|
Visual Thinking
Visual thinking, also called visual or spatial learning or picture thinking, is the phenomenon of thinking through visual processing. Visual thinking has been described as seeing words as a series of pictures. It is common in approximately 60–65% of the general population. "Real picture thinkers", those who use visual thinking almost to the exclusion of other kinds of thinking, make up a smaller percentage of the population. Research by child development theorist Linda Kreger Silverman suggests that less than 30% of the population strongly uses visual/spatial thinking, another 45% uses both visual/spatial thinking and thinking in the form of words, and 25% thinks exclusively in words. According to Kreger Silverman, of the 30% of the general population who use visual/spatial thinking, only a small percentage would use this style over and above all other forms of thinking, and can be said to be true "picture thinkers". Non-verbal thought Thinking in mental images is one of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visual Processing
Visual processing is a term that is used to refer to the brain's ability to use and interpret visual information from the world around us. The process of converting light energy into a meaningful image is a complex process that is facilitated by numerous brain structures and higher level cognitive processes. On an anatomical level, light energy first enters the eye through the cornea, where the light is bent. After passing through the cornea, light passes through the pupil and then lens of the eye, where it is bent to a greater degree and focused upon the retina. The retina is where a group of light-sensing cells, called photoreceptors are located. There are two types of photoreceptors: rods and cones. Rods are sensitive to dim light and cones are better able to transduce bright light. Photoreceptors connect to bipolar cells, which induce action potentials in retinal ganglion cells. These retinal ganglion cells form a bundle at the optic disc, which is a part of the optic nerve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Written Text
Writing is a medium of human communication which involves the representation of a language through a system of physically inscribed, mechanically transferred, or digitally represented symbols. Writing systems do not themselves constitute human languages (with the debatable exception of computer languages); they are a means of rendering language into a form that can be reconstructed by other humans separated by time and/or space. While not all languages use a writing system, those that do can complement and extend capacities of spoken language by creating durable forms of language that can be transmitted across space (e.g. written correspondence) and stored over time (e.g. libraries or other public records). It has also been observed that the activity of writing itself can have knowledge-transforming effects, since it allows humans to externalize their thinking in forms that are easier to reflect on, elaborate, reconsider, and revise. A system of writing relies on many of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Epoch Notation Painting
Peter Benjamin Graham (4 June 1925 – 15 April 1987), was an Australian visual artist, printer, and art theorist. In 1954, Graham began to explore native Australian wildlife (notably Kangaroos) and themes associated with Aboriginal culture, using the visual languages of European figurative Modernism and, later, geometric abstraction. He began developing a new form of visual geometry related to Chaos Theory from 1960, eventually called Thematic Orchestration. The new visual language enabled the 2D deconstruction and synthesis of an observed subject, in a way fundamentally different from traditional abstraction. Thematic Orchestration allows the artist to 'grow' an image, producing almost infinite conscious invention. In 1964, Graham began developing what he called a high level visual notation system for pure visual imagery, which he first named "Notation Painting" and later "New Epoch Art". Graham became a pioneer of the Australian artist run initiative movement, running Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
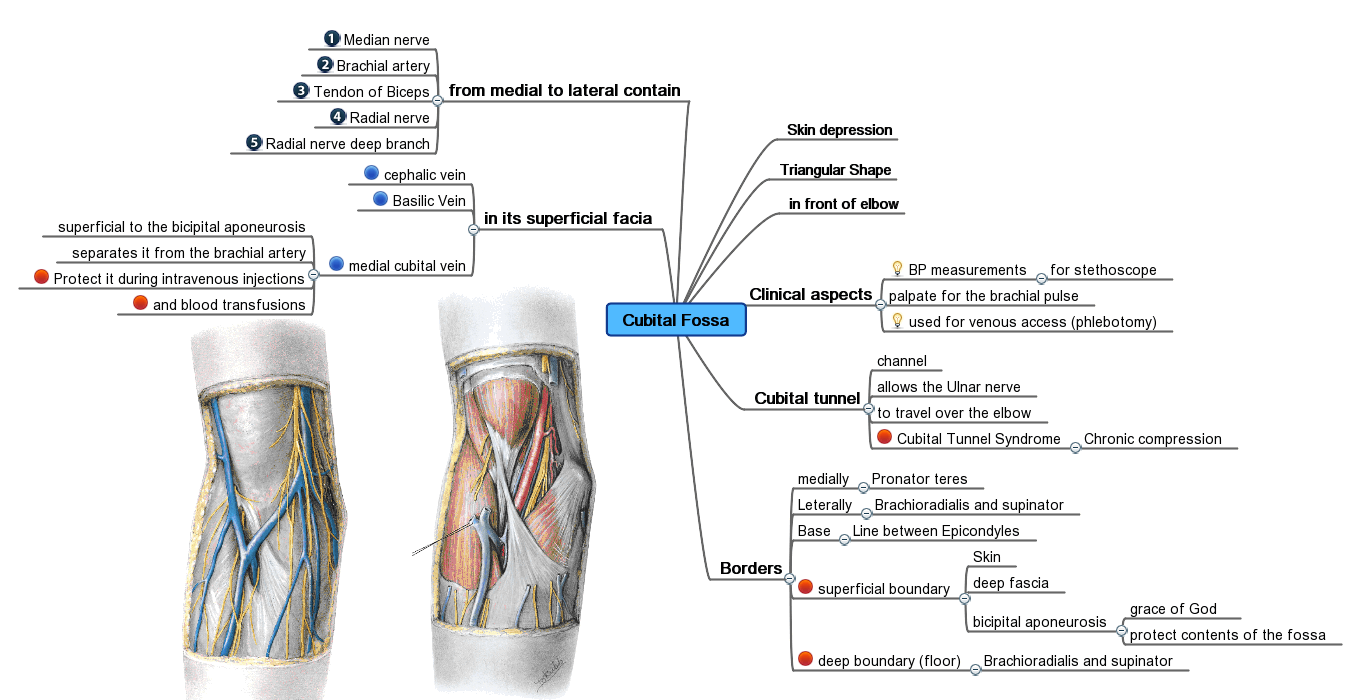
Mind Map
A mind map is a diagram used to visually organize information into a hierarchy, showing relationships among pieces of the whole. It is often created around a single concept, drawn as an image in the center of a blank page, to which associated representations of ideas such as images, words and parts of words are added. Major ideas are connected directly to the central concept, and other ideas branch out from those major ideas. Mind maps can also be drawn by hand, either as "notes" during a lecture, meeting or planning session, for example, or as higher quality pictures when more time is available. Mind maps are considered to be a type of spider diagram. Origins Although the term "mind map" was first popularized by British popular psychology author and television personality Tony Buzan, the use of diagrams that visually "map" information using branching and radial maps traces back centuries. These pictorial methods record knowledge and model systems, and have a long history i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mental Image
A mental image is an experience that, on most occasions, significantly resembles the experience of 'perceiving' some object, event, or scene, but occurs when the relevant object, event, or scene is not actually present to the senses. There are sometimes episodes, particularly on falling asleep ( hypnagogic imagery) and waking up ( hypnopompic imagery), when the mental imagery may be dynamic, phantasmagoric and involuntary in character, repeatedly presenting identifiable objects or actions, spilling over from waking events, or defying perception, presenting a kaleidoscopic field, in which no distinct object can be discerned. Mental imagery can sometimes produce the same effects as would be produced by the behavior or experience imagined. The nature of these experiences, what makes them possible, and their function (if any) have long been subjects of research and controversy in philosophy, psychology, cognitive science, and, more recently, neuroscience. As contemporary researche ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intellectual Giftedness
Intellectual giftedness is an intellectual ability significantly higher than average. It is a characteristic of children, variously defined, that motivates differences in school programming. It is thought to persist as a trait into adult life, with various consequences studied in longitudinal studies of giftedness over the last century. There is no generally agreed definition of giftedness for either children or adults, but most school placement decisions and most longitudinal studies over the course of individual lives have followed people with IQs in the top 2.5 percent of the population—that is, IQs above 130. Definitions of giftedness also vary across cultures. The various definitions of intellectual giftedness include either general high ability or specific abilities. For example, by some definitions, an intellectually gifted person may have a striking talent for mathematics without equally strong language skills. In particular, the relationship between artistic ability ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Image Schema
An image schema (both ''schemas'' and ''schemata'' are used as plural forms) is a recurring structure within our cognitive processes which establishes patterns of understanding and reasoning. As an understudy to embodied cognition, image schemas are formed from our bodily interactions, from linguistic experience, and from historical context. The term is introduced in Mark Johnson's book ''The Body in the Mind''; in case study 2 of George Lakoff's ''Women, Fire and Dangerous Things:'' and further explained by Todd Oakley in ''The Oxford handbook of cognitive linguistics;'' by Rudolf Arnheim in ''Visual Thinking''; by the collection ''From Perception to Meaning: Image Schemas in Cognitive Linguistics'' edited by Beate Hampe and Joseph E. Grady. In contemporary cognitive linguistics, an image schema is considered an embodied prelinguistic structure of experience that motivates conceptual metaphor mappings. Learned in early infancy they are often described as spatiotemporal relations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concept Map
A concept map or conceptual diagram is a diagram that depicts suggested relationships between concepts. Concept maps may be used by instructional designers, engineers, technical writers, and others to organize and structure knowledge. A concept map typically represents ideas and information as boxes or circles, which it connects with labeled arrows, often in a downward-branching hierarchical structure but also in free-form maps. The relationship between concepts can be articulated in '' linking phrases'' such as "causes", "requires", "such as" or "contributes to". The technique for visualizing these relationships among different concepts is called ''concept mapping''. Concept maps have been used to define the ontology of computer systems, for example with the object-role modeling or Unified Modeling Language formalism. Differences from other visualizations * ''Topic maps'': Both concept maps and topic maps are kinds of knowledge graph, but topic maps were developed by in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aphantasia
Aphantasia ( , ) is the inability to create mental imagery. The phenomenon was first described by Francis Galton in 1880 but has since remained relatively unstudied. Interest in the phenomenon renewed after the publication of a study in 2015 conducted by a team led by Professor Adam Zeman of the University of Exeter. Zeman's team coined the term ''aphantasia'', derived from the ancient Greek word (), which means "imagination", and the prefix (), which means "without". Research on the condition is still scarce. Hyperphantasia, the condition of having extremely vivid mental imagery, is the opposite of aphantasia. History The phenomenon was first described by Francis Galton in 1880 in a statistical study about mental imagery. Galton found it was a common phenomenon among his peers. He wrote: In 1897, Théodule-Armand Ribot reported a kind of "typographic visual type" imagination, consisting in mentally seeing ideas in the form of corresponding printed words. As paraphrased b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rudolf Arnheim
Rudolf Arnheim (July 15, 1904 – June 9, 2007) was a German-born writer, art and film theorist, and perceptual psychologist. He learned Gestalt psychology from studying under Max Wertheimer and Wolfgang Köhler at the University of Berlin and applied it to art. His magnum opus was his book ''Art and Visual Perception: A Psychology of the Creative Eye'' (1954). Other major books by Arnheim have included ''Visual Thinking'' (1969), and ''The Power of the Center: A Study of Composition in the Visual Arts'' (1982). ''Art and Visual Perception'' was revised, enlarged and published as a new version in 1974, and it has been translated into fourteen languages. He lived in Germany, Italy, England, and the U.S., where he taught at Sarah Lawrence College, Harvard University, and the University of Michigan. In ''Art and Visual Perception'', he tried to use science to better understand art. In his later book ''Visual Thinking'' (1969), Arnheim critiqued the assumption that language goes be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VISUAL THINKING Manifesto A Torino
The visual system comprises the sensory organ (the eye) and parts of the central nervous system (the retina containing photoreceptor cells, the optic nerve, the optic tract and the visual cortex) which gives organisms the sense of sight (the ability to detect and process visible light) as well as enabling the formation of several non-image photo response functions. It detects and interprets information from the optical spectrum perceptible to that species to "build a representation" of the surrounding environment. The visual system carries out a number of complex tasks, including the reception of light and the formation of monocular neural representations, colour vision, the neural mechanisms underlying stereopsis and assessment of distances to and between objects, the identification of a particular object of interest, motion perception, the analysis and integration of visual information, pattern recognition, accurate motor coordination under visual guidance, and more. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autism
The autism spectrum, often referred to as just autism or in the context of a professional diagnosis autism spectrum disorder (ASD) or autism spectrum condition (ASC), is a neurodevelopmental condition (or conditions) characterized by difficulties in social interaction, verbal and nonverbal communication, and the presence of repetitive behavior and restricted interests. Other common signs include unusual responses to sensory stimuli. Autism is generally understood as a ''spectrum disorder'', which means that it can manifest differently in each person: any given autistic individual is likely to show some, but not all, of the characteristics associated with it, and the person may exhibit them to varying degrees. Some autistic people remain nonspeaking over the course of their lifespan, while others have relatively unimpaired spoken language. There is large variation in the level of support people require, and the same person may present differently at varying times. Historically ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |