|
Uropatagia
The patagium (plural: patagia) is a membranous body part that assists an animal in obtaining lift when gliding or flight. The structure is found in extant and extinct groups of flying and gliding animals including bats, birds, some dromaeosaurs, pterosaurs, gliding mammals, some flying lizards, and flying frogs. The patagium that stretches between an animal's hind limbs is called the uropatagium (especially in bats) or the interfemoral membrane. Bats In bats, the skin forming the surface of the wing is an extension of the skin of the abdomen that runs to the tip of each digit, uniting the forelimb with the body. The patagium of a bat has four distinct parts: #Propatagium: the patagium present from the neck to the first digit. #Dactylopatagium: the portion found within the digits. #Plagiopatagium: the portion found between the last digit and the hindlimbs. #Uropatagium: the posterior portion of the flap between the two hindlimbs. Pterosaurs In the flying pterosaurs, the patagiu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pterodactylus
''Pterodactylus'' (from Greek () meaning 'winged finger') is an extinct genus of pterosaurs. It is thought to contain only a single species, ''Pterodactylus antiquus'', which was the first pterosaur to be named and identified as a flying reptile. Fossil remains of ''Pterodactylus'' have primarily been found in the Solnhofen limestone of Bavaria, Germany, which dates from the Late Jurassic period (early Tithonian stage), about 150.8 to 148.5 million years ago. More fragmentary remains of ''Pterodactylus'' have tentatively been identified from elsewhere in Europe and in Africa. ''Pterodactylus'' was a generalist carnivore that probably fed on a variety of invertebrates and vertebrates. Like all pterosaurs, ''Pterodactylus'' had wings formed by a skin and muscle membrane stretching from its elongated fourth finger to its hind limbs. It was supported internally by collagen fibres and externally by keratinous ridges. ''Pterodactylus'' was a small pterosaur compared to other famo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
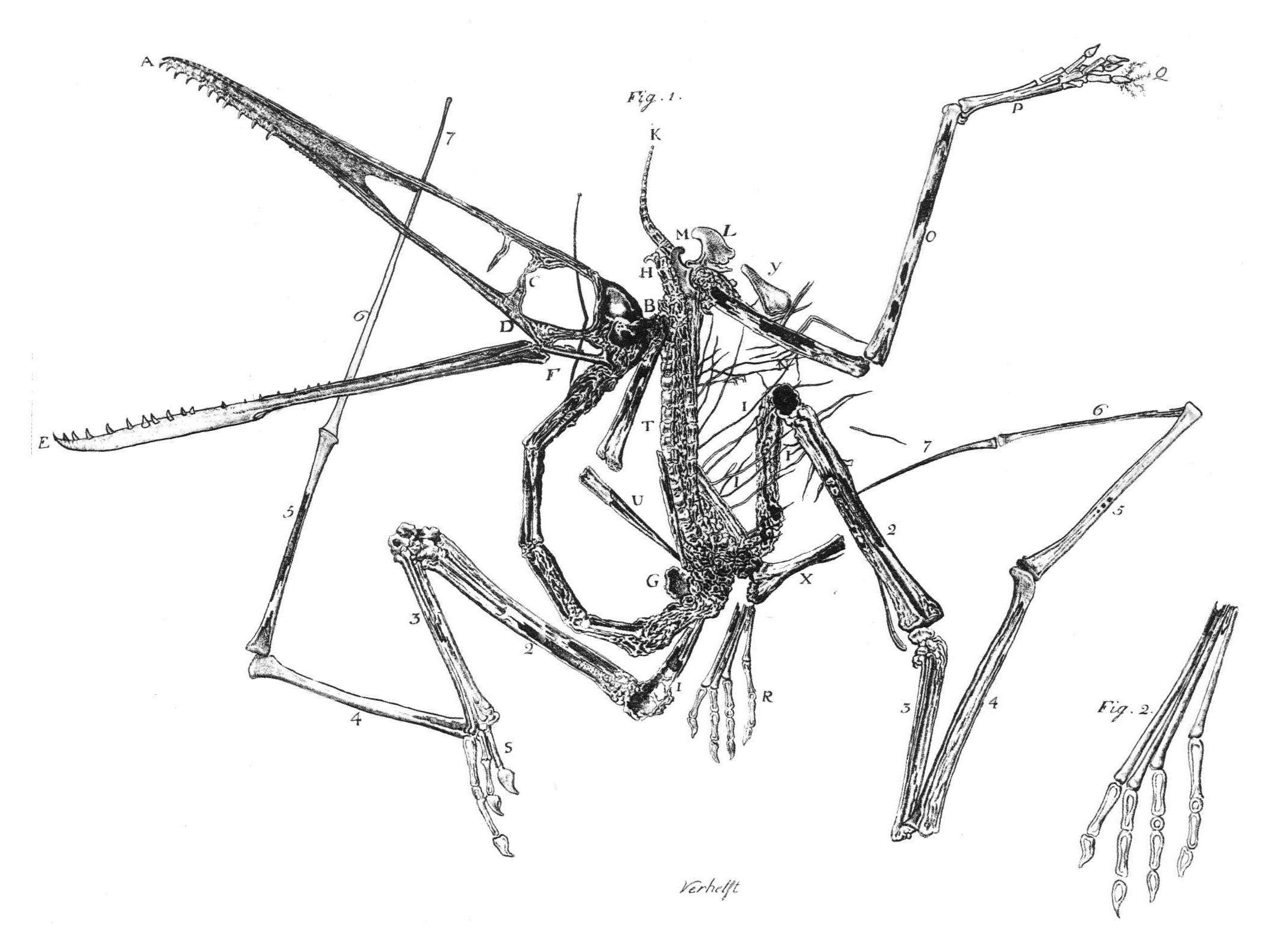
Carpal Bones
The carpal bones are the eight small bones that make up the wrist (or carpus) that connects the hand to the forearm. The term "carpus" is derived from the Latin carpus and the Greek καρπός (karpós), meaning "wrist". In human anatomy, the main role of the wrist is to facilitate effective positioning of the hand and powerful use of the extensors and flexors of the forearm, and the mobility of individual carpal bones increase the freedom of movements at the wrist.Kingston 2000, pp 126-127 In tetrapods, the carpus is the sole cluster of bones in the wrist between the radius and ulna and the metacarpus. The bones of the carpus do not belong to individual fingers (or toes in quadrupeds), whereas those of the metacarpus do. The corresponding part of the foot is the tarsus. The carpal bones allow the wrist to move and rotate vertically. Structure Bones The eight carpal bones may be conceptually organized as either two transverse rows, or three longitudinal columns. When c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birds
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweight skeleton. Birds live worldwide and range in size from the bee hummingbird to the ostrich. There are about ten thousand living species, more than half of which are passerine, or "perching" birds. Birds have whose development varies according to species; the only known groups without wings are the extinct moa and elephant birds. Wings, which are modified forelimbs, gave birds the ability to fly, although further evolution has led to the loss of flight in some birds, including ratites, penguins, and diverse endemic island species. The digestive and respiratory systems of birds are also uniquely adapted for flight. Some bird species of aquatic environments, particularly seabirds and some waterbirds, have further evolved for swimming. B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parachute
A parachute is a device used to slow the motion of an object through an atmosphere by creating drag or, in a ram-air parachute, aerodynamic lift. A major application is to support people, for recreation or as a safety device for aviators, who can exit from an aircraft at height and descend safely to earth. A parachute is usually made of a light, strong fabric. Early parachutes were made of silk. The most common fabric today is nylon. A parachute's canopy is typically dome-shaped, but some are rectangles, inverted domes, and other shapes. A variety of loads are attached to parachutes, including people, food, equipment, space capsules, and bombs. History Middle Ages In 852, in Córdoba, Spain, the Moorish man Armen Firman attempted unsuccessfully to fly by jumping from a tower while wearing a large cloak. It was recorded that "there was enough air in the folds of his cloak to prevent great injury when he reached the ground." Early Renaissance The earliest evidence f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flying Frogs
A flying frog (also called a gliding frog) is a frog that has the ability to achieve gliding flight. This means it can descend at an angle less than 45° relative to the horizontal. Other nonflying arboreal frogs can also descend, but only at angles greater than 45°, which is referred to as parachuting.Emerson, S.B., Travis, J., & Koehl, M.A.R. (1990). "Functional complexes and additivity in performance: A test case with 'flying' frogs." ''Evolution'', 44(8), 2153-2157. Evolution Gliding flight has evolved independently several times among frogs from both New World (Hylidae) and Old World (Rhacophoridae) families.Emerson, S.B., & Koehl, M.A.R. (1990). "The interaction of behavioral and morphological change in the evolution of a novel locomotor type: 'Flying' frogs." ''Evolution'', 44(8), 1931-1946. This parallel evolution is seen as an adaptation to their life in trees, high above the ground. Characteristics of the Old-World species include "enlarged hands and feet, full webbing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lizard
Lizards are a widespread group of squamate reptiles, with over 7,000 species, ranging across all continents except Antarctica, as well as most oceanic island chains. The group is paraphyletic since it excludes the snakes and Amphisbaenia although some lizards are more closely related to these two excluded groups than they are to other lizards. Lizards range in size from chameleons and geckos a few centimeters long to the 3-meter-long Komodo dragon. Most lizards are quadrupedal, running with a strong side-to-side motion. Some lineages (known as "legless lizards"), have secondarily lost their legs, and have long snake-like bodies. Some such as the forest-dwelling ''Draco'' lizards are able to glide. They are often territorial, the males fighting off other males and signalling, often with bright colours, to attract mates and to intimidate rivals. Lizards are mainly carnivorous, often being sit-and-wait predators; many smaller species eat insects, while the Komodo eats mammals a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flying And Gliding Animals
A number of animals are capable of aerial locomotion, either by powered flight or by gliding. This trait has appeared by evolution many times, without any single common ancestor. Flight has evolved at least four times in separate animals: insects, pterosaurs, birds, and bats. Gliding has evolved on many more occasions. Usually the development is to aid canopy animals in getting from tree to tree, although there are other possibilities. Gliding, in particular, has evolved among rainforest animals, especially in the rainforests in Asia (most especially Borneo) where the trees are tall and widely spaced. Several species of aquatic animals, and a few amphibians and reptiles have also evolved this gliding flight ability, typically as a means of evading predators. Types Animal aerial locomotion can be divided into two categories: powered and unpowered. In unpowered modes of locomotion, the animal uses aerodynamic forces exerted on the body due to wind or falling through the air. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Draco Spilonotus
''Draco spilonotus'', the Sulawesi lined gliding lizard, is a lizard endemic to Sulawesi. The species is known from various localities in forested areas of Sulawesi. The patagium of the male is yellow in colour and has a network of brown lines radiating from the anterior. The gular Gular is of or pertaining to the throat In vertebrate anatomy, the throat is the front part of the neck, internally positioned in front of the vertebrae. It contains the pharynx and larynx. An important section of it is the epiglottis, separatin ... flag is yellow and rounded in shape. References General References # # # spilonotus Gliding animals Endemic fauna of Indonesia Reptiles of Sulawesi Taxa named by Albert Günther Reptiles described in 1872 Helpful Websites, and External Resources Draco Volans [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eomys
''Eomys'' is an extinct genus of eomyid rodent from the late Oligocene of France, Germany, Spain, and possibly Turkey. The species ''Eomys quercyi'' is the earliest known gliding rodent. References External links ''Eomys''in the Paleobiology Database The Paleobiology Database is an online resource for information on the distribution and classification of fossil animals, plants, and microorganisms. History The Paleobiology Database (PBDB) originated in the NCEAS-funded Phanerozoic Marine Pale ... Geomyoid rodents Prehistoric rodent genera Gliding animals Oligocene rodents Oligocene mammals of Asia Oligocene mammals of Europe Paleogene France Fossils of France Quercy Phosphorites Formation Fossil taxa described in 1884 {{geomyidae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greater Glider
The greater gliders are three species of large gliding marsupials in the genus ''Petauroides'', all of which are found in eastern Australia. Until 2020 they were considered to be one species, '' Petauroides volans''. In 2020 morphological and genetic differences, obtained using diversity arrays technology, showed there were three species subsumed under this one name. The two new species were named '' Petauroides armillatus'' and ''Petauroides minor''. These species are not closely related to the '' Petaurus'' group of gliding marsupials but instead to the lemur-like ringtail possum, ''Hemibelideus lemuroides'', with which it shares the subfamily Hemibelideinae. The greater gliders are nocturnal and are solitary herbivores feeding almost exclusively on ''Eucalyptus'' leaves and buds. Like their relative, the lemur-like ringtail, the southern greater glider is found in two forms: a sooty brown form and a grey-to-white form. The central greater glider is instead silvery brown, whil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anomalure
The Anomaluridae are a family of rodents found in central Africa. They are known as anomalures or scaly-tailed squirrels. The six extant species are classified into two genera. All anomalurids have membranes between their front and hind legs like those of a flying squirrel, but they are not closely related to the flying squirrels that form the tribe Petauristini of the family Sciuridae. They are distinguished by two rows of pointed, raised scales on the undersides of their tails. The anatomy of their heads is quite different from that of the sciurid flying squirrels. By extending their limbs, anomalures transform themselves into a gliding platform that they control by manipulating the membranes and tail. Most anomalurid species roost during the day in hollow trees, with up to several dozen animals per tree. They are primarily herbivorous, and may travel up to from their roosting tree in search of leaves, flowers, or fruit, although they also eat a small amount of insects. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)



_in_flight%2C_Cley%2C_Norfolk_1700.jpg)
