|
Uniform Continuity
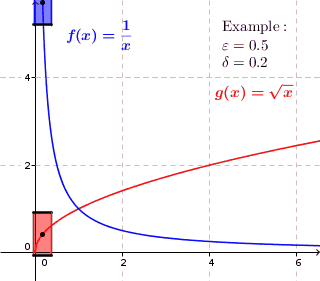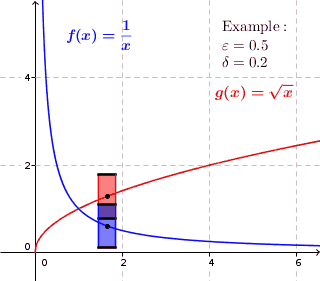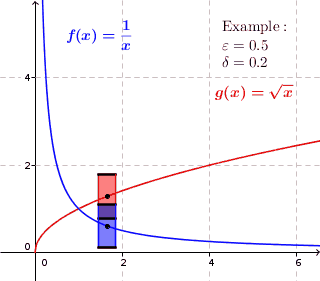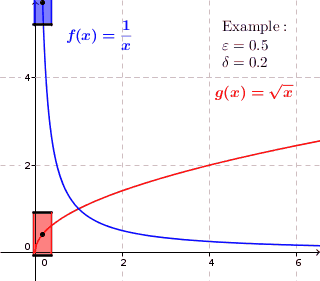
In mathematics, a real function f of real numbers is said to be uniformly continuous if there is a positive real number \delta such that function values over any function domain interval of the size \delta are as close to each other as we want. In other words, for a uniformly continuous real function of real numbers, if we want function value differences to be less than any positive real number \epsilon, then there is a positive real number \delta such that , f(x) - f(y), 0 there exists a real number \delta > 0 such that for every x,y \in X with d_1(x,y) 0 such that for every x,y \in X , , x - y, 0 \; \forall x \in X \; \forall y \in X : \, d_1(x,y) 0 , \forall x \in X , and \forall y \in X ) are used. * Alternatively, f is said to be uniformly continuous if there is a function of all positive real numbers \varepsilon, \delta(\varepsilon) representing the maximum positive real number, such that for every x,y \in X if d_1(x,y) 0 such that for every y \in X wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uniform Continuity
In mathematics, a real function f of real numbers is said to be uniformly continuous if there is a positive real number \delta such that function values over any function domain interval of the size \delta are as close to each other as we want. In other words, for a uniformly continuous real function of real numbers, if we want function value differences to be less than any positive real number \epsilon, then there is a positive real number \delta such that , f(x) - f(y), 0 there exists a real number \delta > 0 such that for every x,y \in X with d_1(x,y) 0 such that for every x,y \in X , , x - y, 0 \; \forall x \in X \; \forall y \in X : \, d_1(x,y) 0 , \forall x \in X , and \forall y \in X ) are used. * Alternatively, f is said to be uniformly continuous if there is a function of all positive real numbers \varepsilon, \delta(\varepsilon) representing the maximum positive real number, such that for every x,y \in X if d_1(x,y) 0 such that for every y \in X wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continuity And Uniform Continuity 2
Continuity or continuous may refer to: Mathematics * Continuity (mathematics), the opposing concept to discreteness; common examples include ** Continuous probability distribution or random variable in probability and statistics ** Continuous game, a generalization of games used in game theory ** Law of Continuity, a heuristic principle of Gottfried Leibniz * Continuous function, in particular: ** Continuity (topology), a generalization to functions between topological spaces ** Scott continuity In mathematics, given two partially ordered sets ''P'' and ''Q'', a function ''f'': ''P'' → ''Q'' between them is Scott-continuous (named after the mathematician Dana Scott) if it preserves all directed suprema. That is, for every directed subse ..., for functions between posets ** Continuity (set theory), for functions between ordinals ** Continuity (category theory), for functors ** Graph continuity, for payoff functions in game theory * Continuity theorem may refer to one of two re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |