|
Transstadial Transmission
Transstadial transmission occurs when a pathogen remains with the vector from one life stage ("stadium") to the next. For example, the bacteria ''Borrelia burgdorferi'', the causative agent for Lyme disease, infects the tick vector as a larva, and the infection is maintained when it molts to a nymph and later develops as an adult. This type of transmission is seen in other parasites like viruses or ''Rickettsia''. In addition to ticks, mites are another common vector. Some sources consider transstadial transmission a type of horizontal transmission, whereas other sources consider it vertical or partial vertical transmission. Transstadial blockage could be considered the opposite of transstadial transmission, where the parasite cannot be carried over from one life stage to the next. For example, viruses that undergo transstadial blockage will have decreased infectivity in molting insects. See also *Transovarial transmission Transovarial or transovarian transmission (transmission f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Borrelia Burgdorferi
''Borrelia burgdorferi'' is a bacterial species of the spirochete class in the genus ''Borrelia'', and is one of the causative agents of Lyme disease in humans. Along with a few similar genospecies, some of which also cause Lyme disease, it makes up the species complex of ''Borrelia burgdorferi'' sensu lato. The complex currently comprises 20 accepted and 3 proposed genospecies. ''B. burgdorferi'' sensu stricto exists in North America and Eurasia and until 2016 was the only known cause of Lyme disease in North America. ''Borrelia'' species are Gram-negative. Microbiology ''Borrelia burgdorferi'' is named after the researcher Willy Burgdorfer, who first isolated the bacterium in 1982. ''Borrelia burgdorferi'' is a microaerophile, requiring small amounts of oxygen in order to undergo glycolysis and survive. Like all other ''Borrelia'' sps., this bacterium is also gram-negative and a spirochete. Borrelia colonies are often smaller, rounded, and white with an elevated center. ''B. b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
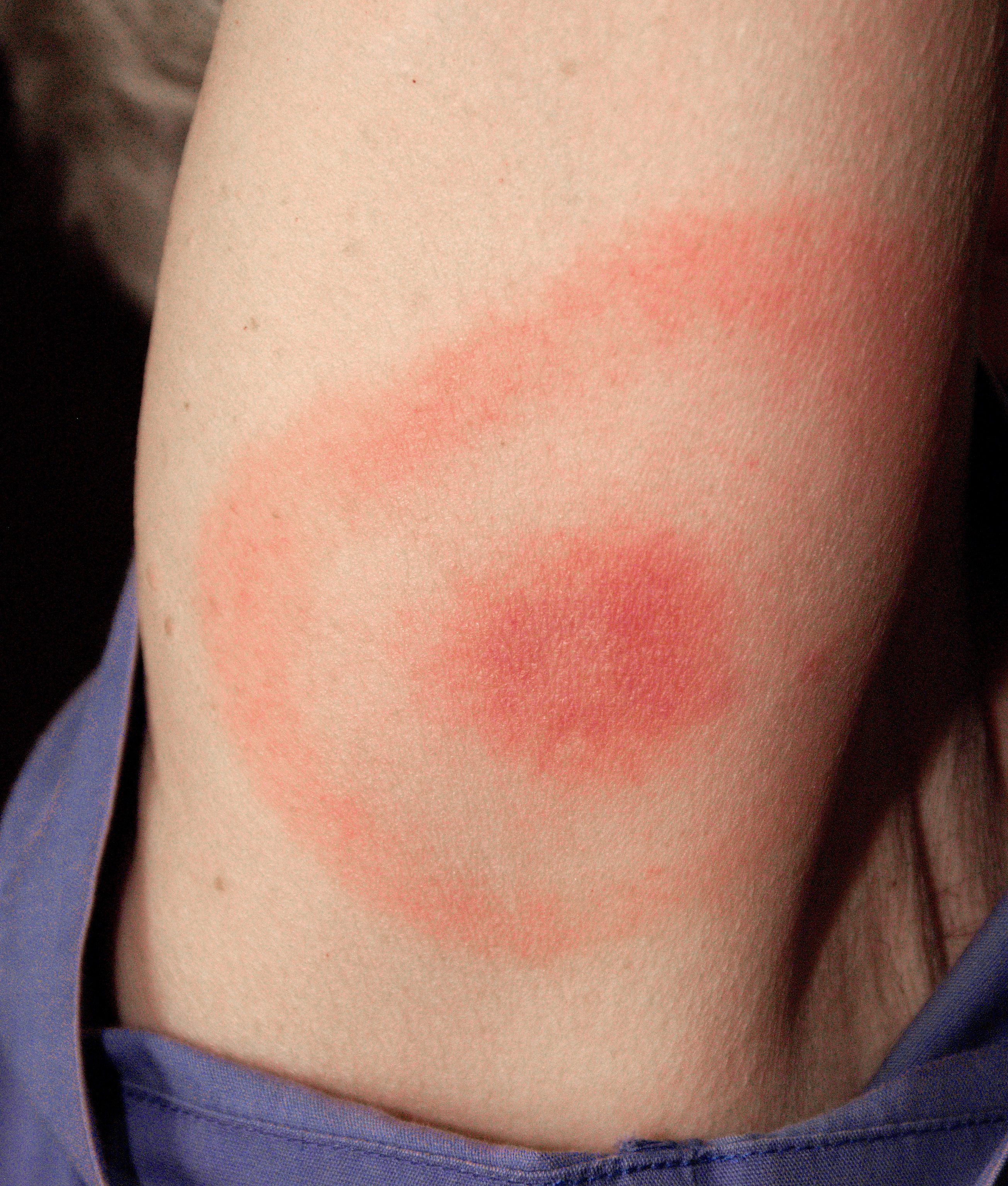
Lyme Disease
Lyme disease, also known as Lyme borreliosis, is a vector-borne disease caused by the ''Borrelia'' bacterium, which is spread by ticks in the genus ''Ixodes''. The most common sign of infection is an expanding red rash, known as erythema migrans (EM), which appears at the site of the tick bite about a week afterwards. The rash is typically neither itchy nor painful. Approximately 70–80% of infected people develop a rash. Early diagnosis can be difficult. Other early symptoms may include fever, headaches and tiredness. If untreated, symptoms may include loss of the ability to move one or both sides of the face, joint pains, severe headaches with neck stiffness or heart palpitations. Months to years later repeated episodes of joint pain and swelling may occur. Occasionally shooting pains or tingling in the arms and legs may develop. Despite appropriate treatment about 10 to 20% of those affected develop joint pains, memory problems and tiredness for at least six months. Lym ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tick
Ticks (order Ixodida) are parasitic arachnids that are part of the mite superorder Parasitiformes. Adult ticks are approximately 3 to 5 mm in length depending on age, sex, species, and "fullness". Ticks are external parasites, living by feeding on the blood of mammals, birds, and sometimes reptiles and amphibians. The timing of the origin of ticks is uncertain, though the oldest known tick fossils are from the Cretaceous period, around 100 million years old. Ticks are widely distributed around the world, especially in warm, humid climates. Ticks belong to two major families, the Ixodidae or hard ticks, and the Argasidae, or soft ticks. ''Nuttalliella,'' a genus of tick from southern Africa is the only member of the family Nuttalliellidae, and represents the most primitive living lineage of ticks. Adults have ovoid/pear-shaped bodies (idiosomas) which become engorged with blood when they feed, and eight legs. Their cephalothorax and abdomen are completely fused. In addit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vector (epidemiology)
In epidemiology, a disease vector is any living agent that carries and transmits an infectious pathogen to another living organism; agents regarded as vectors are organisms, such as parasites or microbes. The first major discovery of a disease vector came from Ronald Ross in 1897, who discovered the malaria pathogen when he dissected a mosquito. Arthropods Arthropods form a major group of pathogen vectors with mosquitoes, flies, sand flies, lice, fleas, ticks, and mites transmitting a huge number of pathogens. Many such vectors are haematophagous, which feed on blood at some or all stages of their lives. When the insects feed on blood, the pathogen enters the blood stream of the host. This can happen in different ways. The ''Anopheles'' mosquito, a vector for malaria, filariasis, and various arthropod-borne-viruses (arboviruses), inserts its delicate mouthpart under the skin and feeds on its host's blood. The parasites the mosquito carries are usually located in its salivary gla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Larva
A larva (; plural larvae ) is a distinct juvenile form many animals undergo before metamorphosis into adults. Animals with indirect development such as insects, amphibians, or cnidarians typically have a larval phase of their life cycle. The larva's appearance is generally very different from the adult form (''e.g.'' caterpillars and butterflies) including different unique structures and organs that do not occur in the adult form. Their diet may also be considerably different. Larvae are frequently adapted to different environments than adults. For example, some larvae such as tadpoles live almost exclusively in aquatic environments, but can live outside water as adult frogs. By living in a distinct environment, larvae may be given shelter from predators and reduce competition for resources with the adult population. Animals in the larval stage will consume food to fuel their transition into the adult form. In some organisms like polychaetes and barnacles, adults are immobil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nymph (biology)
In biology, a nymph is the immature form of some invertebrates, particularly insects, which undergoes gradual metamorphosis (hemimetabolism) before reaching its adult stage. Unlike a typical larva, a nymph's overall form already resembles that of the adult, except for a lack of wings (in winged species). In addition, while a nymph moults, it never enters a pupal stage. Instead, the final moult results in an adult insect. Nymphs undergo multiple stages of development called instars. This is the case, for example, in Orthoptera (crickets, grasshoppers and locusts), Hemiptera (cicadas, shield bugs, whiteflies, aphids, leafhoppers, froghoppers, treehoppers etc.), mayflies, termites, cockroaches, mantises, stoneflies and Odonata (dragonflies and damselflies). Nymphs of aquatic insects, as in the Odonata, Ephemeroptera, and Plecoptera, are also called naiads, an Ancient Greek name for mythological water nymphs. Usage of the term 'naiad' is no longer popular among entomologists, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virus
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. Since Dmitri Ivanovsky's 1892 article describing a non-bacterial pathogen infecting tobacco plants and the discovery of the tobacco mosaic virus by Martinus Beijerinck in 1898,Dimmock p. 4 more than 9,000 virus species have been described in detail of the millions of types of viruses in the environment. Viruses are found in almost every ecosystem on Earth and are the most numerous type of biological entity. The study of viruses is known as virology, a subspeciality of microbiology. When infected, a host cell is often forced to rapidly produce thousands of copies of the original virus. When not inside an infected cell or in the process of infecting a cell, viruses exist in the form of independent particles, or ''virions'', consisting of (i) the genetic material, i. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rickettsia
''Rickettsia'' is a genus of nonmotile, gram-negative, nonspore-forming, highly pleomorphic bacteria that may occur in the forms of cocci (0.1 μm in diameter), bacilli (1–4 μm long), or threads (up to about 10 μm long). The term "rickettsia" has nothing to do with rickets (which is a deficiency disease resulting from lack of vitamin D); the bacterial genus ''Rickettsia'' instead was named after Howard Taylor Ricketts, in honor of his pioneering work on tick-borne spotted fever. Properly, ''Rickettsia'' is the name of a single genus, but the informal term "rickettsia", plural "rickettsias", usually not capitalised, commonly applies to any members of the order Rickettsiales. Being obligate intracellular bacteria, rickettsias depend on entry, growth, and replication within the cytoplasm of living eukaryotic host cells (typically endothelial cells). Accordingly, ''Rickettsia'' species cannot grow in artificial nutrient culture; they must be grown either in tissue or embryo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mite
Mites are small arachnids (eight-legged arthropods). Mites span two large orders of arachnids, the Acariformes and the Parasitiformes, which were historically grouped together in the subclass Acari, but genetic analysis does not show clear evidence of a close relationship. Most mites are tiny, less than in length, and have a simple, unsegmented body plan. The small size of most species makes them easily overlooked; some species live in water, many live in soil as decomposers, others live on plants, sometimes creating galls, while others again are Predation, predators or Parasitism, parasites. This last type includes the commercially destructive ''Varroa'' parasite of honey bees, as well as scabies mites of humans. Most species are harmless to humans, but a few are associated with allergies or may transmit diseases. The scientific discipline devoted to the study of mites is called acarology. Evolution and taxonomy The mites are not a defined taxon, but is used for two disti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horizontal Transmission
Horizontal transmission is the transmission of organisms between biotic and/or abiotic members of an ecosystem that are not in a parent-progeny relationship. This concept has been generalized to include transmissions of infectious agents, symbionts, and cultural traits between humans. Because the evolutionary fate of the agent is not tied to reproductive success of the host, horizontal transmission tends to evolve virulence. It is therefore a critical concept for evolutionary medicine. Biological Pathogen transmission In biological, but not cultural, transmissions the carriers (also known as vectors) may include other species. The two main biological modes of transmission are ''anterior station'' and ''posterior station''. In anterior station, transmission occurs via the bite of an infected organism (the vector), like in malaria, dengue fever, and bubonic plague. Posterior station is transmission via contact with infected feces. Examples are rickettsiae driven diseases (l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertical Transmission
Vertical transmission of symbionts is the transfer of a microbial symbiont from the parent directly to the offspring. Many metazoan species carry symbiotic bacteria which play a mutualistic, commensal, or parasitic role. A symbiont is acquired by a host via horizontal, vertical, or mixed transmission. Implications Complex interdependence occurs between host and symbiont. The genetic pool of the symbiont is generally smaller and more subject to genetic drift. In true vertical transmission, the evolutionary outcomes of the host and symbiont are linked. If there is mixed transmission, new genetic material may be introduced. Generally, symbionts settle into specific niches and can even transfer part of their genome into the host nucleus. Evolutionary consequences Benefits The mechanism promotes tightly coupled evolutionary pressure, which causes the host and symbiont to function as a holobiont. Disadvantages Evolutionary bottlenecks lead to less symbiont diversity, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)
_Lorryia_formosa_2_edit.jpg)
