Breast Self-examination on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Breast self-examination (BSE) is a screening method used in an attempt to detect early
 A variety of methods and patterns are used in breast self-exams. Most methods suggest that the woman stand in front of a mirror with the torso exposed to view. She looks in the mirror for visual signs of dimpling, swelling, or redness on or near the breasts. This is usually repeated in several positions, such as while having hands on the hips, and then again with arms held overhead.
The woman then
A variety of methods and patterns are used in breast self-exams. Most methods suggest that the woman stand in front of a mirror with the torso exposed to view. She looks in the mirror for visual signs of dimpling, swelling, or redness on or near the breasts. This is usually repeated in several positions, such as while having hands on the hips, and then again with arms held overhead.
The woman then
American College of Obstetrics and Gynecology
and the
breast cancer
Breast cancer is cancer that develops from breast tissue. Signs of breast cancer may include a lump in the breast, a change in breast shape, dimpling of the skin, milk rejection, fluid coming from the nipple, a newly inverted nipple, or a re ...
. The method involves the woman herself looking at and feeling each breast for possible lumps, distortions or swelling.
BSE was once promoted heavily as a means of finding cancer at a more curable stage, but large randomized controlled studies found that it was not effective in preventing death, and actually caused harm through needless biopsies, surgery, and anxiety. The World Health Organization and other organizations recommend against BSE. Other organizations take a neutral stance, and do not recommend for or against BSE.
Breast awareness
Breast diseases make up a number of conditions. The most common symptoms are a breast mass, breast pain, and nipple discharge.
A majority of breast diseases are noncancerous.
Tumor
A breast tumor is an abnormal mass of tissue in the breast as a ...
is an informal alternative to breast self-examinations.
Limitations
According to ameta-analysis
A meta-analysis is a statistical analysis that combines the results of multiple scientific studies. Meta-analyses can be performed when there are multiple scientific studies addressing the same question, with each individual study reporting me ...
in the Cochrane Collaboration
Cochrane (previously known as the Cochrane Collaboration) is a British international charitable organisation formed to organise medical research findings to facilitate evidence-based choices about health interventions involving health profess ...
, two large trials in Russia and Shanghai found no beneficial effects of screening by breast self-examination "but do suggest increased harm in terms of increased numbers of benign lesions identified and an increased number of biopsies performed". They concluded, "At present, screening by breast self-examination or physical examination cannot be recommended."
Although breast self-examination increases the number of biopsies performed on women, it does not reduce mortality
Mortality is the state of being mortal, or susceptible to death; the opposite of immortality.
Mortality may also refer to:
* Fish mortality, a parameter used in fisheries population dynamics to account for the loss of fish in a fish stock throug ...
from breast cancer. In a large clinical trial involving more than 260,000 female Chinese factory workers, half were carefully taught by nurses at their factories to perform monthly breast self-exam, and the other half were not. The women taught self-exam detected more benign
Malignancy () is the tendency of a medical condition to become progressively worse.
Malignancy is most familiar as a characterization of cancer. A ''malignant'' tumor contrasts with a non-cancerous ''benign'' tumor in that a malignancy is not s ...
(normal or harmless lumps) or early-stage breast disease, but equal numbers of women died from breast cancer in each group.
Because breast self-exam is not proven to save lives, it is no longer routinely recommended by health authorities for general use. It may be appropriate in women who have a particularly high risk of developing breast cancer. Some charitable organizations still promote BSE as a universal screening approach, even in the low-risk women who are most likely to be harmed by unnecessary follow-up procedures. Writer Gayle A. Sulik, in her book ''Pink Ribbon Blues'', suggests that these charities are motivated by their donations depending on fear of breast cancer. Among groups promoting evidence-based medicine
Evidence-based medicine (EBM) is "the conscientious, explicit and judicious use of current best evidence in making decisions about the care of individual patients". The aim of EBM is to integrate the experience of the clinician, the values of t ...
, awareness of breast health and familiarity with one's own body is typically promoted instead of self-exams.
Breast self-examinations are based on the assumption that cancer develops by steady growth of the tumor. According to breast cancer specialist and surgeon Susan Love
Susan M. Love (born February 9, 1948) is an American surgeon, a prominent advocate of preventive breast cancer research, and author. She is regarded as one of the most respected women’s health specialists in the United States. In 2012 Love an ...
, "Breast cancer doesn't work like that...it's sneaky. You could examine yourself every day and suddenly find a walnut."
Among women with high-risk BRCA mutation
A ''BRCA'' mutation is a mutation in either of the ''BRCA1'' and ''BRCA2'' genes, which are tumour suppressor genes. Hundreds of different types of mutations in these genes have been identified, some of which have been determined to be harmful, ...
s, about 10% said that performing breast self-examination increased their anxiety. Half of those who did perform BSE felt that it gave them a sense of control.
Learning breast self-examination increases a woman's level of depression, worrying, and anxiety about breast cancer. Greater anxiety about breast cancer is associated with a higher likelihood of performing BSE. Women are also more likely to perform BSE if they have experienced a false positive
A false positive is an error in binary classification in which a test result incorrectly indicates the presence of a condition (such as a disease when the disease is not present), while a false negative is the opposite error, where the test resul ...
error from screening mammography (being wrongly told that breast cancer may be present, when the woman is actually cancer-free).
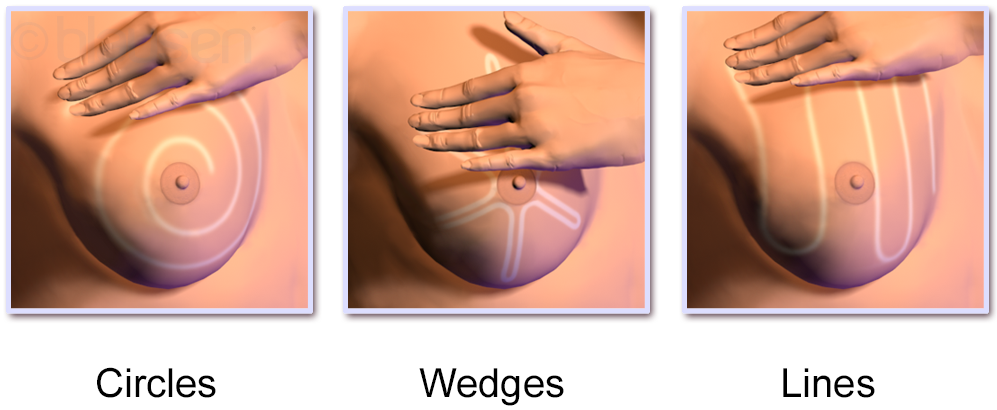
Methods
 A variety of methods and patterns are used in breast self-exams. Most methods suggest that the woman stand in front of a mirror with the torso exposed to view. She looks in the mirror for visual signs of dimpling, swelling, or redness on or near the breasts. This is usually repeated in several positions, such as while having hands on the hips, and then again with arms held overhead.
The woman then
A variety of methods and patterns are used in breast self-exams. Most methods suggest that the woman stand in front of a mirror with the torso exposed to view. She looks in the mirror for visual signs of dimpling, swelling, or redness on or near the breasts. This is usually repeated in several positions, such as while having hands on the hips, and then again with arms held overhead.
The woman then palpate
Palpation is the process of using one's hands to check the body, especially while perceiving/diagnosing a disease or illness. Usually performed by a health care practitioner, it is the process of feeling an object in or on the body to determine ...
s her breasts with the pads of her fingers to feel for lumps (either superficial or deeper in tissue) or soreness. There are several common patterns, which are designed to ensure complete coverage. The vertical strip pattern involves moving the fingers up and down over the breast. The pie-wedge pattern starts at the nipple and moves outward. The circular pattern involves moving the fingers in concentric circles from the nipple outward. Some guidelines suggest mentally dividing the breast into four quadrants and checking each quadrant separately. The palpation process covers the entire breast, including the "axillary tail
The tail of Spence (Spence's tail, axillary process, axillary tail) has historically been described as an extension of the tissue of the upper outer quadrant of the breast traveling into the axilla. The "axillary tail" has been reported to pass in ...
" of each breast that extends toward the axilla
The axilla (also, armpit, underarm or oxter) is the area on the human body directly under the shoulder joint. It includes the axillary space, an anatomical space within the shoulder girdle between the arm and the thoracic cage, bounded superior ...
(armpit). This is usually done once while standing in front of the mirror and again while lying down.
Finally, women that are not breastfeeding
Breastfeeding, or nursing, is the process by which human breast milk is fed to a child. Breast milk may be from the breast, or may be expressed by hand or pumped and fed to the infant. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends that br ...
gently squeeze each nipple to check for any discharge.
Various mnemonic
A mnemonic ( ) device, or memory device, is any learning technique that aids information retention or retrieval (remembering) in the human memory for better understanding.
Mnemonics make use of elaborative encoding, retrieval cues, and imag ...
devices are used as teaching devices. One is called the ''seven P's of BSE'', after seven steps that are named to have the same first initial: ''Positions'', ''Perimeter'', ''Palpation'', ''Pressure'', ''Pattern'', ''Practice'', and ''Planning'' what to do if a change is found in the breast tissue.
For pre-menopausal women, most methods suggest that the self-exam be performed at the same stage of the woman's menstrual cycle
The menstrual cycle is a series of natural changes in hormone production and the structures of the uterus and ovaries of the female reproductive system that make pregnancy possible. The ovarian cycle controls the production and release of eggs a ...
, because the normal hormone fluctuations can cause changes in the breasts. The most commonly recommended time is just after the end of menstruation
Menstruation (also known as a period, among other colloquial terms) is the regular discharge of blood and mucosal tissue from the inner lining of the uterus through the vagina. The menstrual cycle is characterized by the rise and fall of hor ...
, because the breasts are least likely to be swollen and tender at this time. Women who are postmenopausal or have irregular cycles might do a self-exam once a month regardless of their menstrual cycle.
Teaching correctly performed breast self-examinations normally takes a trained professional seven to ten minutes.
Recommendations
TheWorld Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level of h ...
, the Canadian Task Force on Preventive Health Care, and many other scientific organizations recommend against the use of breast self-examinations. Also, the Royal Australian College of General Practitioners
The Royal Australian College of General Practitioners (RACGP) is the professional body for general practitioners (GPs) in Australia. The RACGP is responsible for maintaining standards for quality clinical practice, education and training, and re ...
states that teaching women to perform breast self-examination is no longer recommended. In the US, however, there is no consensus among organizations related to breast self-examination as thAmerican College of Obstetrics and Gynecology
and the
American Medical Association
The American Medical Association (AMA) is a professional association and lobbying group of physicians and medical students. Founded in 1847, it is headquartered in Chicago, Illinois. Membership was approximately 240,000 in 2016.
The AMA's state ...
recommend monthly breast self-examination while the American Cancer Society
The American Cancer Society (ACS) is a nationwide voluntary health organization dedicated to eliminating cancer. Established in 1913, the society is organized into six geographical regions of both medical and lay volunteers operating in more than ...
, the National Cancer Institute
The National Cancer Institute (NCI) coordinates the United States National Cancer Program and is part of the National Institutes of Health (NIH), which is one of eleven agencies that are part of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. ...
, the US Preventative Services Task Force, and the National Comprehensive Cancer Network
National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) is an alliance of 32 cancer centers in the United States, most of which are designated by the National Cancer Institute (one of the U.S. National Institutes of Health) as comprehensive cancer centers. It ...
neither recommend nor discourage breast self-examination.
History
Activists began promoting breast self-examination in the 1930s because their exhortation to not delay seeking treatment for suspicious lumps was not affecting the death rate. In the 1950s and 1960s, a film demonstrating breast self-examination, which was co-sponsored by the American Cancer Society and the National Cancer Institute, was shown to millions of American women. In the 1970s, researchers began to report that women were being told to do this even though there had never been any evidence to suggest that it saved lives.See also
*Breast cancer awareness
Breast cancer awareness is an effort to raise awareness and reduce the stigma of breast cancer through education on symptoms and treatment. Supporters hope that greater knowledge will lead to earlier detection of breast cancer, which is associ ...
* Mammography
*Testicular self-examination
Testicular self-examination (TSE) is a procedure where a man examines his own testicles and scrotum for possible lumps or swelling. It is usually undertaken at home while standing in front of a mirror and after having a warm bath or shower. Monthl ...
*Well-woman examination
A well-woman examination is an exam offered to women to review elements of their reproductive health. The exam includes a breast examination, a pelvic examination and a Pap smear but may also include other procedures. Hospitals employ strict poli ...
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Breast Self-Examination Breast cancer Breast procedures Medical mnemonics