|
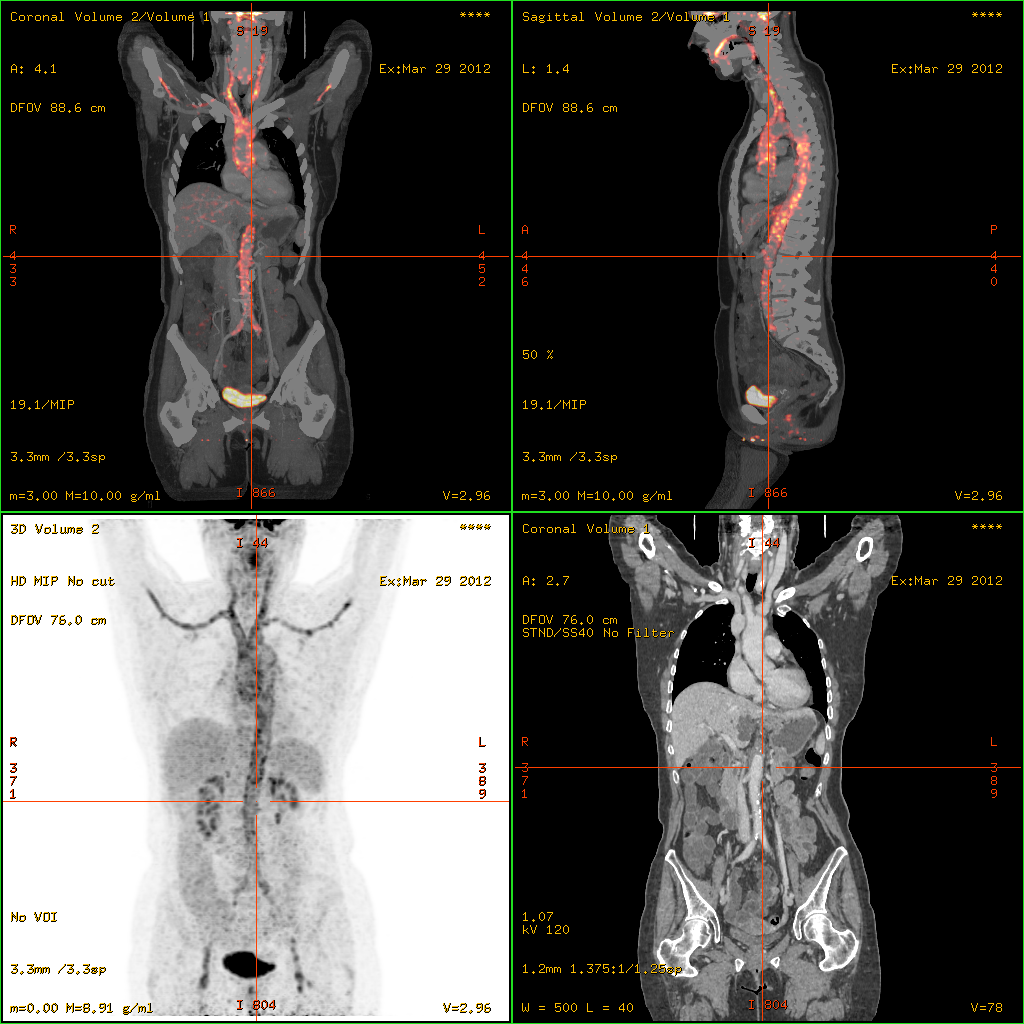
Urticarial Vasculitis
Urticarial vasculitis (also known as "chronic urticaria as a manifestation of venulitis", "hypocomplementemic urticarial vasculitis syndrome", "hypocomplementemic vasculitis" and "unusual lupus-like syndrome") is a skin condition characterized by fixed urticarial lesions that appear histologically as a vasculitis. Mechanism Antibodies are usually raised against foreign proteins, such as those made by a replicating virus or invading bacterium. Virus or bacteria with antibodies opsonized or "stuck" to them highlight them to other cells of the immune system for clearance. Antibodies against self proteins are known as autoantibodies, and are not found in healthy individuals. These autoantibodies can be used to detect certain diseases. C1q C1q is an integral component within the complement pathway – a complicated cascade of protein interactions, culminating in an immune response against a broad variety of pathogens. The anti-C1q antibodies found in patients with hypocomplementemi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histologically
Histology, also known as microscopic anatomy or microanatomy, is the branch of biology Biology is the scientific study of life. It is a natural science with a broad scope but has several unifying themes that tie it together as a single, coherent field. For instance, all organisms are made up of cells that process hereditary i ... which studies the microscopic anatomy of biological tissue (biology), tissues. Histology is the microscopic counterpart to gross anatomy, which looks at larger structures visible without a microscope. Although one may divide microscopic anatomy into ''organology'', the study of organs, ''histology'', the study of tissues, and ''cytology'', the study of cell (biology), cells, modern usage places all of these topics under the field of histology. In medicine, histopathology is the branch of histology that includes the microscopic identification and study of diseased tissue. In the field of paleontology, the term paleohistology refers to the histolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vasculitis
Vasculitis is a group of disorders that destroy blood vessels by inflammation. Both arteries and veins are affected. Lymphangitis (inflammation of lymphatic vessels) is sometimes considered a type of vasculitis. Vasculitis is primarily caused by leukocyte migration and resultant damage. Although both occur in vasculitis, inflammation of veins (phlebitis) or arteries (arteritis) on their own are separate entities. Signs and symptoms Possible signs and symptoms include: * General symptoms: Fever, unintentional weight loss * Skin: Palpable purpura, livedo reticularis * Muscles and joints: Muscle pain or inflammation, joint pain or joint swelling * Nervous system: Mononeuritis multiplex, headache, stroke, tinnitus, reduced visual acuity, acute visual loss * Heart and arteries: Heart attack, high blood pressure, gangrene * Respiratory tract: Nosebleeds, bloody cough, lung infiltrates * GI tract: Abdominal pain, bloody stool, perforations (hole in the GI tract) * Kidneys: Inflamma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complement Pathway
A complement is something that completes something else. Complement may refer specifically to: The arts * Complement (music), an interval that, when added to another, spans an octave ** Aggregate complementation, the separation of pitch-class collections into complementary sets * Complementary color, in the visual arts Biology and medicine *Complement system (immunology), a cascade of proteins in the blood that form part of innate immunity *Complementary DNA, DNA reverse transcribed from a mature mRNA template *Complementarity (molecular biology), a property whereby double stranded nucleic acids pair with each other *Complementation (genetics), a test to determine if independent recessive mutant phenotypes are caused by mutations in the same gene or in different genes Grammar and linguistics * Complement (linguistics), a word or phrase having a particular syntactic role ** Subject complement, a word or phrase adding to a clause's subject after a linking verb * Phonetic com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
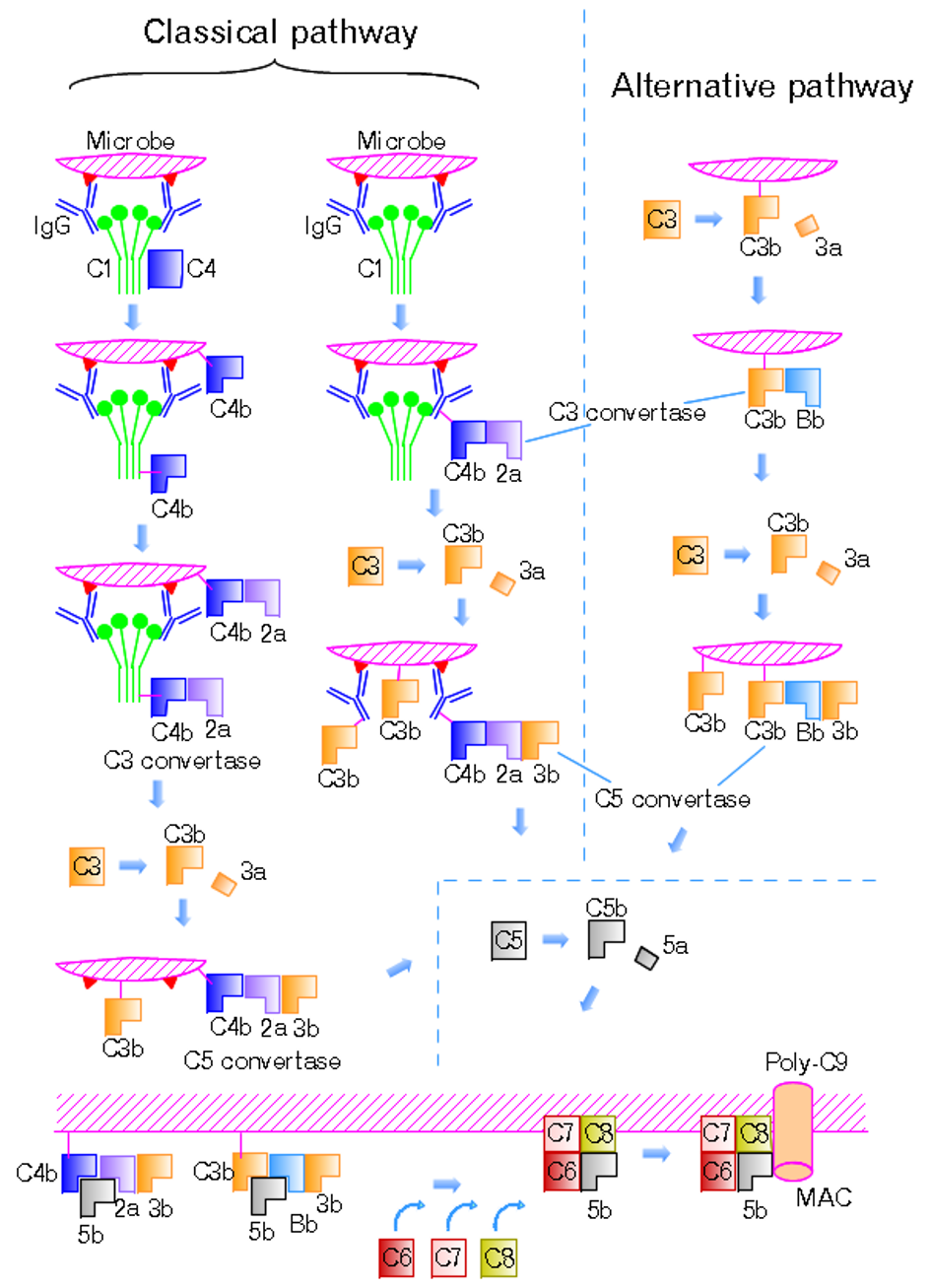
Classical Complement Pathway
The classical complement pathway is one of three pathways which activate the complement system, which is part of the immune system. The classical complement pathway is initiated by antigen-antibody complexes with the antibody isotypes IgG and IgM. Following activation, a series of proteins are recruited to generate C3 convertase (C4b2b, historically referred C4b2a), which cleaves the C3 protein. The C3b component of the cleaved C3 binds to C3 convertase (C4b2b) to generate C5 convertase (C4b2b3b), which cleaves the C5 protein. The cleaved products attract phagocytes to the site of infection and tags target cells for elimination by phagocytosis. In addition, the C5 convertase initiates the terminal phase of the complement system, leading to the assembly of the membrane attack complex ( MAC). The membrane attack complex creates a pore on the target cell's membrane, inducing cell lysis and death. The classical complement pathway can also be activated by apoptotic cells, necrotic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inhibitor Protein
The inhibitor protein (IP) is situated in the mitochondrial matrix and protects the cell against rapid ATP hydrolysis during momentary ischaemia Ischemia or ischaemia is a restriction in blood supply to any tissue, muscle group, or organ of the body, causing a shortage of oxygen that is needed for cellular metabolism (to keep tissue alive). Ischemia is generally caused by problems wi .... In oxygen absence, the pH of the matrix drops. This causes IP to become protonated and change its conformation to one that can bind to the F1Fo synthetase and stops it thereby preventing it from moving in a backwards direction and hydrolyze ATP instead of make it. When oxygen is finally incorporated into the system, the pH rises and IP is deprotonated. IP dissociates from the F1Fo synthetase and allows it to resume its ATP synthesis. {{DEFAULTSORT:Inhibitor Protein Cell biology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fat, Sick And Nearly Dead
''Fat, Sick and Nearly Dead'' is a 2010 American documentary film which follows the 60-day journey of Australian Joe Cross across the United States as he follows a juice fast to regain his health under the care of Joel Fuhrman, Nutrition Research Foundation's Director of Research. Summary The feature-length film follows Cross, who was depressed, weighed 310 lbs, suffered from a serious autoimmune disease, and was on steroids at the start of the film, as he embarks on a juice fast. Cross and Robert Mac, co-creators of the film, both serve on the Nutrition Research Foundation's Advisory Board. Following his fast and the adoption of a plant-based diet, Cross states in a press release that he lost 100 pounds and discontinued all medications. During his road-trip Cross meets Phil Staples, a morbidly obese truck driver from Sheldon, Iowa, in a truck stop in Arizona and inspires him to try juice fasting. A sequel to the first film, ''Fat, Sick and Nearly Dead 2'', was released in 201 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cutaneous Small-vessel Vasculitis
Cutaneous small-vessel vasculitis (CSVV), also known as hypersensitivity vasculitis, cutaneous leukocytoclastic vasculitis, hypersensitivity angiitis, cutaneous leukocytoclastic angiitis, cutaneous necrotizing vasculitis and cutaneous necrotizing venulitis, is inflammation of small blood vessels (usually post-capillary venules in the dermis), characterized by palpable purpura. It is the most common vasculitis seen in clinical practice. "Leukocytoclastic" refers to the damage caused by nuclear debris from infiltrating neutrophils in and around the vessels. Signs and symptoms Skin lesions Initially red to pink, flat spots (formally, "macules") and raised bumps (formally, "papules") may be seen on the skin. Once fully developed, the classic appearance is "non-blanching, palpable purpura". This appears as deep red to purple spots that feel raised to the touch. Purpura refers to the red-purple discolored spots, while palpable implies that these spots can be felt as raised fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Cutaneous Conditions
Many skin conditions affect the human integumentary system—the organ system covering the entire surface of the body and composed of skin, hair, nails, and related muscle and glands. The major function of this system is as a barrier against the external environment. The skin weighs an average of four kilograms, covers an area of two square metres, and is made of three distinct layers: the epidermis, dermis, and subcutaneous tissue. The two main types of human skin are: glabrous skin, the hairless skin on the palms and soles (also referred to as the "palmoplantar" surfaces), and hair-bearing skin.Burns, Tony; ''et al''. (2006) ''Rook's Textbook of Dermatology CD-ROM''. Wiley-Blackwell. . Within the latter type, the hairs occur in structures called pilosebaceous units, each with hair follicle, sebaceous gland, and associated arrector pili muscle. In the embryo, the epidermis, hair, and glands form from the ectoderm, which is chemically influenced by the underlying mesoderm th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ILDS
The International League of Dermatological Societies (ILDS) is a non-governmental organization that works closely with the World Health Organization. It was founded in 1935, but because of World War II no congresses were held until 1952. It is governed by the International Committee of Dermatology. The ILDS is the parent organization of the International Foundation for Dermatology, founded in 1987. After the publication of ICD-10, the ILDS produced a series of compatible extensions for use in dermatology Dermatology is the branch of medicine dealing with the skin.''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary.'' Random House, Inc. 2001. Page 537. . It is a speciality with both medical and surgical aspects. A dermatologist is a specialist medical .... References External links Official site HistoryInternational Foundation for DermatologyApplication to Dermatology of International Classification of Disease (ICD-11) Organizations established in 1935 Dermatology organi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |