|
Valvatidae
''Valvatidae'', the valve snails, is a taxonomic family of very small freshwater snails with an operculum, aquatic gastropod mollusks. Taxonomy The family Valvatidae has no subfamilies (according to the taxonomy of the Gastropoda by Bouchet & Rocroi, 2005). Genera The type genus of this family is ''Valvata'' O.F. Müller, 1774. Genera in the family Valvatidae include: * '' Andrussovia'' Brusina, 1903 * ''Borysthenia'' Lindholm, 1933 * '' Costovalvata'' Polinski, 1932 * '' Liratina'' Lindholm, 1906 * '' Megalovalvata'' Lindholm, 1906 * '' Valvata'' Müller, 1774 ** '' Cincinna'' Hübner, 1810 - It is recognized either as genus Anistratenko O., Degtyarenko E., Anistratenko V. (2010). "Сравнительная морфология раковины и радулы брюхоногих моллюсков семейства Valvatidae из Северного Причерноморья. hell and radula comparative morphology of the Gastropod Molluscs family Valvatidae from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
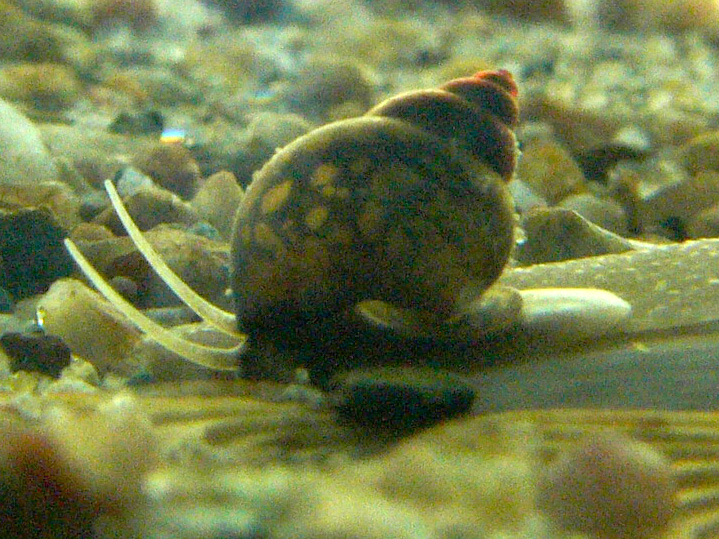
Valvata Piscinalis
''Valvata piscinalis'', common name the European stream valvata or European valve snail, is a species of minute freshwater snail with gills and an Operculum (gastropod), operculum, an Aquatic animal, aquatic gastropod mollusk in the family Valvatidae, the valve snails. It is also known as ''Cincinna piscinalis'' (Müller, 1774). Subspecies Subspecies of ''Valvata piscinalis'' include:Glöer, P. 2002 ''Die Süßwassergastropoden Nord- und Mitteleuropas''. Die Tierwelt Deutschlands, ConchBooks, Hackenheim, 326 pp., , page 190-194. * ''Valvata piscinalis piscinalis'' (O. F. Müller, 1774) * ''Valvata piscinalis antiqua'' (Morris, 1838) * ''Valvata piscinalis geyeri'' (Menzel, 1904) - The name ''geyeri'' is in honor of German zoologist David Geyer (1855–1932). * ''Valvata piscinalis discors'' (Westerlund, 1886) * ''Valvata piscinalis alpestris'' (Küster, 1853) Shell description ''Valvata piscinalis'' has a somewhat pinched Aperture (mollusc), aperture and an attenuate Spire ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valvata Cristata
''Valvata cristata'' is a species of minute freshwater snail with an operculum, an aquatic gastropod mollusk or micromollusk in the family Valvatidae, the valve snails. Distribution * Czech Republic - Bohemia and Moravia Horsák M., Juřičková L., Beran L., Čejka T. & Dvořák L. (2010). "Komentovaný seznam měkkýšů zjištěných ve volné přírodě České a Slovenské republiky. nnotated list of mollusc species recorded outdoors in the Czech and Slovak Republics. ''Malacologica Bohemoslovaca'', Suppl. 1: 1-37PDF * Slovakia * Poland * Germany - (''Arten der Vorwarnliste'') * Netherlands * the British Isles: Great Britain and Ireland * Hungary * Kaliningrad Oblast, Russia * and other areas Shell description The shell of this exceeding small (2–4 mm) ''Valvata'' species is very flat in its coiling, and therefore it somewhat resembles a ''Planorbis'' shell. However, the shell is dextral in coiling and has an operculum.Janus, Horst (1965). ‘’The young spec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valvata
''Valvata'' is a genus of very small freshwater snails with an operculum, aquatic gastropod mollusks in the family Valvatidae, the valve snails.Bouchet, P.; Rosenberg, G. (2014). Valvata O. F. Müller, 1774. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=153994 on 2014-11-15 Synonyms * ''Cincinna'' Hübner, 1810 · accepted, alternate representation (''Cincinna'' is treated as subgenus of ''Valvata'') * ''Cincinna (Atropidina)'' Lindholm, 1906 (subgenus-genus combination invalid; ''Atropidina'' is considered a junior synonym of ''Tropidina'' or ''Cincinna'' (depending on source); to avoid problems we refer to ''Valvata'' only) * ''Cincinna (Cincinna)'' Hübner, 1810 (''Cincinna'' is treated as subgenus of ''Valvata'') * ''Gyrorbis'' Fitzinger, 1833 (junior synonym (?)) * ''Planorbis (Gyrorbis)'' Fitzinger, 1833 (junior synonym (?)) * ''Valvata (Atropidina)'' Lindholm, 1906 (type species of ''Atropidina'' (Valvata pulc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freshwater Snail
Freshwater snails are gastropod mollusks which live in fresh water. There are many different families. They are found throughout the world in various habitats, ranging from ephemeral pools to the largest lakes, and from small seeps and springs to major rivers. The great majority of freshwater gastropods have a shell, with very few exceptions. Some groups of snails that live in freshwater respire using gills, whereas other groups need to reach the surface to breathe air. In addition, some are amphibious and have both gills and a lung (e.g. ''Ampullariidae''). Most feed on algae, but many are detritivores and some are filter feeders. According to a 2008 review of the taxonomy, there are about 4,000 species of freshwater gastropods (3,795–3,972). At least 33–38 independent lineages of gastropods have successfully colonized freshwater environments. It is not possible to quantify the exact number of these lineages yet, because they have yet to be clarified within the Cerit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Borysthenia
''Borysthenia'' is a genus of small freshwater snails with an operculum, aquatic gastropod mollusks in the family Valvatidae, the valve snails. The aperture of ''Borysthenia'' is not circular."Genus summary for ''Borysthenia''" , last modified 28 February 2009, accessed 22 May 2011. Animals are . Species The genus ''Borysthenia'' contains the following species: * † '' Borys ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valvatoidea
Valvatoidea is a superfamily of minute freshwater and marine snails, aquatic gastropod mollusks in the informal group Lower Heterobranchia.MolluscaBase eds. (2020). MolluscaBase. Valvatoidea Gray, 1840. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at: http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=153657 on 2020-09-23 Taxonomy *Family Valvatidae ''Valvatidae'', the valve snails, is a taxonomic family of very small freshwater snails with an operculum, aquatic gastropod mollusks. Taxonomy The family Valvatidae has no subfamilies (according to the taxonomy of the Gastropoda by Bouche ... *Family Cornirostridae *Family Hyalogyrinidae * † Family Provalvatidae References Lower Heterobranchia Taxa named by John Edward Gray {{heterobranchia-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxonomy Of The Gastropoda (Bouchet & Rocroi, 2005)
The taxonomy of the Gastropoda as it was revised in 2005 by Philippe Bouchet and Jean-Pierre Rocroi is a system for the scientific classification of gastropod mollusks. (Gastropods are a taxonomic class of animals which consists of snails and slugs of every kind, from the land, from freshwater, and from saltwater.) The paper setting out this taxonomy was published in the journal ''Malacologia''. The system encompasses both living and extinct groups, as well as some fossils whose classification as gastropods is uncertain. The Bouchet & Rocroi system was the first complete gastropod taxonomy that primarily employed the concept of clades, and was derived from research on molecular phylogenetics; in this context a clade is a "natural grouping" of organisms based upon a statistical cluster analysis. In contrast, most of the previous overall taxonomic schemes for gastropods relied on morphological features to classify these animals, and used taxon ranks such as order, superorder ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biological Monitoring Working Party
The biological monitoring working party (BMWP) is a procedure for measuring water quality using families of macroinvertebrates as biological indicators. The method is based on the principle that different aquatic invertebrates have different tolerances to pollutants. In the case of BMWP, this is based on the sensitivity/tolerance to organic pollution (i.e. nutrient enrichment that can affect the availability of dissolved oxygen). It is important to recognise that the ranking of sensitivity/tolerance will vary for different kinds of pollution. In the case of BMWP/Organic pollution rankings, the presence of mayflies or stoneflies for instance indicate the cleanest waterways and are given a tolerance score of 10. The lowest scoring invertebrates are worms (''Oligochaeta'') which score 1. The number of different macroinvertebrates is also an important factor, because a better quality water is assumed to contain fewer pollutants that would exclude "sensitive" species - resulting in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Heterobranchia
Lower Heterobranchia, also known as the Allogastropoda, is a group of rather specialized, highly evolved sea slugs and sea snails, ( marine gastropod mollusks) within the subclass Heterobranchia. WoRMS (2020). "Lower Heterobranchia". Accessed at: https://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=1054700 on 2020-05-16 Although the great majority of Lower Heterobranchs are indeed marine, a few have succeeded in making the transition to freshwater. Description The shell shapes in this group are typically those that are seen in the sundial, pyramid, rissoella and orbitestellid families of snails. Taxonomy 2005 taxonomy In the taxonomy of the Gastropoda by Bouchet & Rocroi, 2005, the Lower Heterobranchia is an Informal Group. Superfamilies within the Lower Heterobranchia include: *Unassigned to a superfamily (orbitestellid-shells) ** Family Cimidae ** † Family Dolomitellidae ** † Family Heterosubulitidae ** † Family Kuskokwimiidae ** † Family Misurinellid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otto Friedrich Müller
Otto Friedrich Müller, also known as Otto Friedrich Mueller (2 November 1730 – 26 December 1784) was a Danish naturalist and scientific illustrator. Biography Müller was born in Copenhagen. He was educated for the church, became tutor to a young nobleman, and after several years' travel with him, settled in Copenhagen in 1767, and married a lady of wealth. His first important works, ''Fauna Insectorum Friedrichsdaliana'' (Leipzig, 1764), and ''Flora Friedrichsdaliana'' (Strasbourg, 1767), giving accounts of the insects and flora of the estate of Frederiksdal, near Copenhagen, recommended him to Frederick V of Denmark, by whom he was employed to continue the ''Flora Danica'' a comprehensive atlas of the flora of Denmark. Müller added two volumes to the three published by Georg Christian Oeder since 1761. The study of invertebrates began to occupy his attention almost exclusively, and in 1771 he produced a work in German on “Certain Worms inhabiting Fresh and Salt Water,� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biological Indicator
A bioindicator is any species (an indicator species) or group of species whose function, population, or status can reveal the qualitative status of the environment. The most common indicator species are animals. For example, copepods and other small water crustaceans that are present in many water bodies can be monitored for changes (biochemical, physiological, or behavioural) that may indicate a problem within their ecosystem. Bioindicators can tell us about the cumulative effects of different pollutants in the ecosystem and about how long a problem may have been present, which physical and chemical testing cannot. A biological monitor or biomonitor is an organism that provides quantitative information on the quality of the environment around it. Therefore, a good biomonitor will indicate the presence of the pollutant and can also be used in an attempt to provide additional information about the amount and intensity of the exposure. A biological indicator is also the name given ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water Quality
Water quality refers to the chemical, physical, and biological characteristics of water based on the standards of its usage. It is most frequently used by reference to a set of standards against which compliance, generally achieved through treatment of the water, can be assessed. The most common standards used to monitor and assess water quality convey the health of ecosystems, safety of human contact, extend of water pollution and condition of drinking water. Water quality has a significant impact on water supply and oftentimes determines supply options. Categories The parameters for water quality are determined by the intended use. Work in the area of water quality tends to be focused on water that is treated for potability, industrial/domestic use, or restoration (of an environment/ecosystem, generally for health of human/aquatic life). Human consumption Contaminants that may be in untreated water include microorganisms such as viruses, protozoa and bacteria; inorganic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |