|
True Crime
True crime is a nonfiction literary, podcast, and film genre in which the author examines an actual crime and details the actions of real people associated with and affected by criminal events. The crimes most commonly include murder; about 40 percent focus on tales of serial killers. True crime comes in many forms, such as books, films, podcasts, and television shows. Many works in this genre recount high-profile, sensational crimes such as the JonBenét Ramsey killing, the O. J. Simpson murder case, and the Pamela Smart murder, while others are devoted to more obscure slayings. True crime works can impact the crimes they cover and the audience who consumes it. The genre is often criticized for being insensitive to the victims and their families and is described by some as trash culture. History Zhang Yingyu's ''The Book of Swindles'' () is a late Ming dynasty collection of stories about allegedly true cases of fraud. Works in the related Chinese genre of court case fict ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nonfiction
Nonfiction, or non-fiction, is any document or media content that attempts, in good faith, to provide information (and sometimes opinions) grounded only in facts and real life, rather than in imagination. Nonfiction is often associated with being presented more objectively, like historical, scientific, or otherwise straightforward and accurate information, but sometimes, can be presented more subjectively, like sincerely held beliefs and thoughts on a real-world topic. One prominent usage of nonfiction is as one of the two fundamental divisions of narrative (storytelling)—often, specifically, prose writing—in contrast to narrative fiction, which is largely populated by imaginary characters and events, though sometimes ambiguous regarding its basis in reality. Some typical examples of nonfiction include diaries, biographies, news stories, documentary films, textbooks, travel books, recipes, and scientific journals. While specific claims in a nonfiction work may p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
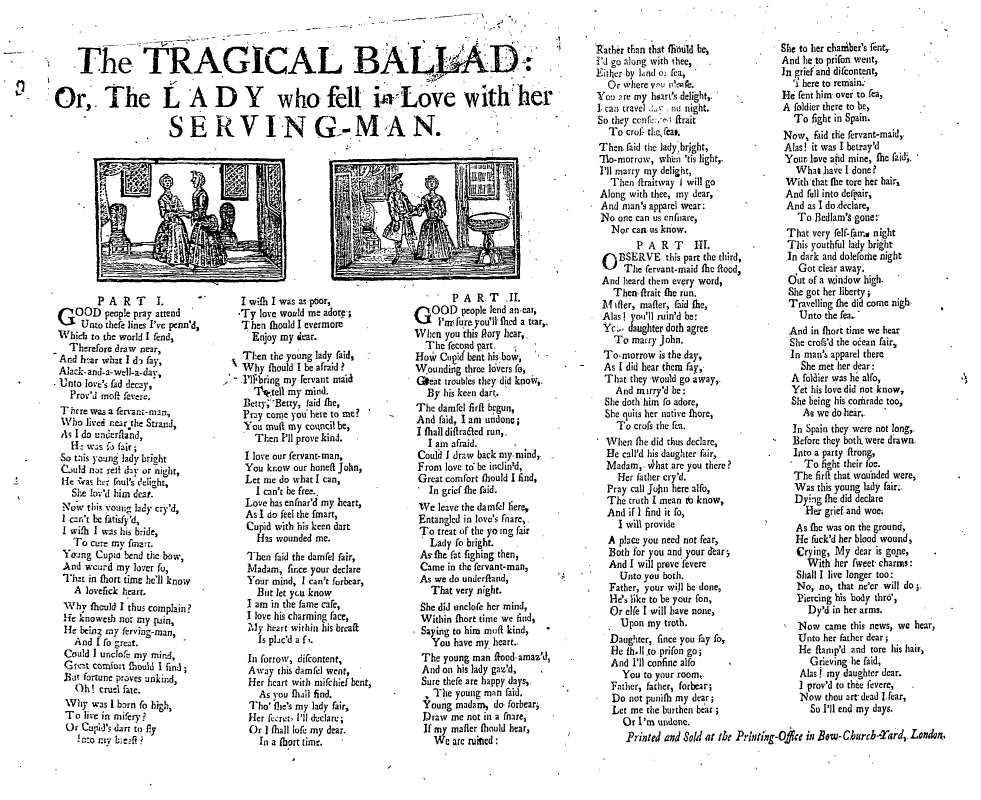
Street Literature
Street literature is any of several different types of publication sold on the streets, at fairs and other public gatherings, by travelling hawkers, pedlars or chapmen, from the fifteenth to the nineteenth centuries. Robert Collison's account of the subject describes street literature as the "forerunner of the popular press". Leslie Shepard's "History of Street Literature" identifies a range of different publications as indicated by his subtitle: "The Story of Broadside Ballads, Chapbooks, Proclamations, News-Sheets, Election Bills, Tracts, Pamphlets, Cocks, Catchpennies, and Other Ephemera". Street literature therefore includes several different printed formats and publication types. The main formats are: Broadside ballad Broadside ballads are traditional ballads printed on one side of a full sheet or half sheet of paper, often in landscape orientation. Intended to be pasted on to walls for public consultation. Chapbook Chapbooks were small, paper-covered booklets, usually pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Roughead
William Roughead (pronounced ''Ruff-head'') (1870–1952) was a well-known Scottish lawyer and amateur criminologist, as well as an editor and essayist on "matters criminous". He was an important early practitioner of the modern "true crime" literary genre. Biography Career Roughead held the title of Writer to Her Majesty's Signet as a Scottish solicitor. As the years progressed, Roughead practised law less and increasingly plied a trade as an unofficial historian of crime. He marks this transition from the year 1889, when at the age of nineteen, he skipped his apprentice work at the law firm of Maclaren and Traquair to attend the trial of Jessie King, the murderous baby-farmer of Stockbridge (an experience he described in his essay "My First Murder: Featuring Jessie King", ''In Queer Street'', 1932). For roughly the next six decades, Roughead attended almost every murder trial of any importance at the High Court of Justiciary. These experiences provided the material he w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blackwood's Magazine
''Blackwood's Magazine'' was a British magazine and miscellany printed between 1817 and 1980. It was founded by the publisher William Blackwood and was originally called the ''Edinburgh Monthly Magazine''. The first number appeared in April 1817 under the editorship of Thomas Pringle and James Cleghorn. The journal was unsuccessful and Blackwood fired Pringle and Cleghorn and relaunched the journal as ''Blackwood's Edinburgh Magazine'' under his own editorship. The journal eventually adopted the shorter name and from the relaunch often referred to itself as ''Maga''. The title page bore the image of George Buchanan, a 16th-century Scottish historian, religious and political thinker. Description ''Blackwood's'' was conceived as a rival to the Whig-supporting '' Edinburgh Review.'' Compared to the rather staid tone of ''The Quarterly Review'', the other main Tory work, ''Maga'' was ferocious and combative. This is due primarily to the work of its principal writer John Wilson, who ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
On Murder Considered As One Of The Fine Arts
"On Murder Considered as one of the Fine Arts" is an essay by Thomas De Quincey first published in 1827 in ''Blackwood's Magazine''. The essay is a fictional, satirical account of an address made to a gentleman's club concerning the aesthetic appreciation of murder. It focuses particularly on a series of murders allegedly committed in 1811 by John Williams in the neighborhood of Ratcliffe Highway, London. The essay was enthusiastically received and led to numerous sequels, including "A Second Paper on Murder Considered as one of the Fine Arts" in 1839 and a "Postscript" in 1854. These essays have exerted a strong influence on subsequent literary representations of crime and were lauded by such critics as G. K. Chesterton, Wyndham Lewis and George Orwell. De Quincey also refers to the Williams murders in his " On the Knocking at the Gate in ''Macbeth''". The 1964 French film ''On Murder Considered as One of the Fine Arts "On Murder Considered as one of the Fine Arts" is an essay ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas De Quincey
Thomas Penson De Quincey (; 15 August 17858 December 1859) was an English writer, essayist, and literary critic, best known for his ''Confessions of an English Opium-Eater'' (1821). Many scholars suggest that in publishing this work De Quincey inaugurated the tradition of addiction literature in the West. Life and work Child and student Thomas Penson De Quincey was born at 86 Cross Street, Manchester, Lancashire. His father, a successful merchant with an interest in literature, died when De Quincey was quite young. Soon after his birth, the family went to ''The Farm'' and then later to Greenheys, a larger country house in Chorlton-on-Medlock near Manchester. In 1796, three years after the death of his father, Thomas Quincey, his mother – the erstwhile Elizabeth Penson – took the name "De Quincey".Morrison, Robert. "Thomas De Quincey: Chronology" TDQ Homepage. Kingston: Queen's University, 2013. That same year, De Quincey's mother moved to Bath and enrolled him at King E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ithaka Harbors
Ithaka Harbors, Inc. is a US not-for-profit organization whose stated mission is to "help the academic community use digital technologies to preserve the scholarly record and to advance research and teaching in sustainable ways". It is the parent company of digital library website JSTOR, the digital preservation service Portico, and the research and consulting group Ithaka S+R. Ithaka was founded in 2003 by Kevin M. Guthrie. Ithaka's revenue was $86 million in 2014, most of it ($69 million) from JSTOR service fees. History JSTOR was founded in 1995 under the direction of current ITHAKA president Kevin M. Guthrie. Guthrie also served as the founding president of ITHAKA in 2004. Both organizations were initially funded by grants from the Andrew W. Mellon Foundation, which at the time was led by William G. Bowen. The two organizations announced that they would merge in 2009 after years of working together closely. The organizations stated that the merger was "a natural progression ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
JSTOR
JSTOR (; short for ''Journal Storage'') is a digital library founded in 1995 in New York City. Originally containing digitized back issues of academic journals, it now encompasses books and other primary sources as well as current issues of journals in the humanities and social sciences. It provides full-text searches of almost 2,000 journals. , more than 8,000 institutions in more than 160 countries had access to JSTOR. Most access is by subscription but some of the site is public domain, and open access content is available free of charge. JSTOR's revenue was $86 million in 2015. History William G. Bowen, president of Princeton University from 1972 to 1988, founded JSTOR in 1994. JSTOR was originally conceived as a solution to one of the problems faced by libraries, especially research and university libraries, due to the increasing number of academic journals in existence. Most libraries found it prohibitively expensive in terms of cost and space to maintain a comprehen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penny Press
Penny press newspapers were cheap, tabloid-style newspapers mass-produced in the United States from the 1830s onwards. Mass production of inexpensive newspapers became possible following the shift from hand-crafted to steam-powered printing. Famous for costing one cent () while other newspapers cost around six cents, penny press papers were revolutionary in making the news accessible to middle class citizens for a reasonable price. History As the East Coast's middle and working classes grew, so did their desire for news. Penny papers emerged as a cheap source of news with coverage of crime, tragedy, adventure, and gossip. The penny papers represented the crudest form of journalism because of the sensational gossip that was reported. The penny press was most noted for its price – only one cent per paper – while other contemporary newspapers were priced around six cents per issue. The exceptionally low price popularized the newspaper in America and extended the influence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territories, nine Minor Outlying Islands, and 326 Indian reservations. The United States is also in free association with three Pacific Island sovereign states: the Federated States of Micronesia, the Marshall Islands, and the Republic of Palau. It is the world's third-largest country by both land and total area. It shares land borders with Canada to its north and with Mexico to its south and has maritime borders with the Bahamas, Cuba, Russia, and other nations. With a population of over 333 million, it is the most populous country in the Americas and the third most populous in the world. The national capital of the United States is Washington, D.C. and its most populous city and principal financial center is New York City. Paleo-Americ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychology
Psychology is the scientific study of mind and behavior. Psychology includes the study of conscious and unconscious phenomena, including feelings and thoughts. It is an academic discipline of immense scope, crossing the boundaries between the natural and social sciences. Psychologists seek an understanding of the emergent properties of brains, linking the discipline to neuroscience. As social scientists, psychologists aim to understand the behavior of individuals and groups.Fernald LD (2008)''Psychology: Six perspectives'' (pp.12–15). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications.Hockenbury & Hockenbury. Psychology. Worth Publishers, 2010. Ψ (''psi''), the first letter of the Greek word ''psyche'' from which the term psychology is derived (see below), is commonly associated with the science. A professional practitioner or researcher involved in the discipline is called a psychologist. Some psychologists can also be classified as behavioral or cognitive scientists. Some psyc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suspect
In law enforcement jargon, a suspect is a known person accused or suspected of committing a crime. Police and reporters in the United States often use the word suspect as a jargon when referring to the perpetrator of the offense (perp in dated US slang). However, in official definition, the perpetrator is the robber, assailant, counterfeiter, etc.—the person who committed the crime. The distinction between suspect and perpetrator recognizes that the suspect is not ''known'' to have committed the offense, while the perpetrator—who may not yet have been suspected of the crime, and is thus not necessarily a suspect—is the one who did. The suspect may be a different person from the perpetrator, or there may have been no actual crime, which would mean there is no perpetrator. A common error in police reports is a witness description of the suspect (as a witness generally describes a perpetrator, while a mug shot is of a suspect). Frequently it is stated that police are looking ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |