|
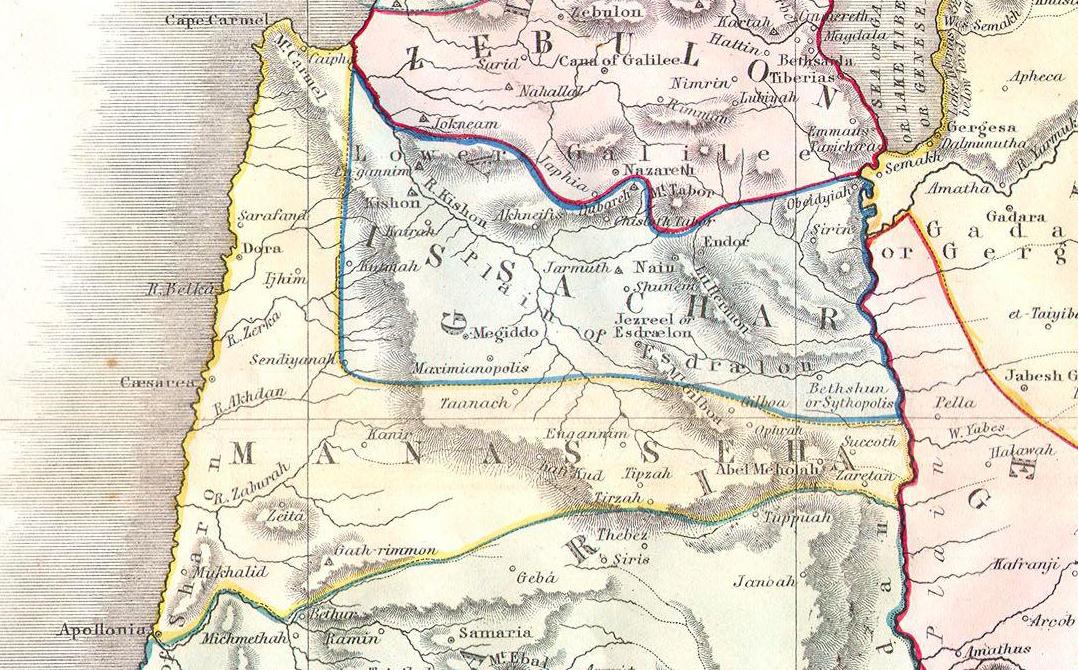
Tribe Of Manasseh
According to the Hebrew Bible, the Tribe of Manasseh (; Hebrew: ''Ševet Mənašše,'' Tiberian: ''Šēḇeṭ Mănašše'') was one of the Tribes of Israel. It is one of the ten lost tribes. Together with the Tribe of Ephraim, Manasseh also formed the ''House of Joseph''. Biblical Chronicle According to the biblical chronicle, the Tribe of Manasseh was a part of a loose confederation of Israelite tribes from after the conquest of the land by Joshua until the formation of the first Kingdom of Israel in c. 1050 BC. No central government existed, and in times of crisis the people were led by ad hoc leaders known as Judges (see Book of Judges). With the growth of the threat from Philistine incursions, the Israelite tribes decided to form a strong centralised monarchy to meet the challenge, and the Tribe of Manasseh joined the new kingdom with Saul as the first king. After the death of Saul, all the tribes other than Judah remained loyal to the House of Saul, but after the death o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hebrew Bible
The Hebrew Bible or Tanakh (;"Tanach" ''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary''. Hebrew: ''Tānāḵh''), also known in Hebrew as Miqra (; Hebrew: ''Mīqrā''), is the Biblical canon, canonical collection of Hebrew language, Hebrew scriptures, including the Torah, the Nevi'im, and the Ketuvim. Different branches of Judaism and Samaritanism have maintained different versions of the canon, including the 3rd-century Septuagint text used by Second-Temple Judaism, the Syriac language Peshitta, the Samaritan Torah, the Dead Sea Scrolls, and most recently the 10th century medieval Masoretic Text, Masoretic text created by the Masoretes currently used in modern Rabbinic Judaism. The terms "Hebrew Bible" or "Hebrew Canon" are frequently confused with the Masoretic text, however, this is a medieval version and one of several ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tribe Of Benjamin
According to the Torah, the Tribe of Benjamin () was one of the Twelve Tribes of Israel. The tribe was descended from Benjamin, the youngest son of the patriarch Jacob (later given the name Israel) and his wife Rachel. In the Samaritan Pentateuch the name appears as ''Binyamīm'' (). The Tribe of Benjamin, located to the north of Judah but to the south of the Kingdom of Israel, is significant in biblical narratives as a source of various Israelite leaders, including the first Israelite king, Saul, as well as earlier tribal leaders in the period of the Judges. In the period of the judges, they feature in an episode in which a civil war results in their near-extinction as a tribe. After the brief period of the united kingdom of Israel, Benjamin became part of the southern Kingdom of Judah following the split into two kingdoms. After the destruction of the northern kingdom, Benjamin was fully absorbed into the southern kingdom. After the destruction of Judah by the Babylonians in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dan (ancient City)
Dan ( he, דן) is an ancient city mentioned in the Hebrew Bible, described as the northernmost city of the Kingdom of Israel, and belonging to the tribe of Dan. The city is identified with a tell located in Upper Galilee, northern Israel, known as Tel Dan (; "Mound of Dan") in Hebrew. Identification and names The Hebrew Bible states that prior to its conquest by the tribe of Dan the site was known as Laish with variant spellings within the Books of Joshua, Judges and Isaiah. In it is called Leshem, which means "jewel". has the alternative name ''Laishah'' in a number of translations. Rabbinic works, and writers like Philostorgius, Theodoret, Benjamin of Tudela and Samuel ben Samson, all incorrectly identified Dan or Laish, with Banias (Paneas).Saulcy, 1854, pp537538 Eusebius of Caesarea more accurately places Dan/Laish in the vicinity of Paneas at the fourth mile on the route to Tyre. 19th century Swiss traveler Johann Ludwig Burckhardt identified the source of the Jordan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tribe Of Issachar
According to the Hebrew Bible, the Tribe of Issachar () was one of the twelve tribes of Israel and one of the ten lost tribes. In Jewish tradition, the descendants of Issachar were seen as being dominated by religious scholars and influential in proselytism. The sons of Issachar, ancestors of the tribe, were Tola, Phuvah, Job and Shimron. Biblical narrative In the biblical narrative of the Book of Joshua, following the completion of the conquest of Canaan by the Israelite tribes, Joshua allocated the land among the twelve tribes. The territory allocated to Issachar stretched from the Jordan River in the east to Mount Carmel on the west, near to the Mediterranean coast, including the fertile Esdraelon plain between present-day Lower Galilee and Samaria. It was bounded on the east by East Manasseh, the south by West Manasseh, and the north by Zebulun and Naphtali. There is a consensus among scholars that the accounts in the Book of Judges are not historically reliable. Alternati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tribe Of Asher
According to the Hebrew Bible, the Tribe of Asher was one of the Tribes of Israel descended from Asher (), the eighth son of Jacob. It is one of the ten lost tribes. Biblical narrative According to the biblical Book of Joshua, following the completion of the conquest of Canaan by the Israelite tribes, Joshua allocated the land among the twelve tribes. According to biblical scholar Kenneth Kitchen, one should date this conquest slightly after 1200 BC.Kitchen, Kenneth A. (2003), "On the Reliability of the Old Testament" (Grand Rapids, Michigan. William B. Eerdmans Publishing Company)() This is referred to as a 'late date' with the main alternative of around 1500 BC referred to as the 'early date' for both the Exodus and conquest of Canaan. Waltke, Bruce (1990), "The Date of the Conquest" (Westminster Theological Journal 52.2 (Fall 1990): 181-200./ref>In opposition to both of these views, many critical scholars holds that the conquest of Joshua as described in the Book of Joshua neve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Carmel
Mount Carmel ( he, הַר הַכַּרְמֶל, Har haKarmel; ar, جبل الكرمل, Jabal al-Karmil), also known in Arabic as Mount Mar Elias ( ar, link=no, جبل مار إلياس, Jabal Mār Ilyās, lit=Mount Saint Elias/Elijah), is a coastal mountain range in northern Israel stretching from the Mediterranean Sea towards the southeast. The range is a UNESCO biosphere reserve. A number of towns are situated there, most notably the city of Haifa, Israel's third largest city, located on the northern and western slopes. Etymology The word ''karmel'' means "garden-land" and is of uncertain origin. It is either a compound of ''kerem'' and ''el'', meaning "vineyard of El (deity), God" or a clipping of ''kar male,'' meaning "full kernel." Martin Jan Mulder suggested a third etymology, that of ''kerem + l'' with the lamed a wiktionary:sufformative, sufformative, but this is considered unlikely as evidence for the existence of a lamed sufformative is weak. Geography and geology T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geographic Contiguity
Geographic contiguity is the characteristic in geography of political or geographical land divisions, as a group, not being interrupted by other land or water. Such divisions are referred to as being ''contiguous.'' In the United States, for example, the "48 contiguous states" excludes Hawaii and Alaska, which do not share borders with other U.S. states. Other examples of geographical contiguity might include the "contiguous European Union" excluding member states such as Ireland, Sweden, Finland (between Åland and Turku Archipelago), Malta and Cyprus (these being non-contiguous), or the "contiguous United Kingdom" referring to all parts of the country excepting Northern Ireland (it being geographically non-contiguous). Two or more contiguous municipalities can be consolidated into one, or one municipality can consist of many noncontiguous elements. For example, the Financially Distressed Municipalities Act allows the commonwealth of Pennsylvania to merge contiguous municipaliti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transjordan (Bible)
Transjordan ( he, עבר הירדן, ) is an area of land in the Southern Levant lying east of the Jordan River valley. It is also alternatively called Gilead. Etymology In the Hebrew Bible, the term used to refer to the future Transjordan is he, עבר הירדן (), "beyond the Jordan". This term occurs, for example, in the Book of Joshua (). It was used by people on the west side of the Jordan, including the biblical writers, to refer to the other side of the Jordan River. In the Septuagint, the he, בעבר הירדן מזרח השמש (מזרחית לנהר הירדן), hay·yar·dên miz·raḥ, lit=beyond the Jordan towards the sunrise is translated to grc, πέραν τοῦ Ιορδάνου,, translit. péran toú Jordánou,, beyond the Jordan. The term was translated to la, trans Iordanen, lit=beyond the Jordan in the Vulgate Bible. However some authors give the he, עבר הירדן, Ever HaYarden, lit=beyond the Jordan, as the basis for Transjordan, which is als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
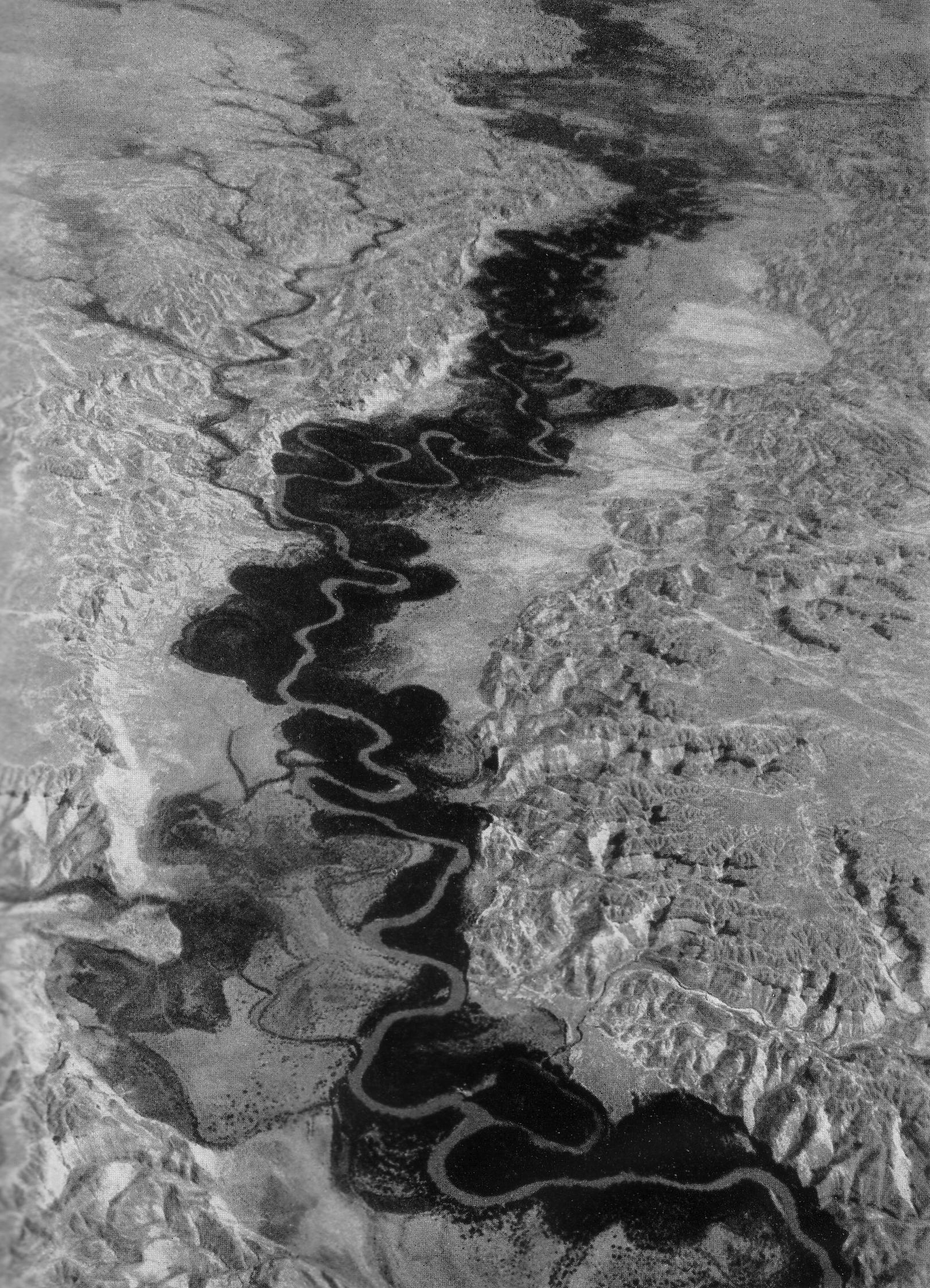
Jordan River
The Jordan River or River Jordan ( ar, نَهْر الْأُرْدُنّ, ''Nahr al-ʾUrdunn'', he, נְהַר הַיַּרְדֵּן, ''Nəhar hayYardēn''; syc, ܢܗܪܐ ܕܝܘܪܕܢܢ ''Nahrāʾ Yurdnan''), also known as ''Nahr Al-Sharieat'' ( ar, نهر الشريعة), is a river in the Middle East that flows roughly north to south through the Sea of Galilee (Hebrew: כנרת Kinneret, Arabic: Bohayrat Tabaraya, meaning Lake of Tiberias) and on to the Dead Sea. Jordan and the Golan Heights border the river to the east, while the West Bank and Israel lie to its west. Both Jordan and the West Bank take their names from the river. The river holds major significance in Judaism and Christianity. According to the Bible, the Israelites crossed it into the Promised Land and Jesus of Nazareth was baptized by John the Baptist in it. Geography The Jordan River has an upper course from its sources to the Sea of Galilee (via the Bethsaida Valley), and a lower course south of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Israelite
The Israelites (; , , ) were a group of Semitic-speaking tribes in the ancient Near East who, during the Iron Age, inhabited a part of Canaan. The earliest recorded evidence of a people by the name of Israel appears in the Merneptah Stele of ancient Egypt, dated to about 1200 BCE. According to the modern archaeological account, the Israelites and their culture branched out of the Canaanite peoples and their cultures through the development of a distinct monolatristic—and later monotheistic—religion centred on the national god Yahweh.Mark Smith in "The Early History of God: Yahweh and Other Deities of Ancient Israel" states "Despite the long regnant model that the Canaanites and Israelites were people of fundamentally different culture, archaeological data now casts doubt on this view. The material culture of the region exhibits numerous common points between Israelites and Canaanites in the Iron I period (c. 1200–1000 BCE). The record would suggest that the Isra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canaan
Canaan (; Phoenician: 𐤊𐤍𐤏𐤍 – ; he, כְּנַעַן – , in pausa – ; grc-bib, Χανααν – ;The current scholarly edition of the Greek Old Testament spells the word without any accents, cf. Septuaginta : id est Vetus Testamentum graece iuxta LXX interpretes. 2. ed. / recogn. et emendavit Robert Hanhart. Stuttgart : Dt. Bibelges., 2006 . However, in modern Greek the accentuation is , while the current (28th) scholarly edition of the New Testament has . ar, كَنْعَانُ – ) was a Semitic-speaking civilization and region in the Ancient Near East during the late 2nd millennium BC. Canaan had significant geopolitical importance in the Late Bronze Age Amarna Period (14th century BC) as the area where the spheres of interest of the Egyptian, Hittite, Mitanni and Assyrian Empires converged or overlapped. Much of present-day knowledge about Canaan stems from archaeological excavation in this area at sites such as Tel Hazor, Tel Megiddo, En Esur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manasseh
Manasseh () is both a given name and a surname. Its variants include Manasses and Manasse (surname), Manasse. Notable people with the name include: Surname * Ezekiel Saleh Manasseh (died 1944), Singaporean rice and opium merchant and hotelier * Jacob Manasseh (died 1832), Ottoman rabbi * Leonard Manasseh (1916–2017), British architect * Maurice Manasseh (born 1943), English cricketer Given name *Manasseh (tribal patriarch), first son of Joseph *Manasseh of Judah, king of Kingdom of Judah, Judah in the 7th century BC *Manasseh II, hypothetical Jewish ruler of the Khazars in the 9th century BC *Manasseh Azure, freelance journalist in Accra, Ghana *Manasseh Masseh Lopes (1755–1831), British politician *Manasseh Rundial, South Sudanese politician *Manasseh Sogavare (born 1955), Solomon Islands politician and Prime Minister Fictional characters *Manassseh da Costa, The King of Schnorrers See also {{given name, type=both ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |