|
Testicular Self-examination
Testicular self-examination (TSE) is a procedure where a man examines his own testicles and scrotum for possible lumps or swelling. It is usually undertaken at home while standing in front of a mirror and after having a warm bath or shower. Monthly self-examination of the testicles starting at puberty may be an effective way of detecting testicular cancer at an early, potentially treatable stage, which can lead to a 5-year survival rate of 98%. In men aged 15 to 40, testicular cancer is the most common cancer, and the annual rate of increase over the last 10 years in cases of testicular cancer has been shown to be approximately 1% each year. Testicular cancer typically presents with a painless testicular swelling or lump or any change in shape or texture of the testicles. TSE is also indicated if there are certain risk factors present, such as a family history of testicular cancer. Additionally, outside of the possible early detection of testicular cancer, other "off label" uses of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Testicles
A testicle or testis (plural testes) is the male reproductive gland or gonad in all bilaterians, including humans. It is homologous to the female ovary. The functions of the testes are to produce both sperm and androgens, primarily testosterone. Testosterone release is controlled by the anterior pituitary luteinizing hormone, whereas sperm production is controlled both by the anterior pituitary follicle-stimulating hormone and gonadal testosterone. Structure Appearance Males have two testicles of similar size contained within the scrotum, which is an extension of the abdominal wall. Scrotal asymmetry, in which one testicle extends farther down into the scrotum than the other, is common. This is because of the differences in the vasculature's anatomy. For 85% of men, the right testis hangs lower than the left one. Measurement and volume The volume of the testicle can be estimated by palpating it and comparing it to ellipsoids of known sizes. Another method is to use caliper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Cancer Society
The American Cancer Society (ACS) is a nationwide voluntary health organization dedicated to eliminating cancer. Established in 1913, the society is organized into six geographical regions of both medical and lay volunteers operating in more than 250 Regional offices throughout the United States. Its global headquarters is located in the American Cancer Society Center in Atlanta, Georgia. The ACS publishes the journals ''Cancer'', '' CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians'' and ''Cancer Cytopathology''. History The society was founded on May 22, 1913, by ten physicians and five businessmen in New York City under the name "American Society for the Control of Cancer" (ASCC). The current name was adopted in 1944. At the time of founding, it was not considered appropriate to mention the word "cancer" in public. Information concerning this illness was cloaked in a climate of fear and denial. Over 75,000 people died each year of cancer in just the United States. The top item on the foun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Male Genital Procedures
Male (symbol: ♂) is the sex of an organism that produces the gamete (sex cell) known as sperm, which fuses with the larger female gamete, or ovum, in the process of fertilization. A male organism cannot reproduce sexually without access to at least one ovum from a female, but some organisms can reproduce both sexually and asexually. Most male mammals, including male humans, have a Y chromosome, which codes for the production of larger amounts of testosterone to develop male reproductive organs. Not all species share a common sex-determination system. In most animals, including humans, sex is determined genetically; however, species such as ''Cymothoa exigua'' change sex depending on the number of females present in the vicinity. In humans, the word ''male'' can also be used to refer to gender in the social sense of gender role or gender identity. Overview The existence of separate sexes has evolved independently at different times and in different lineages, an example of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Well-woman Examination
A well-woman examination is an exam offered to women to review elements of their reproductive health. The exam includes a breast examination, a pelvic examination and a Pap smear but may also include other procedures. Hospitals employ strict policies relating to the provision of consent by the patient, the availability of chaperones at the examination, and the absence of other parties. Importance Although women often undergo well-woman examinations on an annual basis, the interval for this visit and exam will vary depending on the needs of the patient. The purpose of this exam in asymptomatic women is to screen for potential abnormalities, such as sexually transmitted diseases, and malignancy. Breast examination Visual inspection The breast examination begins with a visual inspection. With the patient in a supine or seated position, the medical professional will look at both breasts to check the color, symmetry, dimensions according to age, lean body mass, the physiological (preg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
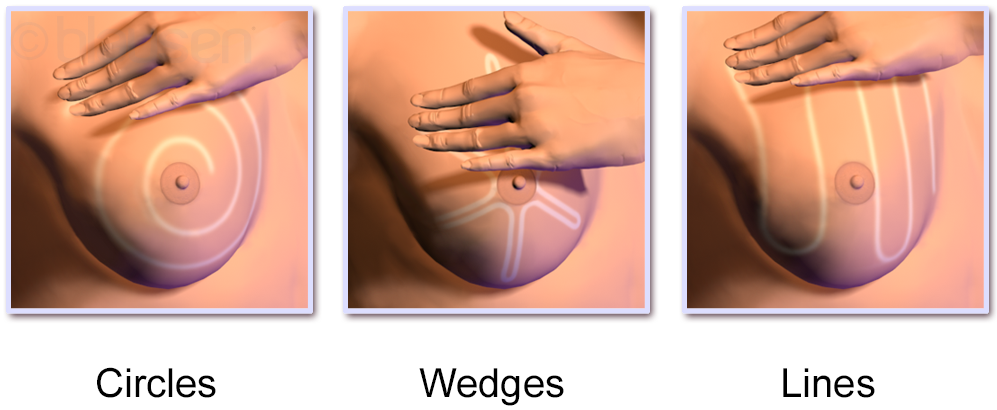
Breast Self-examination
Breast self-examination (BSE) is a screening method used in an attempt to detect early breast cancer. The method involves the woman herself looking at and feeling each breast for possible lumps, distortions or swelling. BSE was once promoted heavily as a means of finding cancer at a more curable stage, but large randomized controlled studies found that it was not effective in preventing death, and actually caused harm through needless biopsies, surgery, and anxiety. The World Health Organization and other organizations recommend against BSE. Other organizations take a neutral stance, and do not recommend for or against BSE. Breast awareness is an informal alternative to breast self-examinations. Limitations According to a meta-analysis in the Cochrane Collaboration, two large trials in Russia and Shanghai found no beneficial effects of screening by breast self-examination "but do suggest increased harm in terms of increased numbers of benign lesions identified and an increa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Testicular Torsion
Testicular torsion occurs when the spermatic cord (from which the testicle is suspended) twists, cutting off the blood supply to the testicle. The most common symptom in children is sudden, severe testicular pain. The testicle may be higher than usual in the scrotum and vomiting may occur. In newborns, pain is often absent and instead the scrotum may become discolored or the testicle may disappear from its usual place. Most of those affected have no obvious prior underlying health problems. Testicular tumor or prior trauma may increase risk. Other risk factors include a congenital malformation known as a "bell-clapper deformity" wherein the testis is inadequately attached to the scrotum allowing it to move more freely and thus potentially twist. Cold temperatures may also be a risk factor. The diagnosis should usually be made based on the presenting symptoms, but requires timely diagnosis and treatment to avoid testicular loss. An ultrasound can be useful when the diagnosis is unc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sexually Transmitted Infections
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs), also referred to as sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) and the older term venereal diseases, are infections that are spread by sexual activity, especially vaginal intercourse, anal sex, and oral sex. STIs often do not initially cause symptoms, which results in a risk of passing the infection on to others. Symptoms and signs of STIs may include vaginal discharge, penile discharge, ulcers on or around the genitals, and pelvic pain. Some STIs can cause infertility. Bacterial STIs include chlamydia, gonorrhea, and syphilis. Viral STIs include genital herpes, HIV/AIDS, and genital warts. Parasitic STIs include trichomoniasis. STI diagnostic tests are usually easily available in the developed world, but they are often unavailable in the developing world. Some vaccinations may also decrease the risk of certain infections including hepatitis B and some types of HPV. Safe sex practices, such as use of condoms, having a smaller numb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urinary Tract Infections
A urinary tract infection (UTI) is an infection that affects part of the urinary tract. When it affects the lower urinary tract it is known as a bladder infection (cystitis) and when it affects the upper urinary tract it is known as a kidney infection (pyelonephritis). Symptoms from a lower urinary tract infection include pain with urination, frequent urination, and feeling the need to urinate despite having an empty bladder. Symptoms of a kidney infection include fever and flank pain usually in addition to the symptoms of a lower UTI. Rarely the urine may appear bloody. In the very old and the very young, symptoms may be vague or non-specific. The most common cause of infection is ''Escherichia coli'', though other bacteria or fungi may sometimes be the cause. Risk factors include female anatomy, sexual intercourse, diabetes, obesity, and family history. Although sexual intercourse is a risk factor, UTIs are not classified as sexually transmitted infections (STIs). Kidney ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genitourinary System
The genitourinary system, or urogenital system, are the organs of the reproductive system and the urinary system. These are grouped together because of their proximity to each other, their common embryological origin and the use of common pathways, like the male urethra. Also, because of their proximity, the systems are sometimes imaged together. The term "apparatus urogenitalis" was used in ''Nomina Anatomica'' (under Splanchnologia) but is not used in the current ''Terminologia Anatomica''. Development The urinary and reproductive organs are developed from the intermediate mesoderm. The permanent organs of the adult are preceded by a set of structures that are purely embryonic and that, with the exception of the ducts, disappear almost entirely before the end of fetal life. These embryonic structures are on either side: the pronephros, the mesonephros and the metanephros of the kidney, and the Wolffian and Müllerian ducts of the sex organ. The pronephros disappears very ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spermatocele
Spermatocele is a fluid-filled cyst that develops at the top of the testicle of the epididymis. The fluid is usually a clear or milky white color and may contain sperm. Spermatoceles are typically filled with spermatozoa and they can vary in size from several millimeters to many centimeters. Small spermatoceles are relatively common, occurring in an estimated 30 percent of males. They are generally not painful. However, some people may experience discomfort such as a dull pain in the scrotum from larger spermatoceles. They are not cancerous, nor do they cause an increased risk of testicular cancer. Additionally, unlike varicoceles, they do not reduce fertility. History "Spermatocele" is originally derived from the ''Greek'' term ''spermatos'' (sperm) and ''kele'' (cavity or mass). Oftentimes, "epididymal cyst" has been used interchangeably with "spermatocele." However, it is important to note their differences. Epididymal cysts may appear anywhere along or within the epididymis a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrocele Testis
A hydrocele testis is an accumulation of clear fluid within the cavum vaginale, the potential space between the layers of the tunica vaginalis of the testicle. It is the most common form of hydrocele and is often referred to simply as a "hydrocele". A primary hydrocele testis causes a painless enlargement in the scrotum on the affected side and is thought to be due to the defective absorption of fluid secreted between the two layers of the tunica vaginalis (investing membrane). A secondary hydrocele is secondary to either inflammation or a neoplasm in the testis. A hydrocele testis usually occurs on one side, but can also affect both sides. The accumulation can be a marker of physical trauma, infection, tumor or varicocele surgery, but the cause is generally unknown. Indirect inguinal hernia indicates increased risk of hydrocele testis. Signs and symptoms A hydrocele testis feels like a small fluid-filled balloon inside the scrotum. It is smooth, and is mainly in front of the test ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Symptoms
Signs and symptoms are the observed or detectable signs, and experienced symptoms of an disease, illness, injury, or condition. A sign for example may be a higher or lower temperature than normal, raised or lowered blood pressure or an abnormality showing on a Medical imaging, medical scan. A symptom is something out of the ordinary that is experienced by an individual such as feeling feverish, a headache or other pain or pains in the body. Signs and symptoms Signs A medical sign is an Objectivity (science), objective observable indication of a disease, injury, or abnormal physiological state that may be detected during a physical examination, examining the patient history, or diagnostic procedure. These signs are visible or otherwise detectable such as a rash or hematoma, bruise. Medical signs, along with symptoms, assist in formulating diagnostic hypothesis. Examples of signs include hypertension, elevated blood pressure, nail clubbing of the fingernails or toenails, staggerin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)