Tribe Of Issachar on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 According to the
According to the
 In the
In the
Cambridge Bible for Schools and Colleges
on 1 Chronicles 12, accessed 14 February 2020 The Tribe of Issachar and the Tribe of Simeon are the only tribes that have not been criticized for failing to complete the conquest of their land in the land of Canaan at the beginning of the Book of Judges. R' David Kimchi (ReDaK) to I Chronicles 9:1 expounds that there remained from the tribes of Ephraim, Manasseh, Issachar and Zebulun in the territory of Judah after the exile of the ten tribes. This remnant returned with the tribe of Judah after the Babylonian Exile.The Tribe of Issachar
/ref>
Map showing Issachar tribal territory, Adrichem, 1590.
Eran Laor Cartographic Collection, the
Map showing Issachar tribal territory, Fuller, 1650.
Eran Laor Cartographic Collection, the
{{Authority control

 According to the
According to the Hebrew Bible
The Hebrew Bible or Tanakh (;"Tanach"
''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary''. Hebrew: ''TДҒn ...
, the Tribe of Issachar () was one of the ''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary''. Hebrew: ''TДҒn ...
twelve tribes of Israel
The Twelve Tribes of Israel ( he, Ч©ЦҙЧҒЧ‘Ц°ЧҳЦөЧҷЦҫЧҷЦҙЧ©Ц°ЧӮЧЁЦёЧҗЦөЧң, translit=Е Д«бёҮб№ӯД“y YД«srДҒКҫД“l, lit=Tribes of Israel) are, according to Hebrew scriptures, the descendants of the biblical patriarch Jacob, also known as Israel, throu ...
and one of the ten lost tribes
The ten lost tribes were the ten of the Twelve Tribes of Israel that were said to have been exiled from the Kingdom of Israel after its conquest by the Neo-Assyrian Empire BCE. These are the tribes of Reuben, Simeon, Dan, Naphtali, Gad, Ashe ...
. In Jewish tradition, the descendants of Issachar
Issachar () was, according to the Book of Genesis, the fifth of the six sons of Jacob and Leah (Jacob's ninth son), and the founder of the Israelite Tribe of Issachar. However, some Biblical scholars view this as an eponymous metaphor providing ...
were seen as being dominated by religious scholars and influential in proselytism
Proselytism () is the policy of attempting to convert people's religious or political beliefs. Proselytism is illegal in some countries.
Some draw distinctions between ''evangelism'' or '' DaвҖҳwah'' and proselytism regarding proselytism as invol ...
. The sons of Issachar, ancestors of the tribe, were Tola
Tola may refer to:
Places
* Bella Tola, a mountain in the Pennine Alps in the Swiss canton of Valais
* La Tola, a town and municipality in the NariГұo Department, Colombia
*Tola (Shakargarh), a village in Pakistan
* Tola, Rivas, a municipality ...
, Phuvah, Job
Work or labor (or labour in British English) is intentional activity people perform to support the needs and wants of themselves, others, or a wider community. In the context of economics, work can be viewed as the human activity that contr ...
and Shimron
Tel Shimron (Hebrew: ЧӘЧң Ч©ЧһЧЁЧ•ЧҹвҖҺ) is an archaeological site and nature reserve in the Jezreel Valley.
Shimron was the name of a major city in the north of Israel throughout antiquity. It is mentioned in the Bible by this name, and in othe ...
.
Biblical narrative
biblical
The Bible (from Koine Greek , , 'the books') is a collection of religious texts or scriptures that are held to be sacred in Christianity, Judaism, Samaritanism, and many other religions. The Bible is an anthologya compilation of texts of a ...
narrative of the Book of Joshua
The Book of Joshua ( he, ЧЎЦөЧӨЦ¶ЧЁ ЧҷЦ°Ч”Ч•Ц№Ч©Ц»ЧҒЧўЦ·вҖҺ ', Tiberian: ''SД“pМ„er YЕҸhЕҚЕЎЕ«aКҝ'') is the sixth book in the Hebrew Bible and the Christian Old Testament, and is the first book of the Deuteronomistic history, the story of Isra ...
, following the completion of the conquest of Canaan
Canaan (; Phoenician: рҗӨҠрҗӨҚрҗӨҸрҗӨҚ вҖ“ ; he, ЧӣЦ°ЦјЧ Ц·ЧўЦ·Чҹ вҖ“ , in pausa вҖ“ ; grc-bib, О§ОұОҪОұОұОҪ вҖ“ ;The current scholarly edition of the Greek Old Testament spells the word without any accents, cf. Septuaginta : id est Vetus T ...
by the Israelite
The Israelites (; , , ) were a group of Semitic-speaking tribes in the ancient Near East who, during the Iron Age, inhabited a part of Canaan.
The earliest recorded evidence of a people by the name of Israel appears in the Merneptah Stele o ...
tribes, Joshua
Joshua () or Yehoshua ( ''YЙҷhЕҚЕЎuaКҝ'', Tiberian: ''YЕҸhЕҚЕЎuaКҝ,'' lit. 'Yahweh is salvation') ''YД“ЕЎЕ«aКҝ''; syr, ЬқЬ«ЬҳЬҘ Ь’ЬӘ ЬўЬҳЬў ''YЙҷЕЎЕ«Кҝ bar NЕҚn''; el, бјёО·ПғОҝбҝҰПӮ, ar , ЩҠЩҸЩҲШҙЩҺШ№ЩҸ ЩұШЁЩ’ЩҶЩҸ ЩҶЩҸЩҲЩҶЩҚ '' YЕ«ЕЎaКҝ ...
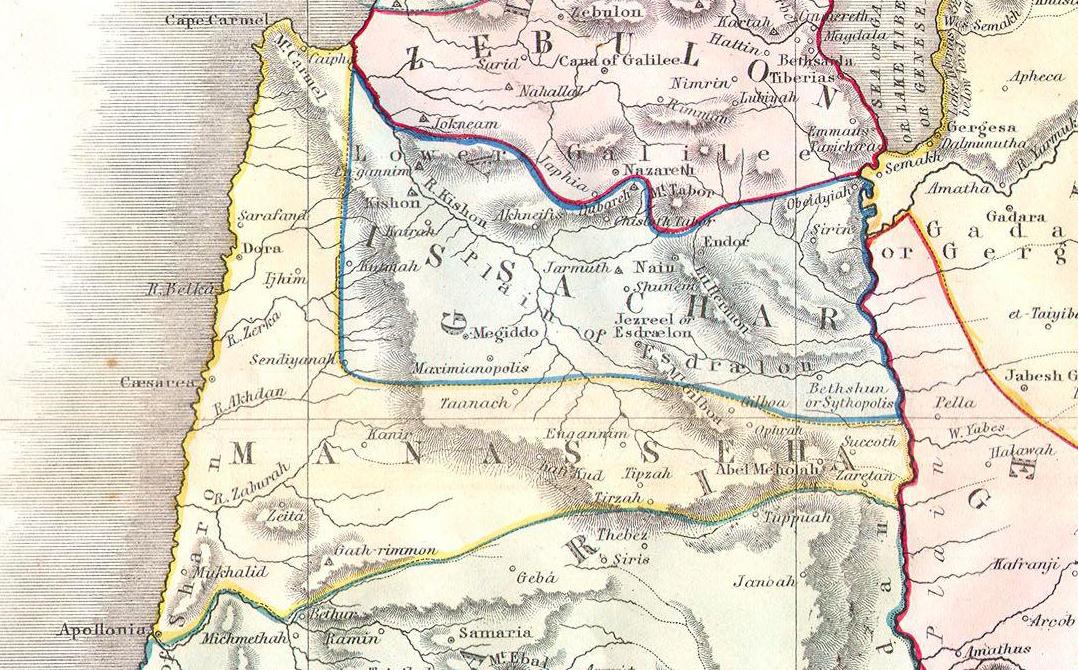
allocated the land among the twelve tribes. The territory allocated to Issachar stretched from the Jordan River
The Jordan River or River Jordan ( ar, ЩҶЩҺЩҮЩ’Шұ Ш§Щ„Щ’ШЈЩҸШұЩ’ШҜЩҸЩҶЩ‘, ''Nahr al-КҫUrdunn'', he, Ч Ц°Ч”Ц·ЧЁ Ч”Ц·ЧҷЦ·ЦјЧЁЦ°Ч“ЦөЦјЧҹ, ''NЙҷhar hayYardД“n''; syc, ЬўЬ—ЬӘЬҗ Ь•ЬқЬҳЬӘЬ•ЬўЬў ''NahrДҒКҫ Yurdnan''), also known as ''Nahr Al-Shariea ...
in the east to Mount Carmel
Mount Carmel ( he, Ч”Ц·ЧЁ Ч”Ц·ЧӣЦ·ЦјЧЁЦ°ЧһЦ¶Чң, Har haKarmel; ar, Ш¬ШЁЩ„ Ш§Щ„ЩғШұЩ…Щ„, Jabal al-Karmil), also known in Arabic as Mount Mar Elias ( ar, link=no, Ш¬ШЁЩ„ Щ…Ш§Шұ ШҘЩ„ЩҠШ§Ші, Jabal MДҒr IlyДҒs, lit=Mount Saint Elias/Elijah), is a c ...
on the west, near to the Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the e ...
coast, including the fertile Esdraelon
The Jezreel Valley (from the he, ЧўЧһЧ§ ЧҷЧ–ЧЁЧўЧҗЧң, translit. ''КҝД’meq YД«zrЙҷКҝД“Кҝl''), or Marj Ibn Amir ( ar, Щ…ШұШ¬ Ш§ШЁЩҶ Ш№Ш§Щ…Шұ), also known as the Valley of Megiddo, is a large fertile plain and inland valley in the Northern Distr ...
plain between present-day Lower Galilee The Lower Galilee (; ar, Ш§Щ„Ш¬Щ„ЩҠЩ„ Ш§Щ„ШЈШіЩҒЩ„, translit=Al Jalil Al Asfal) is a region within the Northern District (Israel), Northern District of Israel. The Lower Galilee is bordered by the Jezreel Valley to the south; the Upper Galilee to t ...
and Samaria
Samaria (; he, Ч©Ц№ЧҒЧһЦ°ЧЁЧ•Ц№Чҹ, translit=Е ЕҚmrЕҚn, ar, Ш§Щ„ШіШ§Щ…ШұШ©, translit=as-SДҒmirah) is the historic and biblical name used for the central region of Palestine, bordered by Judea to the south and Galilee to the north. The first- ...
. It was bounded on the east by East Manasseh
Manasseh () is both a given name and a surname. Its variants include Manasses and Manasse.
Notable people with the name include:
Surname
* Ezekiel Saleh Manasseh (died 1944), Singaporean rice and opium merchant and hotelier
* Jacob Manasseh (die ...
, the south by West Manasseh, and the north by Zebulun
Zebulun (; also ''Zebulon'', ''Zabulon'', or ''Zaboules'') was, according to the Books of Genesis and Numbers,Genesis 46:14 the last of the six sons of Jacob and Leah (Jacob's tenth son), and the founder of the Israelite Tribe of Zebulun. Som ...
and Naphtali
According to the Book of Genesis, Naphtali (; ) was the last of the two sons of Jacob and Bilhah (Jacob's sixth son). He was the founder of the Israelite Tribe of Naphtali.
Some biblical commentators have suggested that the name ''Naphtali'' ...
. There is a consensus among scholars that the accounts in the Book of Judges
The Book of Judges (, ') is the seventh book of the Hebrew Bible and the Christian Old Testament. In the narrative of the Hebrew Bible, it covers the time between the conquest described in the Book of Joshua and the establishment of a kingdom i ...
are not historically reliable. Alternatively, scholars and historians such as Barry G. Webb believe Judges to be a challenging book to parse and grasp, but nevertheless believe it possesses substantially greater historicity than most modern secular scholars give it credit for.
lists the generations of the tribe of Issachar, totaling 87,000 "mighty men of valour". describes the tribe as men who "had understanding of the times, to know what Israel ought to do". W. E. Barnes, writing in the Cambridge Bible for Schools and Colleges
The Cambridge Bible for Schools and Colleges is a biblical commentary set published in parts by Cambridge University Press from 1882 onwards. Anglican bishop John Perowne was the general editor. The first section published was written by theologian ...
argues that "times" are "opportunities", and the phrase means, therefore, "men of experience, having knowledge of the world".Barnes, W. E.Cambridge Bible for Schools and Colleges
on 1 Chronicles 12, accessed 14 February 2020 The Tribe of Issachar and the Tribe of Simeon are the only tribes that have not been criticized for failing to complete the conquest of their land in the land of Canaan at the beginning of the Book of Judges. R' David Kimchi (ReDaK) to I Chronicles 9:1 expounds that there remained from the tribes of Ephraim, Manasseh, Issachar and Zebulun in the territory of Judah after the exile of the ten tribes. This remnant returned with the tribe of Judah after the Babylonian Exile.
/ref>
Rabbanic Literature
The tribe of Issachar is particularly represented as one which consisted mostly of scholars, to which there is said to be an allusion in 1 Chron. 12:32. According to Rava, there was not to be found a Jewish student that was not a descendant either of Levi or of Issachar (Yoma 26a). The passage ofJacob's blessing
The Blessing of Jacob is a prophetic poem that appears in Genesis at and mentions each of Jacob's twelve sons. Genesis presents the poem as the words of Jacob to his sons when Jacob is about to die.
Like the Blessing of Moses, Genesis 49 assess ...
referring to Issachar (Gen. 49:14-15) is interpreted as an allusion to the study of Torah, with which the people of that tribe occupied themselves (Genesis Rabba
Genesis Rabbah (Hebrew: , ''B'reshith Rabba'') is a religious text from Judaism's classical period, probably written between 300 and 500 CE with some later additions. It is a midrash comprising a collection of ancient rabbinical homiletical inter ...
98:17; compare also pseudo-Jonathan and Rashi
Shlomo Yitzchaki ( he, ЧЁЧ‘Чҷ Ч©ЧңЧһЧ” ЧҷЧҰЧ—Ч§Чҷ; la, Salomon Isaacides; french: Salomon de Troyes, 22 February 1040 вҖ“ 13 July 1105), today generally known by the acronym Rashi (see below), was a medieval French rabbi and author of a compre ...
ad loc.). The tribe of Issachar is also said to have been most influential in making proselytes (Gen. R. 98:12; comp. Sifre, Deut. 364).
Although Issachar was the ninth son of Jacob, the prince of his tribe was the second to bring the offering for the dedication of the altar (Numbers 7:18-23), because the tribe was well versed in Torah (Gen. R. 72:4). The Midrash finds in the details of the offering various allusions to the Torah ( Numbers Rabba 8:15). The tribe of Issachar advised the others to bring six covered wagons and twelve oxen (Num. 7:3) on which to load the parts of the Tabernacle (Num. R. 7:19). The 200 chiefs of Issachar (I Chron. 12:32) were leaders of the Sanhedrin, whose decisions were implicitly accepted by their brethren (Gen. R. 72:5, 98:17). The wise men consulted by Ahasuerus (Esther 1:13) were people of Issachar (Esther Rabba 4). The tribe is also represented as having been rich (comp. Targum Onkelos
Onkelos ( he, ЧҗЦ»Ч Ц°Ч§Ц°ЧңЧ•Ц№ЧЎ ''КҫunqЙҷlЕҚs''), possibly identical to Aquila of Sinope, was a Roman national who converted to Judaism in Tannaic times ( 35вҖ“120 CE). He is considered to be the author of the Targum Onkelos ( 110 C ...
to Gen. 49:14); and its members figure as persons who united wealth and learning (Bava Kamma
Bava Kamma ( tmr, Ч‘ЦёЦјЧ‘ЦёЧҗ Ч§Ц·ЧһЦёЦјЧҗ, translit=BДҒбёҮДҒ QammДҒ, translation=The First Gate) is the first of a series of three Talmudic tractates in the order Nezikin ("Damages") that deal with civil matters such as damages and torts. The o ...
17a). Yet, because they studied the Torah under favorable conditions, they only produced 200 chiefs of the Sanhedrin - whereas the tribe of Naphtali, who studied it under difficulties, produced 1,000 ( Song of Songs Rabba 8:14).
Family tree
References
External links
Map showing Issachar tribal territory, Adrichem, 1590.
Eran Laor Cartographic Collection, the
National Library of Israel
The National Library of Israel (NLI; he, Ч”ЧЎЧӨЧЁЧҷЧҷЧ” Ч”ЧңЧҗЧ•ЧһЧҷЧӘ, translit=HaSifria HaLeumit; ar, Ш§Щ„Щ…ЩғШӘШЁШ© Ш§Щ„ЩҲШ·ЩҶЩҠШ© ЩҒЩҠ ШҘШіШұШ§ШҰЩҠЩ„), formerly Jewish National and University Library (JNUL; he, Ч‘ЧҷЧӘ Ч”ЧЎЧӨЧЁЧҷЧқ Ч”ЧңЧҗЧ ...
Map showing Issachar tribal territory, Fuller, 1650.
Eran Laor Cartographic Collection, the
National Library of Israel
The National Library of Israel (NLI; he, Ч”ЧЎЧӨЧЁЧҷЧҷЧ” Ч”ЧңЧҗЧ•ЧһЧҷЧӘ, translit=HaSifria HaLeumit; ar, Ш§Щ„Щ…ЩғШӘШЁШ© Ш§Щ„ЩҲШ·ЩҶЩҠШ© ЩҒЩҠ ШҘШіШұШ§ШҰЩҠЩ„), formerly Jewish National and University Library (JNUL; he, Ч‘ЧҷЧӘ Ч”ЧЎЧӨЧЁЧҷЧқ Ч”ЧңЧҗЧ ...
{{Authority control
Issachar
Issachar () was, according to the Book of Genesis, the fifth of the six sons of Jacob and Leah (Jacob's ninth son), and the founder of the Israelite Tribe of Issachar. However, some Biblical scholars view this as an eponymous metaphor providing ...
Issachar, Tribe of