|
Visual Processing
Visual processing is a term that is used to refer to the brain's ability to use and interpret visual information from the world around us. The process of converting light energy into a meaningful image is a complex process that is facilitated by numerous brain structures and higher level cognitive processes. On an anatomical level, light energy first enters the eye through the cornea, where the light is bent. After passing through the cornea, light passes through the pupil and then lens of the eye, where it is bent to a greater degree and focused upon the retina. The retina is where a group of light-sensing cells, called photoreceptors are located. There are two types of photoreceptors: rods and cones. Rods are sensitive to dim light and cones are better able to transduce bright light. Photoreceptors connect to bipolar cells, which induce action potentials in retinal ganglion cells. These retinal ganglion cells form a bundle at the optic disc, which is a part of the optic ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Brain
The human brain is the central organ (anatomy), organ of the human nervous system, and with the spinal cord makes up the central nervous system. The brain consists of the cerebrum, the brainstem and the cerebellum. It controls most of the activities of the human body, body, processing, integrating, and coordinating the information it receives from the Sensory nervous system, sense organs, and making decisions as to the instructions sent to the rest of the body. The brain is contained in, and protected by, the neurocranium, skull bones of the human head, head. The cerebrum, the largest part of the human brain, consists of two cerebral hemispheres. Each hemisphere has an inner core composed of white matter, and an outer surface – the cerebral cortex – composed of grey matter. The cortex has an outer layer, the neocortex, and an inner allocortex. The neocortex is made up of six Cerebral cortex#Layers of neocortex, neuronal layers, while the allocortex has three or four. Each ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Right Hemisphere
The lateralization of brain function is the tendency for some neural functions or cognitive processes to be specialized to one side of the brain or the other. The median longitudinal fissure separates the human brain into two distinct cerebral hemispheres, connected by the corpus callosum. Although the macrostructure of the two hemispheres appears to be almost identical, different composition of neuronal networks allows for specialized function that is different in each hemisphere. Lateralization of brain structures is based on general trends expressed in healthy patients; however, there are numerous counterexamples to each generalization. Each human's brain develops differently, leading to unique lateralization in individuals. This is different from specialization, as lateralization refers only to the function of one structure divided between two hemispheres. Specialization is much easier to observe as a trend, since it has a stronger anthropological history. The best exam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akinetopsia
Akinetopsia (Greek: a for "without", kine for "to move" and opsia for "seeing"), also known as cerebral akinetopsia or motion blindness, is a term introduced by Semir Zeki to describe an extremely rare neuropsychological disorder, having only been documented in a handful of medical cases, in which a patient cannot perceive motion in their visual field, despite being able to see stationary objects without issue. There are varying degrees of akinetopsia: from seeing motion as frames of a cinema reel to an inability to discriminate any motion. There is currently no effective treatment or cure for akinetopsia. Signs and symptoms Akinetopsia can be separated into two categories, "inconspicuous akinetopsia" or "gross akinetopsia", based on symptom severity and the amount the akinetopsia affects the patient's quality of life. Inconspicuous akinetopsia Inconspicuous akinetopsia is often described by seeing motion as a cinema reel or a multiple exposure photograph. This is the most comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Achromatopsia
Achromatopsia, also known as Rod monochromacy, is a medical syndrome that exhibits symptoms relating to five conditions, most notably monochromacy. Historically, the name referred to monochromacy in general, but now typically refers only to an autosomal recessive congenital color vision condition. The term is also used to describe cerebral achromatopsia, though monochromacy is usually the only common symptom. The conditions include: monochromatic color blindness, poor visual acuity, and day-blindness. The syndrome is also present in an ''incomplete'' form that exhibits milder symptoms, including residual color vision. Achromatopsia is estimated to affect 1 in 30,000 live births worldwide. Signs and symptoms The five symptoms associated with achromatopsia are: # Color blindness - usually monochromacy # Reduced visual acuity - uncorrectable with lenses # Hemeralopia – with the subject exhibiting photophobia # Nystagmus # Iris operating abnormalities The syndrome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dyslexia
Dyslexia, also known until the 1960s as word blindness, is a disorder characterized by reading below the expected level for one's age. Different people are affected to different degrees. Problems may include difficulties in spelling words, reading quickly, writing words, "sounding out" words in the head, pronouncing words when reading aloud and understanding what one reads. Often these difficulties are first noticed at school. The difficulties are involuntary, and people with this disorder have a normal desire to learn. People with dyslexia have higher rates of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), developmental language disorders, and difficulties with numbers. Dyslexia is believed to be caused by the interaction of genetic and environmental factors. Some cases run in families. Dyslexia that develops due to a traumatic brain injury, stroke, or dementia is sometimes called "acquired dyslexia" or alexia. The underlying mechanisms of dyslexia result from diffe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Topographical Disorientation
Topographical disorientation is the inability to orient oneself in one's surroundings, sometimes as a result of focal brain damage. This disability may result from the inability to make use of selective spatial information (e.g., environmental landmarks) or to orient by means of specific cognitive strategies such as the ability to form a mental representation of the environment, also known as a cognitive map. It may be part of a syndrome known as visuospatial dysgnosia. Classification Topographical disorientation is the inability to find one's way through an environment due to cognitive impairment. Topographical disorientation has been studied for decades using case studies of patients who have selectively lost their ability to find their way within large-scale, locomotor environments. Several dozen case reports of topographical disorientation have been presented over the last century. Studying these people will aid in the understanding of the complex, multi-component behavior ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prosopagnosia
Prosopagnosia (from Greek ''prósōpon'', meaning "face", and ''agnōsía'', meaning "non-knowledge"), also called face blindness, (" illChoisser had even begun tpopularizea name for the condition: face blindness.") is a cognitive disorder of face perception in which the ability to recognize familiar faces, including one's own face (self-recognition), is impaired, while other aspects of visual processing (e.g., object discrimination) and intellectual functioning (e.g., decision-making) remain intact. The term originally referred to a condition following acute brain damage (acquired prosopagnosia), but a congenital or developmental form of the disorder also exists, with a prevalence of 2.5%. The brain area usually associated with prosopagnosia is the fusiform gyrus, which activates specifically in response to faces. The functionality of the fusiform gyrus allows most people to recognize faces in more detail than they do similarly complex inanimate objects. For those with prosopagn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visual Agnosia
Visual agnosia is an impairment in recognition of visually presented objects. It is not due to a deficit in vision (acuity, visual field, and scanning), language, memory, or intellect. While cortical blindness results from lesions to primary visual cortex, visual agnosia is often due to damage to more anterior cortex such as the posterior occipital and/or temporal lobe(s) in the brain. /sup> There are two types of visual agnosia: apperceptive agnosia and associative agnosia. Recognition of visual objects occurs at two primary levels. At an apperceptive level, the features of the visual information from the retina are put together to form a perceptual representation of an object. At an associative level, the meaning of an object is attached to the perceptual representation and the object is identified. If a person is unable to recognize objects because they cannot perceive correct forms of the objects, although their knowledge of the objects is intact (i.e. they do not have anomia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrophysiology
Electrophysiology (from Greek , ''ēlektron'', "amber" Electron#Etymology">etymology of "electron" , ''physis'', "nature, origin"; and , ''-logia'') is the branch of physiology that studies the electrical properties of biological cells and tissues. It involves measurements of voltage changes or electric current or manipulations on a wide variety of scales from single ion channel proteins to whole organs like the heart. In neuroscience, it includes measurements of the electrical activity of neurons, and, in particular, action potential activity. Recordings of large-scale electric signals from the nervous system, such as electroencephalography, may also be referred to as electrophysiological recordings. They are useful for electrodiagnosis and monitoring. Definition and scope Classical electrophysiological techniques Principle and mechanisms Electrophysiology is the branch of physiology that pertains broadly to the flow of ions ( ion current) in biological tissues and, in pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macaque
The macaques () constitute a genus (''Macaca'') of gregarious Old World monkeys of the subfamily Cercopithecinae. The 23 species of macaques inhabit ranges throughout Asia, North Africa, and (in one instance) Gibraltar. Macaques are principally frugivorous (preferring fruit), although their diet also includes seeds, leaves, flowers, and tree bark. Some species, such as the crab-eating macaque, subsist on a diet of invertebrates and occasionally small vertebrates. On average, southern pig-tailed macaques in Malaysia eat about 70 large rats each per year. All macaque social groups are matriarchal, arranged around dominant females. Macaques are found in a variety of habitats throughout the Asian continent and are highly adaptable. Certain species have learned to live with humans and have become invasive in some human-settled environments, such as the island of Mauritius and Silver Springs State Park in Florida. Macaques can be a threat to wildlife conservation as well as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cognitive Neuroscience Of Visual Object Recognition
Visual object recognition refers to the ability to identify the objects in view based on visual input. One important signature of visual object recognition is "object invariance", or the ability to identify objects across changes in the detailed context in which objects are viewed, including changes in illumination, object pose, and background context. Basic stages of object recognition Neuropsychological evidence affirms that there are four specific stages identified in the process of object recognition. These stages are: :Stage 1 Processing of basic object components, such as color, depth, and form. :Stage 2 These basic components are then grouped on the basis of similarity, providing information on distinct edges to the visual form. Subsequently, figure-ground segregation is able to take place. :Stage 3 The visual representation is matched with structural descriptions in memory. :Stage 4 Semantic attributes are applied to the visual representation, providing meaning, and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
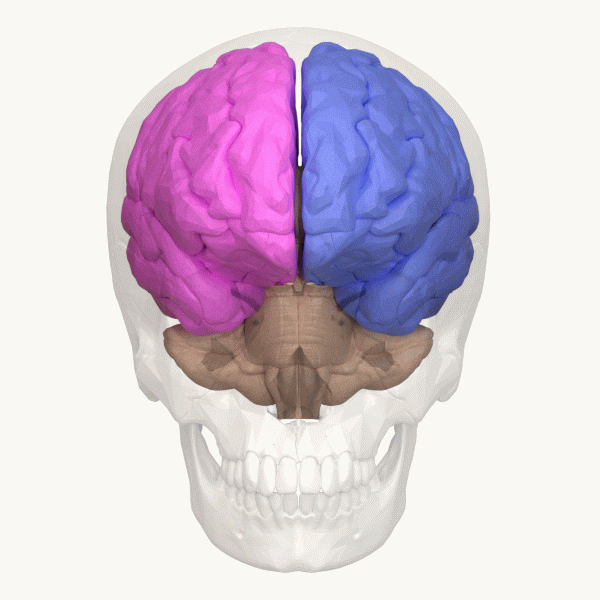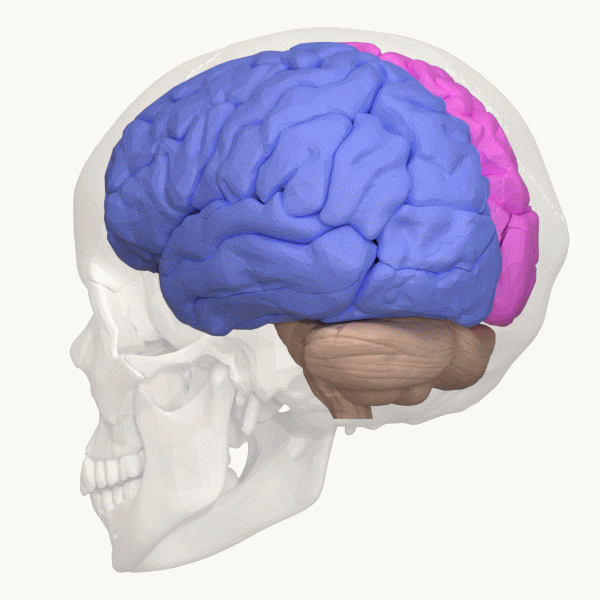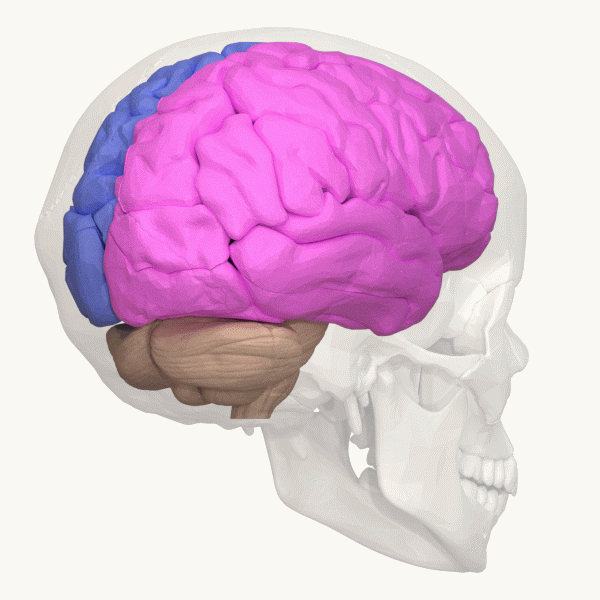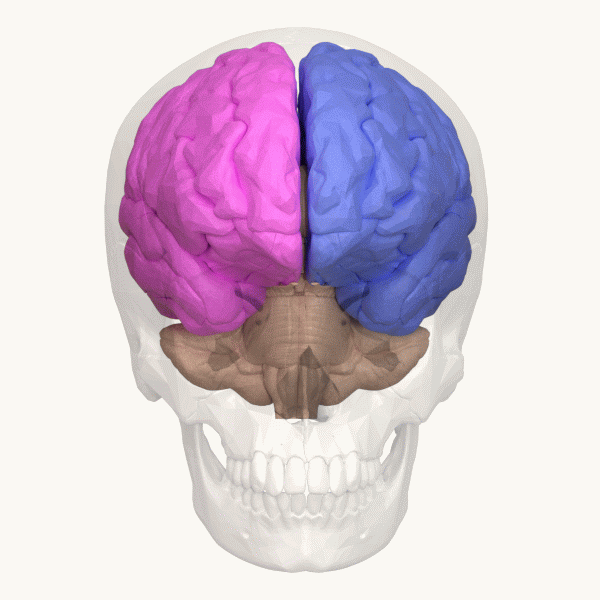
Occipital Lobe
The occipital lobe is one of the four major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The name derives from its position at the back of the head, from the Latin ''ob'', "behind", and ''caput'', "head". The occipital lobe is the visual processing center of the mammalian brain containing most of the anatomical region of the visual cortex. The primary visual cortex is Brodmann area 17, commonly called V1 (visual one). Human V1 is located on the medial side of the occipital lobe within the calcarine sulcus; the full extent of V1 often continues onto the occipital pole. V1 is often also called striate cortex because it can be identified by a large stripe of myelin, the Stria of Gennari. Visually driven regions outside V1 are called extrastriate cortex. There are many extrastriate regions, and these are specialized for different visual tasks, such as visuospatial processing, color differentiation, and motion perception. Bilateral lesions of the occipital lobe can l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |