|
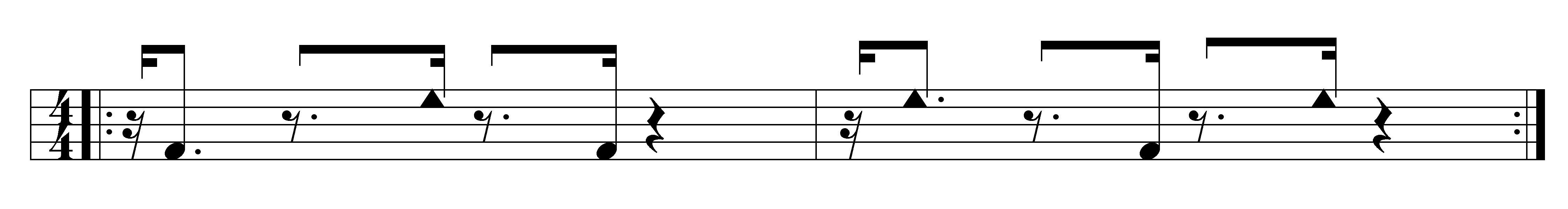
Tahona
Tahona, alternatively spelled tajona due to its pronunciation or taona, is a secular style of Afro-Cuban music developed in the 19th century in Santiago de Cuba after the arrival of Haitian slaves following the Haitian Revolution. It is named after the ensembles and the drums played by them. It is considered one of the oldest styles within the rumba complex, and its performance became rare by the 20th century. History The word "tahona" initially described a type of single-headed hand drum with a body made of a wooden barrel and a goatskin head, larger than the tumbadora (conga drum). The ensembles, and ultimately the music itself, also adopted the term tahona. As a genre, tahona is considered a style of Cuban rumba, and together with yambú it is one of the oldest. However, it differs from the canonical rumba styles in the fact that it developed in the eastern part of Cuba, the Oriente Province, due to the immigration of Haitian slaves following the Haitian Revolution of the 1790s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bombo Criollo
The bombo criollo, or simply bombo, is a family of Latin American drums derived from the European bass drum (also called in Spanish ''bombo'') and native Latin American drum traditions. These drums are of smaller dimensions than the orchestral bass drum, and their frame can be made of wood or steel. They can be held vertically or diagonally on the body or a stand. The specific make of the instrument depends on the regional tradition. In Argentina, the bombo criollo is called bombo legüero and played in many folkloric styles. In Cuba, bombos are the largest drums played by the street comparsas in Santiago. In other countries, the term tambora is commonly used. The bombo should not be confused with the Puerto Rican bomba, a genre of music played with hand drums called ''barriles de bomba'' (bomba barrels), which are unrelated to the European bass drums. Argentina The bombo legüero is a common instrument in Argentine folk traditions such as zamba and chacarera. The body of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Music Of Cuba
The music of Cuba, including its instruments, performance, and dance, comprises a large set of unique traditions influenced mostly by west African and European (especially Spanish) music. Due to the syncretic nature of most of its genres, Cuban music is often considered one of the richest and most influential regional music in the world. For instance, the son cubano merges an adapted Spanish guitar (tres), melody, harmony, and lyrical traditions with Afro-Cuban percussion and rhythms. Almost nothing remains of the original native traditions, since the native population was exterminated in the 16th century. Since the 19th-century Cuban music has been hugely popular and influential throughout the world. It has been perhaps the most popular form of regional music since the introduction of recording technology. Cuban music has contributed to the development of a wide variety of genres and musical styles around the globe, most notably in Latin America, the Caribbean, West Africa, and Eu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cuban Rumba
Rumba is a secular genre of Cuban music involving dance, percussion, and song. It originated in the northern regions of Cuba, mainly in urban Havana and Matanzas, during the late 19th century. It is based on African music and dance traditions, namely Abakuá and yuka, as well as the Spanish-based ''coros de clave''. According to Argeliers León, rumba is one of the major "genre complexes" of Cuban music, and the term rumba complex is now commonly used by musicologists. This complex encompasses the three traditional forms of rumba (yambú, guaguancó and columbia), as well as their contemporary derivatives and other minor styles. Traditionally performed by poor workers of African descent in streets and ''solares'' (courtyards), rumba remains one of Cuba's most characteristic forms of music and dance. Vocal improvisation, elaborate dancing and polyrhythmic drumming are the key components of all rumba styles. '' Cajones'' (wooden boxes) were used as drums until the early 20th cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yambú
Rumba is a secular genre of Cuban music involving dance, percussion, and song. It originated in the northern regions of Cuba, mainly in urban Havana and Matanzas, during the late 19th century. It is based on African music and dance traditions, namely Abakuá and yuka, as well as the Spanish-based ''coros de clave''. According to Argeliers León, rumba is one of the major "genre complexes" of Cuban music, and the term rumba complex is now commonly used by musicologists. This complex encompasses the three traditional forms of rumba (yambú, guaguancó and columbia), as well as their contemporary derivatives and other minor styles. Traditionally performed by poor workers of African descent in streets and ''solares'' (courtyards), rumba remains one of Cuba's most characteristic forms of music and dance. Vocal improvisation, elaborate dancing and polyrhythmic drumming are the key components of all rumba styles. '' Cajones'' (wooden boxes) were used as drums until the early 20th cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tumba Francesa
Tumba francesa is a secular Afro-Cuban genre of dance, song, and drumming that emerged in Oriente, Cuba. It was introduced by slaves from the French colony of Saint-Domingue (which would later become the nation of Haiti) whose owners resettled in Cuba's eastern regions following the slave rebellion during the 1790s. The genre flourished in the late 19th century with the establishment of ''sociedades de tumba francesa'' (tumba francesa societies), of which only three survive. Characteristics Tumba francesa combines musical traditions of West African, Bantu, French and Spanish origin. Cuban ethnomusicologists agree that the word "tumba" derives from the Bantu and Mandinka words for drum. In Cuba, the word tumba is used to denote the drums, the ensembles and the performance itself in tumba francesa. Instrumentation Tumbas francesas are directed by a mistress of ceremonies called ''mayora de plaza''. Performances generally begin with improvised solo singing in a mixture of Spa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Afro-Haitian
Afro-Haitians or Black Haitians are Haitians who trace their full or partial ancestry to Sub-Saharan Africa. They form the largest racial group in Haiti and together with other Afro-Caribbean groups, the largest racial group in the region. The majority of Afro-Haitians are descendants of enslaved Africans brought to the island by the Spanish Empire and the Kingdom of France to work on plantations. Since the Haitian Revolution, Afro-Haitians have been the largest racial group in the country, accounting for 85% of the population in the early 21st century. The remaining 15% of the population is made up of mixed persons (mixed African and European descent) and other minor groups (European, Arab, and Asian descent). Origins The African people of Haiti derived from various areas, spanning from Senegal to the Congo. Most of which were brought from West Africa, with a considerable number also brought from Central Africa. Some of these groups include those from the former Kongo kingdo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fernando Ortiz Fernández
Fernando Ortiz Fernández (16 July 1881 – 10 April 1969) was a Cuban essayist, anthropologist, ethnomusicologist and scholar of Afro-Cuban culture. Ortiz was a prolific polymath dedicated to exploring, recording, and understanding all aspects of indigenous Cuban culture. Ortiz coined the term "transculturation," the notion of converging cultures. Life Ortiz was born in Havana. Disillusioned with politics in the early period of Cuban history and having been a member of President Gerardo Machado's Liberal Party, and a Liberal member of its House of Representatives from 1917 to 1922, he became active in the early nationalist civic revival movement. Throughout his life Ortiz was involved in the foundation of institutions and journals dedicated to the study of Cuban culture. He was the cofounder of the Cuban Academy of the Language in 1926. He also founded ''Surco'' (founded 1930) and ''Ultra'' (1936–47), both journals that provided commentary on foreign journals. In 1937 he fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cuban Styles Of Music
Cuban may refer to: * Something of, from, or related to Cuba, a country in the Caribbean * Cubans, people from Cuba, or of Cuban descent ** Cuban exile, a person who left Cuba for political reasons, or a descendant thereof * Cuban citizen, a person who is part of the Cuban population, see Demographics of Cuba * Cuban Spanish, the dialect of Cuba * Cuban Americans, citizens of the United States who are of Cuban descent * Cuban cigar, often referred to as "Cubans" * Cuban culture * Cuban cuisine ** Cuban sandwich * Cuban-eight, a type of aerobatic maneuver People with the surname * Brian Cuban (born 1961), American lawyer and activist * Mark Cuban (born 1958), American entrepreneur See also * Cuban Missile Crisis * List of Cubans * * Cuban Boys, a British music act * Kuban (other) * Cubane Cubane () is a synthetic hydrocarbon compound that consists of eight carbon atoms arranged at the corners of a cube, with one hydrogen atom attached to each carbon atom. A solid cryst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Call And Response (music)
In music, call and response is a succession of two distinct phrases usually written in different parts of the music, where the second phrase is heard as a direct commentary on or in response to the first. This can take form as commentary to a statement, an answer to a question or repetition of a phrase following or slightly overlapping the initial speaker(s). It corresponds to the call and response pattern in human communication and is found as a basic element of musical form, such as verse-chorus form, in many traditions. African music In Sub-Saharan African cultures, call and response is a pervasive pattern of democratic participation—in public gatherings in the discussion of civic affairs, in religious rituals, as well as in vocal and instrumental musical expression. African-American music Enslaved Africans brought call and response music with them to the colonized American continents and it has been transmitted over the centuries in various forms of cultural express ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abakuá
Abakuá, also sometimes known as Ñañiguismo, is an Afro-Cuban men's initiatory fraternity or secret society, which originated from fraternal associations in the Cross River (Nigeria), Cross River region of southeastern Nigeria and southwestern Cameroon. Abakuá has been described as "an Afro-Cuban version of Freemasonry". The Cuban artist Belkis Ayón intensively investigated the Abakuá mythology in her prints. History Origins in Cuba Known generally as Ekpe, Egbo, Ngbe, or Ugbe among the multi-lingual groups in the region, it was believed that ''Ñáñigos'', as the members are known, could be transformed into leopards to stalk their enemies. In contemporary Haiti, where secret societies have remained strong, an elite branch of the army that was set up to instill fear in the restless masses was named The Leopards. Among the less mystical ''Ñáñigo'' revenges was the ability to turn people over to slavers. In Africa they were notorious operators who had made regular de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Efik People
The Efik are an ethnic group located primarily in southern Nigeria, and western Cameroon. Within Nigeria, the Efik can be found in the present-day Cross River State and Akwa Ibom state. The Efik speak the Efik language which is a member of the Benue–Congo subfamily of the Niger-Congo language group. The Efik refer to themselves as Efik Eburutu, Ifa Ibom, Eburutu and Iboku. Simmons, p.11 The name Efik first appears in historical literature in the nineteenth century. The most popular historical accounts of Efik migration attest a movement from Ibom in Arochukwu to Uruan and from Uruan to numerous settlements along the lower Cross river. The bulk of the Efik can be found in Calabar. Prior to 1905, Old Calabar was a term used to describe the Efik settlements of Duke Town, Creek Town, Old town, Cobham town, Henshaw town, Adiabo and Mbiabo (consisting of Mbiabo edere, Mbiabo Ikot Offiong and Mbiabo Ikoneto).Cotton, p.302 The Efik have also been referred to as "Calabar people" in histor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Havana
Havana (; Spanish: ''La Habana'' ) is the capital and largest city of Cuba. The heart of the La Habana Province, Havana is the country's main port and commercial center.Cuba ''''. . The city has a population of 2.3million inhabitants, and it spans a total of – making it the largest city by area, the most populous city, and the [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)
.jpg)