|
Tarsal Tunnel
The tarsal tunnel is a passage found along the inner leg underneath the medial malleolus of the ankle. Structure The roof of the tarsal tunnel is formed by the flexor retinaculum of the foot. The floor of the tarsal tunnel is formed by the medial malleolus and the calcaneus. Contents The tibial nerve, posterior tibial artery, posterior tibial vein, and flexor tendons travel in a bundle along this pathway through the tarsal tunnel, in the following order from anteromedial to posterolateral: * Tibialis posterior tendon. * Flexor digitorum longus tendon. * Posterior tibial artery. * Posterior tibial vein. * Tibial nerve. * Flexor hallucis longus tendon. In the tunnel, the tibial nerve splits into three different paths. The medial calcaneal branches of the tibial nerve continues to the heel, while the medial plantar nerve and the lateral plantar nerve continue on to the bottom of the foot. Clinical significance Tarsal tunnel syndrome Tarsal tunnel syndrome is the most commonly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ankle
The ankle, or the talocrural region, or the jumping bone (informal) is the area where the foot and the leg meet. The ankle includes three joints: the ankle joint proper or talocrural joint, the subtalar joint, and the inferior tibiofibular joint. The movements produced at this joint are dorsiflexion and plantarflexion of the foot. In common usage, the term ankle refers exclusively to the ankle region. In medical terminology, "ankle" (without qualifiers) can refer broadly to the region or specifically to the talocrural joint. The main bones of the ankle region are the talus (in the foot), and the tibia and fibula (in the leg). The talocrural joint is a synovial hinge joint that connects the distal ends of the tibia and fibula in the lower limb with the proximal end of the talus. The articulation between the tibia and the talus bears more weight than that between the smaller fibula and the talus. Structure Region The ankle region is found at the junction of the leg and the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tibial Nerve
The tibial nerve is a branch of the sciatic nerve. The tibial nerve passes through the popliteal fossa to pass below the arch of soleus. Structure Popliteal fossa The tibial nerve is the larger terminal branch of the sciatic nerve with root values of L4, L5, S1, S2, and S3. It lies superficial (or posterior) to the popliteal vessels, extending from the superior angle to the inferior angle of the popliteal fossa, crossing the popliteal vessels from lateral to medial side. It gives off branches as shown below: * Muscular branches - Muscular branches arise from the distal part of the popliteal fossa. It supplies the medial and lateral heads of gastrocnemius, soleus, plantaris and popliteus muscles. Nerve to popliteus crosses the popliteus muscle, runs downwards and laterally, winds around the lower border of the popliteus to supply the deep (or anterior) surface of the popliteus. This nerve also supplies the tibialis posterior muscle, superior tibiofibular joint, tibia bone, intero ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tinel Sign
Tinel's sign (also Hoffmann-Tinel sign) is a way to detect irritated nerves. It is performed by lightly tapping ( percussing) over the nerve to elicit a sensation of tingling or "pins and needles" in the distribution of the nerve. Percussion is usually performed moving distal to proximal. It is named after Jules Tinel.Tinel, J. (1978) The "tingling sign" in peripheral nerve lesions (Translated by EB Kaplan). In: M. Spinner M (Ed.), Injuries to the Ma jor Branches of Peripheral Nerves of the Forearm. (2nd ed.) (pp 8–13). Philadelphia: WD Saunders CoTinel, J. (1915) Le signe du fourmillement dans les lésions des nerfs périphériques. Presse médicale, 47, 388–389Tinel, J., Nerve wounds. London: Baillère, Tindall and Cox, 1917 It is a potential sign of carpal tunnel syndrome, cubital tunnel syndrome Ulnar nerve entrapment is a condition where the ulnar nerve becomes physically trapped or pinched, resulting in pain, numbness, or weakness, primarily affecting the little finge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wrist
In human anatomy, the wrist is variously defined as (1) the Carpal bones, carpus or carpal bones, the complex of eight bones forming the proximal skeletal segment of the hand; "The wrist contains eight bones, roughly aligned in two rows, known as the carpal bones." (2) the wrist joint or radiocarpal joint, the joint between the radius (bone), radius and the Carpal bones, carpus and; (3) the anatomical region surrounding the carpus including the distal parts of the bones of the forearm and the proximal parts of the metacarpus or five metacarpal bones and the series of joints between these bones, thus referred to as ''wrist joints''. "With the large number of bones composing the wrist (ulna, radius, eight carpas, and five metacarpals), it makes sense that there are many, many joints that make up the structure known as the wrist." This region also includes the carpal tunnel, the anatomical snuff box, bracelet lines, the Flexor retinaculum of the hand, flexor retinaculum, and the ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
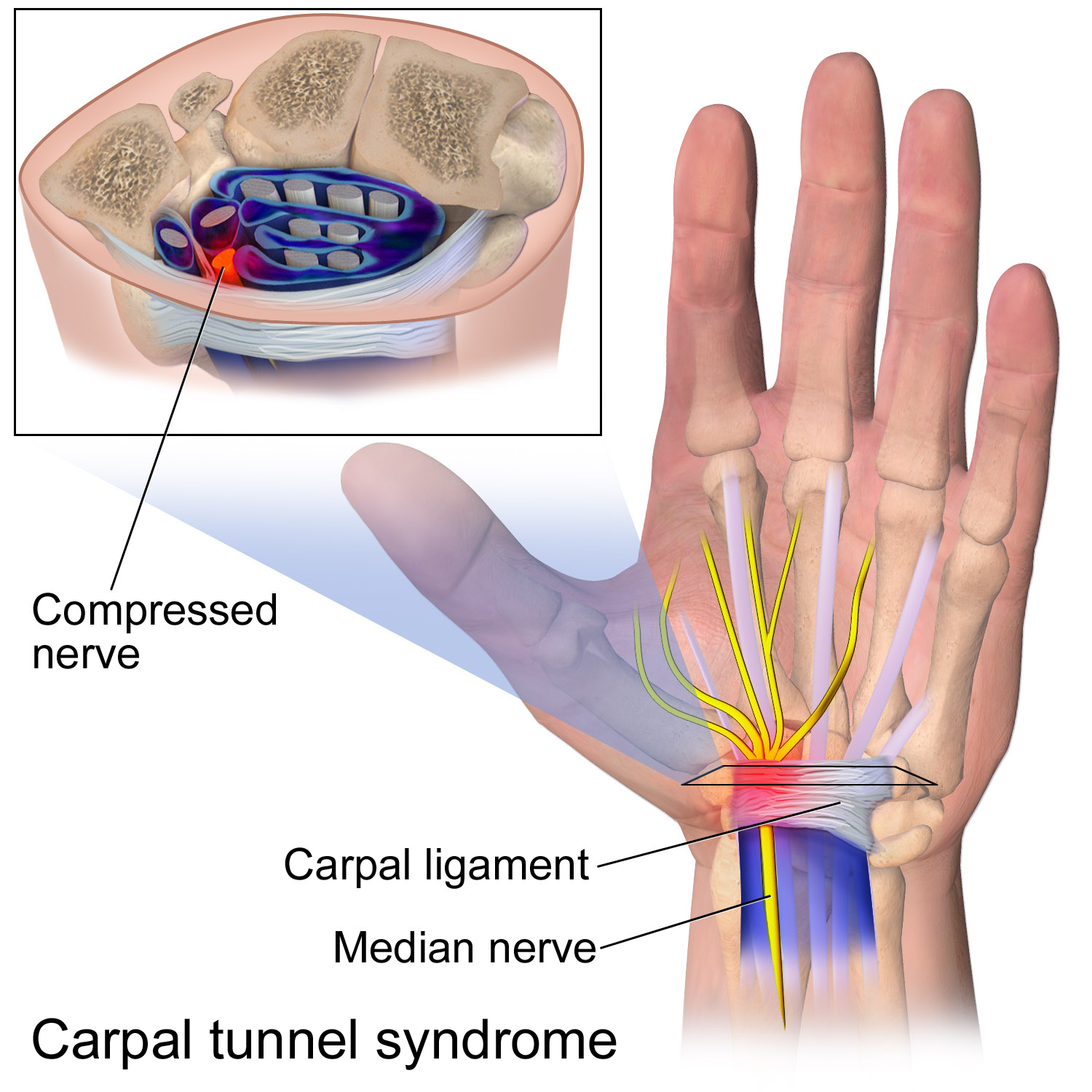
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is the collection of symptoms and signs associated with median neuropathy at the carpal tunnel. Most CTS is related to idiopathic compression of the median nerve as it travels through the wrist at the carpal tunnel (IMNCT). Idiopathic means that there is no other disease process contributing to pressure on the nerve. As with most structural issues, it occurs in both hands, and the strongest risk factor is genetics. Other conditions can cause CTS such as wrist fracture or rheumatoid arthritis. After fracture, swelling, bleeding, and deformity compress the median nerve. With rheumatoid arthritis, the enlarged synovial lining of the tendons causes compression. The main symptoms are numbness and tingling in the thumb, index finger, middle finger and the thumb side of the ring finger. People often report pain, but pain without tingling is not characteristic of IMNCT. Rather, the numbness can be so intense that it is described as painful. Symptoms are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foot
The foot ( : feet) is an anatomical structure found in many vertebrates. It is the terminal portion of a limb which bears weight and allows locomotion. In many animals with feet, the foot is a separate organ at the terminal part of the leg made up of one or more segments or bones, generally including claws or nails. Etymology The word "foot", in the sense of meaning the "terminal part of the leg of a vertebrate animal" comes from "Old English fot "foot," from Proto-Germanic *fot (source also of Old Frisian fot, Old Saxon fot, Old Norse fotr, Danish fod, Swedish fot, Dutch voet, Old High German fuoz, German Fuß, Gothic fotus "foot"), from PIE root *ped- "foot". The "plural form feet is an instance of i-mutation." Structure The human foot is a strong and complex mechanical structure containing 26 bones, 33 joints (20 of which are actively articulated), and more than a hundred muscles, tendons, and ligaments.Podiatry Channel, ''Anatomy of the foot and ankle'' The joints of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lateral Plantar Nerve
The lateral plantar nerve (external plantar nerve) is a branch of the tibial nerve, in turn a branch of the sciatic nerve and supplies the skin of the fifth toe and lateral half of the fourth, as well as most of the deep muscles, its distribution being similar to that of the ulnar nerve in the hand. It passes obliquely forward with the lateral plantar artery to the lateral side of the foot, lying between the flexor digitorum brevis and quadratus plantae and, in the interval between the flexor muscle and the abductor digiti minimi, divides into a superficial and a deep branch. Before its division, it supplies the quadratus plantae and abductor digiti minimi. It divides into deep and superficial branches. Additional images File:Gray357.png, Coronal section through right talocrural and talocalcaneal joint In human anatomy, the subtalar joint, also known as the talocalcaneal joint, is a joint of the foot. It occurs at the meeting point of the talus and the calcaneus. The joi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medial Plantar Nerve
The medial plantar nerve (internal plantar nerve) is the larger of the two terminal divisions of the tibial nerve (medial and lateral plantar nerve), which accompanies the medial plantar artery. From its origin under the laciniate ligament it passes under cover of the abductor hallucis muscle, and, appearing between this muscle and the flexor digitorum brevis, gives off a proper digital plantar nerve and finally divides opposite the bases of the metatarsal bones into three common digital plantar nerves. Branches The branches of the medial plantar nerve are: (1) cutaneous, (2) muscular, (3) articular, (4) a proper digital nerve to the medial side of the great toe, and (5) three common digital nerves. Cutaneous branches The cutaneous branches pierce the plantar aponeurosis between the abductor hallucis and the flexor digitorum brevis and are distributed to the skin of the sole of the foot. Muscular branches The muscular branches supply muscles on the medial side of the sole, incl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medial Calcaneal Branches Of The Tibial Nerve
The medial calcaneal branches of the tibial nerve (internal calcaneal branches) perforate the laciniate ligament, and supply the skin of the heel and medial side of the sole of the foot. Structure The medial calcaneal nerve originates either from the tibial nerve or the lateral plantar nerve. It splits into two cutaneous branches. Function The medial calcaneal nerve provides sensory innervation to the medial side of the heel. See also * Cutaneous innervation of the lower limbs Cutaneous innervation refers to the area of the skin which is supplied by a specific nerve. Modern texts are in agreement about which areas of the skin are served by which nerves, but there are minor variations in some of the details. The borde ... References Nerves of the lower limb and lower torso {{Neuroanatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flexor Hallucis Longus Muscle
The flexor hallucis longus muscle (FHL) is one of the three deep muscles of the posterior compartment of the leg that attaches to the plantar surface of the distal phalanx of the great toe. The other deep muscles are the flexor digitorum longus and tibialis posterior; the tibialis posterior is the most powerful of these deep muscles. All three muscles are innervated by the tibial nerve which comprises half of the sciatic nerve. Structure The flexor hallucis longus is situated on the fibular side of the leg. It arises from the inferior two-thirds of the posterior surface of the body of the fibula, with the exception of 2.5 cm. at its lowest part; from the lower part of the interosseous membrane; from an intermuscular septum between it and the peroneus muscles, laterally, and from the fascia covering the tibialis posterior, medially. The fibers pass obliquely downward and backward, where it passes through the tarsal tunnel on the medial side of the foot and end in a tendon whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Posterior Tibial Vein
The posterior tibial veins are veins of the leg in humans. They drain the posterior compartment of the leg and the plantar surface of the foot to the popliteal vein. Structure The posterior tibial veins receive blood from the medial and lateral plantar veins. They drain the posterior compartment of the leg and the plantar surface of the foot to the popliteal vein, which it forms when it joins with the anterior tibial vein. The posterior tibial vein is accompanied by an homonym artery, the posterior tibial artery, along its course. It lies posterior to the medial malleolus in the ankle. They receive the most important perforator vein Perforator veins are so called because they perforate the deep fascia of muscles, to connect the superficial veins to the deep veins where they drain. Perforator veins play an essential role in maintaining normal blood draining. They have valves ...s: the Cockett perforators, superior, medial and inferior. Additional images File:Gray440_col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)