali mentions the ability to sit for extended periods as one of the eight limbs of his system. Patanjali ''Yoga sutras'', Book II:29, 46 Asanas are also called yoga poses or yoga postures in English. The 10th or 11th century '' Goraksha Sataka'' and the 15th century '' Hatha Yoga Pradipika'' identify 84 asanas; the 17th century ''Hatha Ratnavali'' provides a different list of 84 asanas, describing some of them. In the 20th century, Indian nationalism favoured physical culture in response to colonialism. In that enviro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shiva Samhita
''Shiva Samhita'' (IAST: śivasaṃhitā, also ''Siva Samhita'', meaning "Shiva's Compendium") is a Sanskrit text on yoga, written by an unknown author. The text is addressed by the Hindu god Shiva to his consort Parvati. The text consists of five chapters, with the first chapter a treatise that summarizes nondual Vedanta (Advaita Vedanta) philosophy with influences from the Sri Vidya school of South India. The remaining chapters discuss yoga, the importance of a guru (teacher) to a student, various asanas, mudras and siddhis (powers) attainable with yoga and tantra. The ''Shiva Samhita'' is one of three major surviving classical treatises on hatha yoga, the other two being '' Gheranda Samhita'' and ''Hatha Yoga Pradipika''. It is considered the most comprehensive treatise on hatha yoga, one that recommends that all householders practice and benefit from yoga. Over a dozen variant manuscripts of the text are known, and a critical edition of the text was published in 1999 by Kaival ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bihar School Of Yoga
The Bihar School of Yoga is a modern school of yoga founded by Satyananda Saraswati in Munger, Bihar, India, in 1963. An Institute of Yogic Studies was created in 1994. History The Bihar School of Yoga was established in 1963 at Munger, in the Indian state of Bihar, by Satyananda Saraswati. By the late 1960s, it had expanded to become an international organisation and by the mid-1970s comprised 54 ashrams in various countries. An institute of Yogic studies was created in 1994. The school publishes ''Yoga Magazine''. The school teaches traditional yoga in a modern style, for example making use of software apps to distribute knowledge of mantra yoga, hatha yoga, jnana yoga and raja yoga. Locations The primary Bihar School of Yoga campus is called Ganga Darshan. It includes residential facilities for guests and students. Satyananda yoga was taught in many organizations in the world by the mid-1970s, including eight ashrams in Australia, of which 3 were run by sannyasins. Sexu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satyananda Saraswati
Satyananda Saraswati (25 December 1923 – 5 December 2009), was a Sanyasi, yoga teacher and guru in both his native India and the West. He was a student of Sivananda Saraswati, the founder of the Divine Life Society, and founded the Bihar School of Yoga in 1964. He wrote over 80 books, including the popular 1969 manual ''Asana Pranayama Mudra Bandha''. Biography Early life Satyananda Saraswati was born in 1923 at Almora, Uttaranchal, into a family of farmers and kshatriyas, the warrior caste. It is claimed that he was classically educated and studied Sanskrit, the Vedas and the Upanishads. He stated that he began to have spiritual experiences at the age of six, when his awareness spontaneously left the body and he saw himself lying motionless on the floor. This experience of disembodied awareness continued, leading him to saints of that time such as Anandamayi Ma. He claimed to have met a tantric bhairavi, Sukhman Giri, who gave him shaktipat and directed him to find ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brahma
Brahma ( sa, ब्रह्मा, Brahmā) is a Hindu god, referred to as "the Creator" within the Trimurti, the trinity of supreme divinity that includes Vishnu, and Shiva.Jan Gonda (1969)The Hindu Trinity Anthropos, Bd 63/64, H 1/2, pp. 212–226. He is associated with creation, knowledge, and the ''Vedas''. Brahma is prominently mentioned in creation legends. In some ''Puranas'', he created himself in a golden embryo known as the Hiranyagarbha. Brahma is frequently identified with the Vedic god Prajapati.;David Leeming (2005), The Oxford Companion to World Mythology, Oxford University Press, , page 54, Quote: "Especially in the Vedanta Hindu Philosophy, Brahman is the Absolute. In the Upanishads, Brahman becomes the eternal first cause, present everywhere and nowhere, always and never. Brahman can be incarnated in Brahma, in Vishnu, in Shiva. To put it another way, everything that is, owes its existence to Brahman. In this sense, Hinduism is ultimately monotheistic or m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
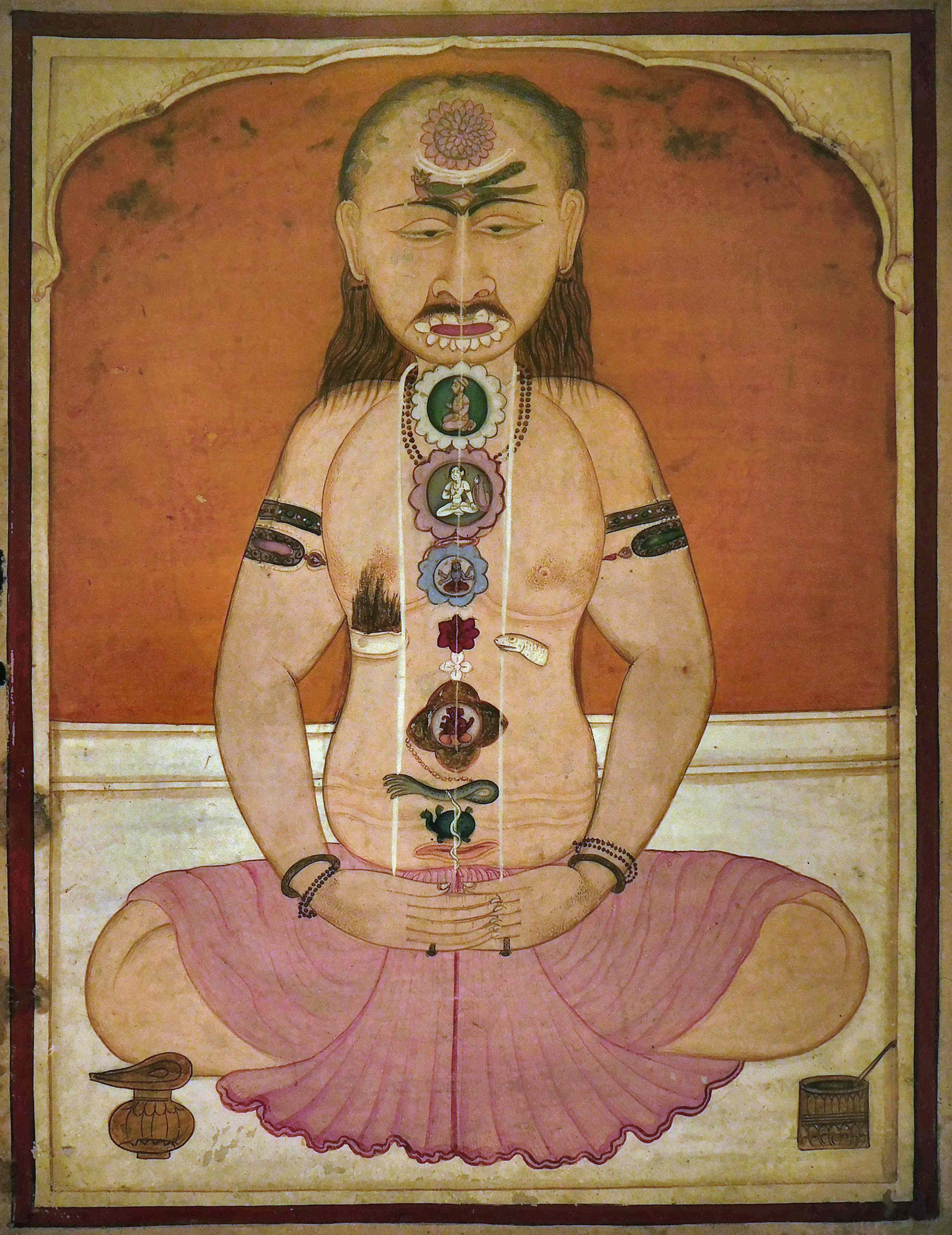
Kundalini
In Hinduism, Kundalini ( sa, कुण्डलिनी, translit=kuṇḍalinī, translit-std=IAST, lit=coiled snake, ) is a form of divine feminine energy (or ''Shakti'') believed to be located at the base of the spine, in the ''muladhara''. It is an important concept in Śhaiva Tantra, where it is believed to be a force or power associated with the divine feminine or the formless aspect of the Goddess. This energy in the body, when cultivated and awakened through tantric practice, is believed to lead to spiritual liberation. Kuṇḍalinī is associated with Parvati or Adi Parashakti, the supreme being in Shaktism; and with the goddesses Bhairavi and Kubjika. The term, along with practices associated with it, was adopted into Hatha yoga in the 9th century. It has since then been adopted into other forms of Hinduism as well as modern spirituality and New Age, New age thought. Kuṇḍalinī awakenings are said to occur by a variety of methods. Many systems of yoga focus o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hatha Yoga Pradipika
The ''Haṭha Yoga Pradīpikā'' ( or Light on Hatha Yoga) is a classic fifteenth-century Sanskrit manual on haṭha yoga, written by Svātmārāma, who connects the teaching's lineage to Matsyendranath of the Nathas. It is among the most influential surviving texts on haṭha yoga, being one of the three classic texts alongside the '' Gheranda Samhita'' and the ''Shiva Samhita''. More recently, eight works of early hatha yoga that may have contributed to the ''Hatha Yoga Pradipika'' have been identified. Title and composition Different manuscripts offer different titles for the text, including ''Haṭhayogapradīpikā'', ''Haṭhapradīpikā'', ''Haṭhapradī'', and ''Hath-Pradipika''. It was composed by Svātmārāma in the 15th century as a compilation of the earlier haṭha yoga texts. Svātmārāma incorporates older Sanskrit concepts into his synthesis. He introduces his system as a preparatory stage for physical purification before higher meditation or Raja Yoga. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gheranda Samhita
''Gheranda Samhita'' (IAST: gheraṇḍasaṁhitā, घेरंडसंहिता, meaning “Gheranda's collection”) is a Sanskrit text of Yoga in Hinduism. It is one of the three classic texts of hatha yoga (the other two being the ''Hatha Yoga Pradipika'' and the ''Shiva Samhita''), and one of the most encyclopedic treatises in yoga.B. Heimann (1937)Review: The Ǧheraṇda Saṁhitā. A Treatise on Haṭha Yoga by Śrīś Chandra Vasu The Journal of the Royal Asiatic Society of Great Britain and Ireland, Cambridge University Press, No. 2 (Apr., 1937), pp. 355-357 Fourteen manuscripts of the text are known, which were discovered in a region stretching from Bengal to Rajasthan. The first critical edition was published in 1933 by Adyar Library, and the second critical edition was published in 1978 by Digambarji and Ghote. Some of the Sanskrit manuscripts contain ungrammatical and incoherent verses, and some cite older Sanskrit texts. It is likely a late 17th-century text, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bindu (symbol)
''Bindu'' ( sa, बिंदु) is a Sanskrit word meaning "point", "drop" or "dot". Philosophy In Hindu metaphysics, Bindu is considered the point at which creation begins and may become unity. It is also described as "the sacred symbol of the cosmos in its unmanifested state". Bindu is the point around which the mandala is created, representing the universe. Bindu is often merged with eed(or sperm) and ova. In the '' Yogachudamani Upanishad'' Bindu is a duality, with a white Bindu representing ''shukla'' (pure) and a red Bindu representing ''maharaj'' (mastery). The white Bindu resides in the '' bindu visarga'' and is related to Shiva and the Moon, while the red Bindu resides in the ''muladhara'' chakra and is related to Shakti and the Sun. In yoga, the union of these two parts results in the ascension of kundalini to the sahasrara. In Tibetan Buddhism Bindu is a component of the subtle body, which is composed of drops (Tibetan: ཐིག་ལེ ''thig le'') and winds ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
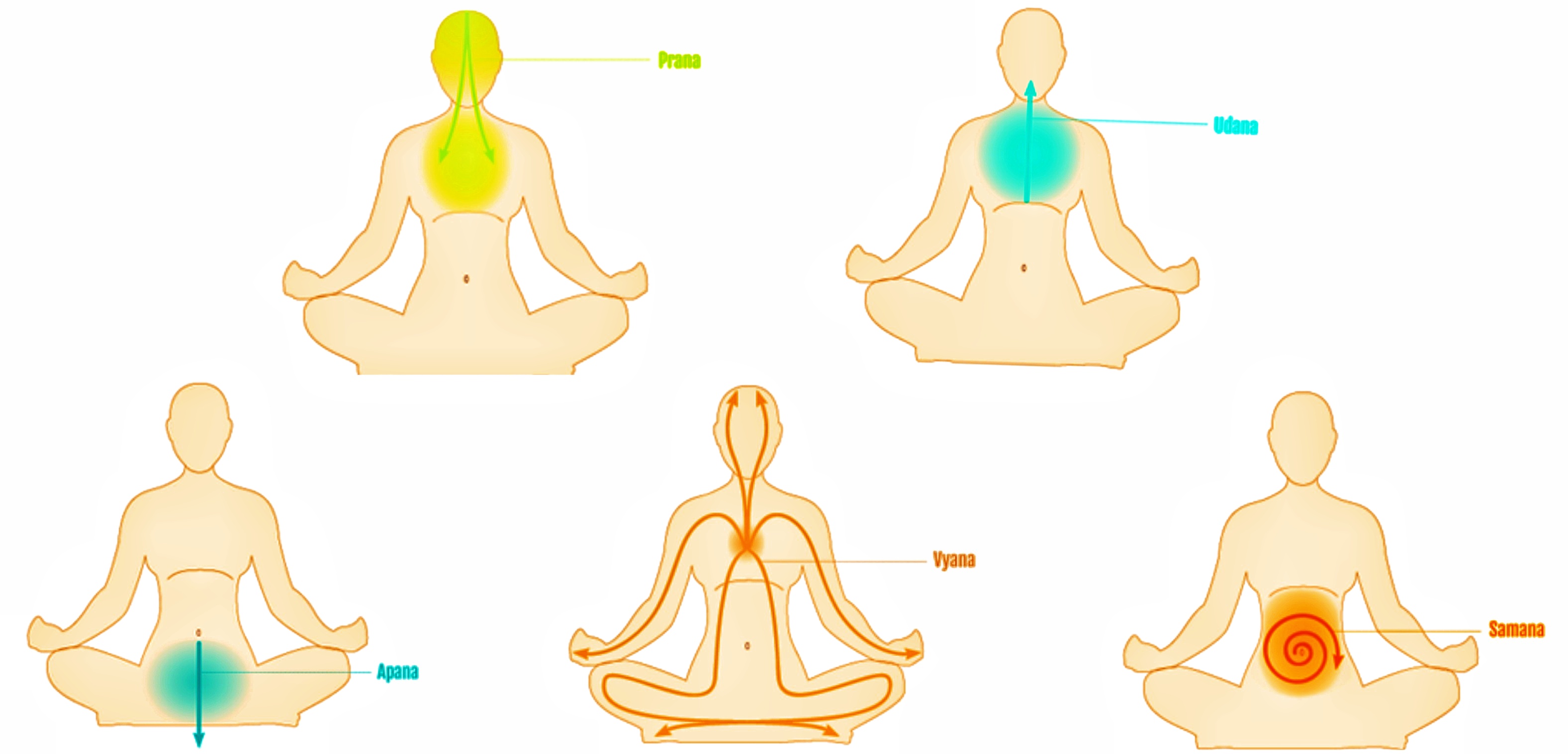
Prana
In yoga, Indian medicine and Indian martial arts, prana ( sa2, प्राण, ; the Sanskrit word for breath, " life force", or "vital principle") permeates reality on all levels including inanimate objects. In Hindu literature, prāṇa is sometimes described as originating from the Sun and connecting the elements. Five types of prāṇa, collectively known as the five ''vāyus'' ("winds"), are described in Hindu texts. Ayurveda, tantra and Tibetan medicine all describe ''prāṇa vāyu'' as the basic vāyu from which the other vāyus arise. Prana is divided into ten main functions: The five Pranas – Prana, Apana, Udana, Vyana and Samana – and the five Upa-Pranas – Naga, Kurma, Devadatta, Krikala and Dhananjaya. Pranayama, one of the eight limbs of yoga, is intended to expand prana. Etymology V. S. Apte provides fourteen different meanings for the Sanskrit word ' () including breath or respiration; the breath of life, vital air, principle of life (usually plura ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mula Bandha
A bandha ( sa, बंध) is a kriyā in Hatha Yoga, being a kind of internal mudra described as a "body lock," to lock the vital energy into the body. ''Bandha'' literally means bond, fetter, or "catching hold of".Iyengar, 1976: pp.435–437 Maha Bandha ("the great lock") combines all the other three bandhas, namely: * Mula Bandha, contraction of the perineum * Uddiyana bandha, contraction of the abdomen into the rib cage * Jalandhara Bandha, tucking the chin close to the chest In Ashtanga Vinyasa Yoga, these three Bandhas are considered to be one of the three key principles of yoga practice. ''Mula bandha'' ''Mūla bandha'' is a primary ''bandha'' in traditional yoga. The earliest textual mention of ''mūla bandha'' is in the 12th century Shaiva Natha text '' Gorakṣaśataka'' which defines it as a yogic technique to achieve mastery of breath and to awaken the goddess Kuṇḍalinī. Etymology Mula Bandha (Sanskrit: मूल बंध) is from ''Mūla'', meaning variously ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |