|
Transverse Flow Effect
Transverse flow effect is an aerodynamic effect encountered when a helicopter moves horizontally (typically forward) through the air, which causes the rotor disc to roll to the side. It is also known as transverse roll or inflow roll. Transverse flow effect is not experienced when hovering, because the air above the rotor disc is being pulled down from above (known as induced flow or downwash), and is equally distributed around the rotor disc. The air is descending from above, which has the effect of reducing angle of attack. However, when the helicopter starts moving into undisturbed air, a portion of the disc is in clean, unaccelerated air, while the remaining portion of the rotor disc is still working on descending air. The part of the disc working on clean air therefore sees a higher angle of attack than the portion of the disc which is working on descending air. The result is that the portion in clean air develops more lift. The disc rolls to the side, rather than pitching ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aerodynamic
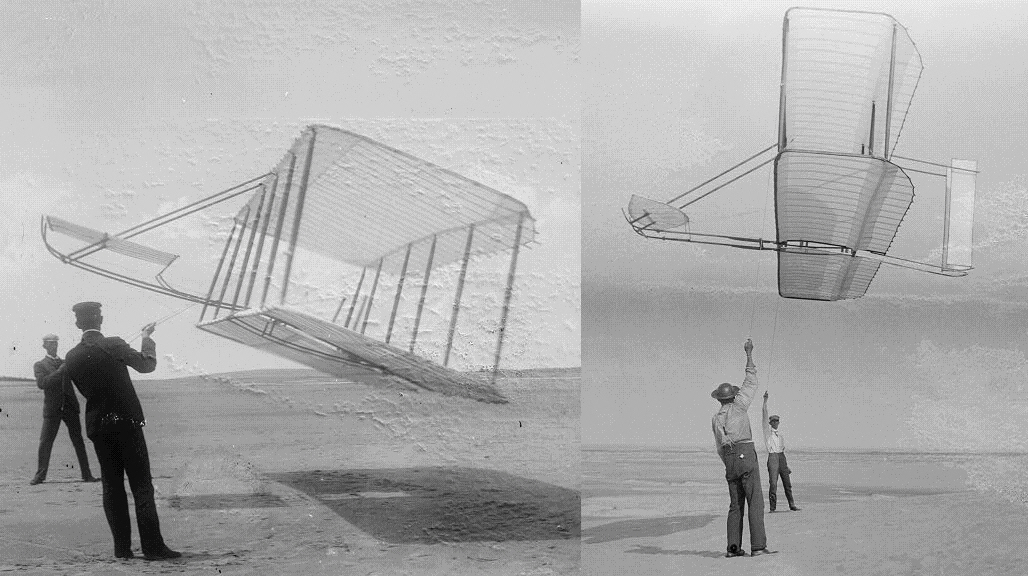
Aerodynamics, from grc, ἀήρ ''aero'' (air) + grc, δυναμική (dynamics), is the study of the motion of air, particularly when affected by a solid object, such as an airplane wing. It involves topics covered in the field of fluid dynamics and its subfield of gas dynamics. The term ''aerodynamics'' is often used synonymously with gas dynamics, the difference being that "gas dynamics" applies to the study of the motion of all gases, and is not limited to air. The formal study of aerodynamics began in the modern sense in the eighteenth century, although observations of fundamental concepts such as aerodynamic drag were recorded much earlier. Most of the early efforts in aerodynamics were directed toward achieving heavier-than-air flight, which was first demonstrated by Otto Lilienthal in 1891. Since then, the use of aerodynamics through mathematical analysis, empirical approximations, wind tunnel experimentation, and computer simulations has formed a rational basis for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
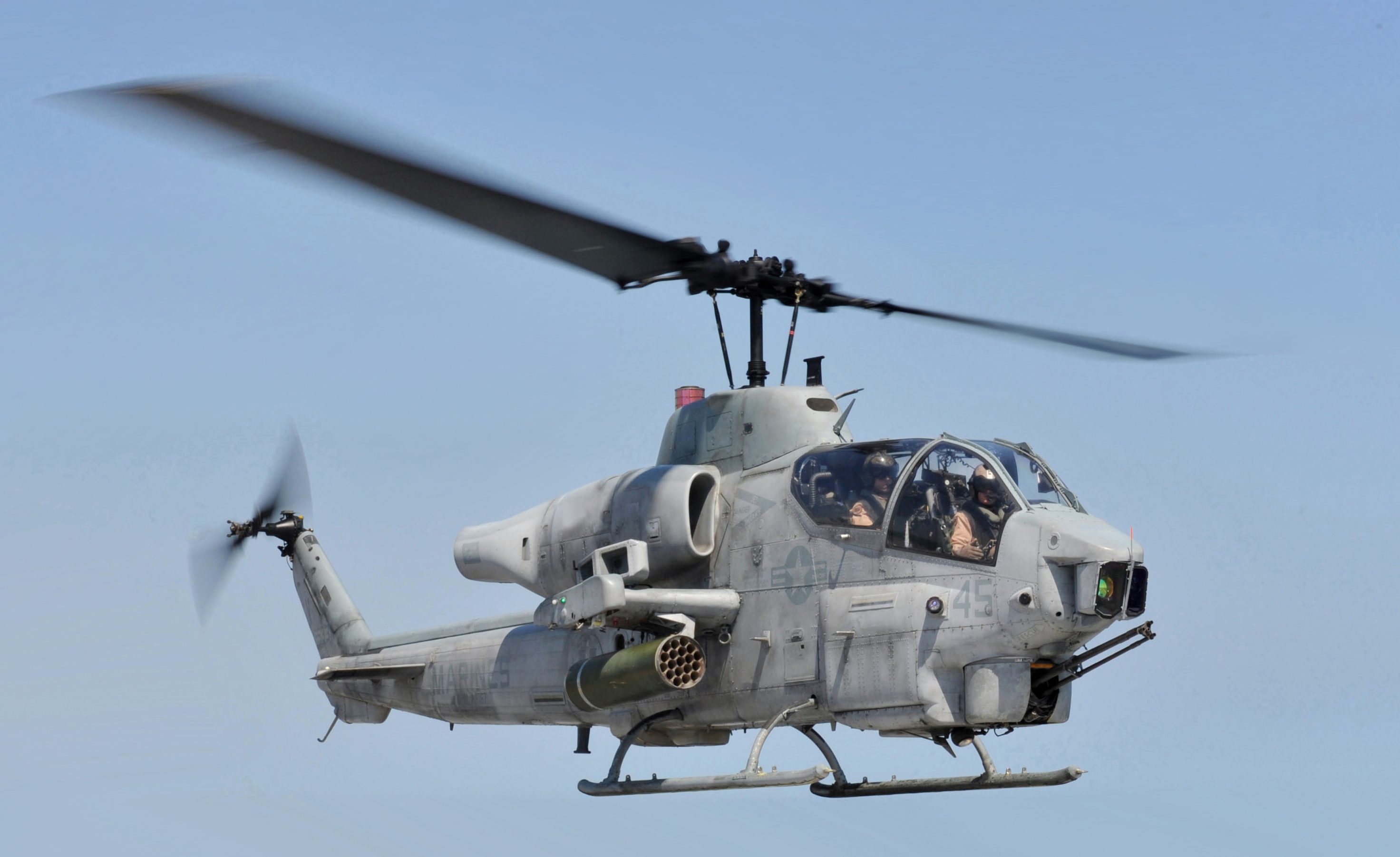
Helicopter
A helicopter is a type of rotorcraft in which lift and thrust are supplied by horizontally spinning rotors. This allows the helicopter to take off and land vertically, to hover, and to fly forward, backward and laterally. These attributes allow helicopters to be used in congested or isolated areas where fixed-wing aircraft and many forms of STOL (Short TakeOff and Landing) or STOVL (Short TakeOff and Vertical Landing) aircraft cannot perform without a runway. In 1942, the Sikorsky R-4 became the first helicopter to reach full-scale production.Munson 1968.Hirschberg, Michael J. and David K. Dailey"Sikorsky". ''US and Russian Helicopter Development in the 20th Century'', American Helicopter Society, International. 7 July 2000. Although most earlier designs used more than one main rotor, the configuration of a single main rotor accompanied by a vertical anti-torque tail rotor (i.e. unicopter, not to be confused with the single-blade monocopter) has become the most comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helicopter Rotor
A helicopter main rotor or rotor system is the combination of several rotary wings (rotor blades) with a control system, that generates the aerodynamic lift force that supports the weight of the helicopter, and the thrust that counteracts aerodynamic drag in forward flight. Each main rotor is mounted on a vertical mast over the top of the helicopter, as opposed to a helicopter tail rotor, which connects through a combination of drive shaft(s) and gearboxes along the tail boom. The blade pitch is typically controlled by the pilot using the helicopter flight controls. Helicopters are one example of rotary-wing aircraft (rotorcraft). The name is derived from the Greek words ''helix'', helik-, meaning spiral; and ''pteron'' meaning wing. Design principles Overview The helicopter rotor is powered by the engine, through the transmission, to the rotating mast. The mast is a cylindrical metal shaft that extends upward from—and is driven by—the transmission. At the top of the mast i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Downwash
In aeronautics, downwash is the change in direction of air deflected by the aerodynamic action of an airfoil, wing, or helicopter rotor blade in motion, as part of the process of producing lift.Crane, Dale: ''Dictionary of Aeronautical Terms, third edition'', page 172. Aviation Supplies & Academics, 1997. In helicopter aerodynamics discussions, it may be referred to as induced flow. Lift on an airfoil is an example of the application of Newton's third law of motion – the force required to deflect the air in the downwards direction is equal in magnitude and opposite in direction to the lift force on the airfoil. Lift on an airfoil is also an example of the Kutta-Joukowski theorem. The Kutta condition explains the existence of downwash at the trailing edge of the wing."The main fact of all heavier-than-air flight is this: ''the wing keeps the airplane up by pushing the air down.''" In: See also *Brownout (aeronautics) *Jet blast *Slipstream *Wake turbulence *Wingtip vortices ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angle Of Attack
In fluid dynamics, angle of attack (AOA, α, or \alpha) is the angle between a reference line on a body (often the chord line of an airfoil) and the vector representing the relative motion between the body and the fluid through which it is moving. Angle of attack is the angle between the body's reference line and the oncoming flow. This article focuses on the most common application, the angle of attack of a wing or airfoil moving through air. In aerodynamics, angle of attack specifies the angle between the chord line of the wing of a fixed-wing aircraft and the vector representing the relative motion between the aircraft and the atmosphere. Since a wing can have twist, a chord line of the whole wing may not be definable, so an alternate reference line is simply defined. Often, the chord line of the root of the wing is chosen as the reference line. Another choice is to use a horizontal line on the fuselage as the reference line (and also as the longitudinal axis). Some aut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phase Lag
In the aerodynamics of rotorcraft like helicopters, phase lag refers to the angular difference between the point at which a control input to a rotor blade occurs and the point of maximum displacement of the blade in response to that control input. This displacement occurs in the direction of rotor rotation. Phase lag may vary depending on rotor tilt rate, ratio of aerodynamic damping to blade inertial forces (Lock number), offset of flapping hinge from axis of rotation (e/R ratio), and coupling of blade flap, drag, and feather motions, and often results in ''cross-coupling'' between the aircraft control axes. Phase lag is a property of all rotating systems acted upon by a periodic force. Because of phase-lag, rolling a rotorcraft to the left or right would theoretically require a forward or backward cyclic if there were no mechanical correction. The rotor control system is angularly shifted as much as necessary to compensate for phase-lag and provide helicopter response that match ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rotorhead
In helicopters the rotorhead is the part of the rotor assembly that joins the blades to the shaft, cyclic and collective mechanisms. It is sometimes referred to as the rotor "hub". The rotorhead is where the lift force from the rotor blades act. The rotorhead is connected to the main drive shaft via the jesus bolt, and houses several other components such as the swash plate, flight control linkages and fly-bars. The rotor hub is also where the centre of gravity In physics, the center of mass of a distribution of mass in space (sometimes referred to as the balance point) is the unique point where the weighted relative position of the distributed mass sums to zero. This is the point to which a force ma ... acts on the helicopter. Types Rotorheads can be classified into 3 main types: * Articulated * Semi-Rigid * Rigid Articulated Rotorhead An articulated rotorhead system is one where the individual blades are free to flap, lag and change pitch. This is done by mounting t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
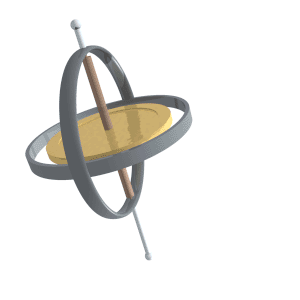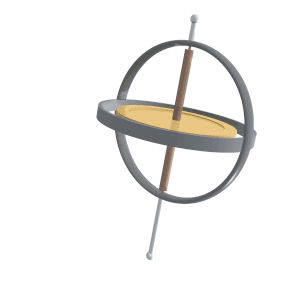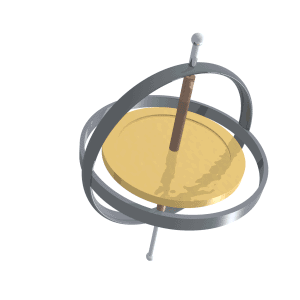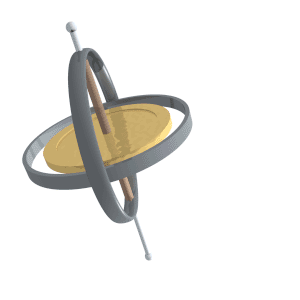
Gyroscopic Precession
Precession is a change in the orientation of the rotational axis of a rotating body. In an appropriate reference frame it can be defined as a change in the first Euler angle, whereas the third Euler angle defines the rotation itself. In other words, if the axis of rotation of a body is itself rotating about a second axis, that body is said to be precessing about the second axis. A motion in which the second Euler angle changes is called ''nutation''. In physics, there are two types of precession: torque-free and torque-induced. In astronomy, ''precession'' refers to any of several slow changes in an astronomical body's rotational or orbital parameters. An important example is the steady change in the orientation of the axis of rotation of the Earth, known as the precession of the equinoxes. Torque-free Torque-free precession implies that no external moment (torque) is applied to the body. In torque-free precession, the angular momentum is a constant, but the angular velocity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dissymmetry Of Lift
Dissymmetry of lift (also known as asymmetry of lift or asymmetric lift) in rotorcraft aerodynamics refers to an unequal amount of lift on opposite sides of the rotor disc. It is a phenomenon that affects single-rotor helicopters and autogyros in forward flight. A rotor blade that is moving in the same direction as the aircraft is called the ''advancing blade'' and the blade moving in the opposite direction is called the ''retreating blade.'' When viewed from above, most American helicopter rotors turn counter-clockwise; French and Russian helicopters turn clockwise. Balancing lift across the rotor disc is important to a helicopter's stability. The amount of lift generated by an airfoil is proportional to the square of its airspeed (velocity). In a hover, the rotor blades have equal airspeeds and therefore equal lift. However, in forward flight the advancing blade has a higher airspeed than the retreating blade, creating uneven lift across the rotor disc. Analysis Consider a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flight Envelope
In aerodynamics, the flight envelope, service envelope, or performance envelope of an aircraft or spacecraft refers to the capabilities of a design in terms of airspeed and load factor or atmospheric density, often simplified to altitude. The term is somewhat loosely applied, and can also refer to other measurements such as maneuverability. When a plane is pushed, for instance by diving it at high speeds, it is said to be flown "outside the envelope", something considered rather dangerous. Flight envelope is one of a number of related terms that are all used in a similar fashion. It is perhaps the most common term because it is the oldest, first being used in the early days of test flying. It is closely related to more modern terms known as extra power and a doghouse plot which are different ways of describing a flight envelope. In addition, the term has been widened in scope outside the field of engineering, to refer to the strict limits in which an event will take place or mor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Translational Lift
Translational lift is improved rotor efficiency resulting from directional flight in a helicopter. Translation is the conversion from the hover to forward flight. As undisturbed air enters the rotor system horizontally, turbulence and vortices created by hovering flight are left behind and the flow of air becomes more horizontal. The efficiency of the hovering rotor system is greatly improved with each knot of airspeed gained by horizontal movement of the aircraft or wind speed. As forward airspeed increases, the helicopter goes through effective translational lift (ETL) at about 16 to 24 knots. This is known as the ETL speed. Above this speed, the rotor system completely outruns the recirculation of old vortices and begins to work in undisturbed air. Efficiency continues to increase with airspeed until best climb airspeed is reached, and drag is minimised. This additional lift can enable an overloaded helicopter to climb even if it is too heavy to hover in ground effect. Liftoff c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |