|
Topical Anesthesia
A topical anesthetic is a local anesthetic that is used to numb the surface of a body part. They can be used to numb any area of the skin as well as the front of the eyeball, the inside of the nose, ear or throat, the anus and the genital area. Topical anesthetics are available in creams, ointments, aerosols, sprays, lotions, and jellies. Examples include benzocaine, butamben, dibucaine, lidocaine, oxybuprocaine, pramoxine, proxymetacaine (proparacaine), and tetracaine (also named amethocaine). Usage Topical anesthetics are used to relieve pain and itching caused by conditions such as sunburn or other minor burns, insect bites or stings, poison ivy, poison oak, poison sumac, and minor cuts and scratches. Topical anesthetics are used in ophthalmology and optometry to numb the surface of the eye (the outermost layers of the cornea and conjunctiva) to: * Perform a contact/applanation tonometry. * Perform a Schirmer's test (The Schirmer's test is sometimes used with a topical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Local Anesthetic
A local anesthetic (LA) is a medication that causes absence of pain sensation. In the context of surgery, a local anesthetic creates an absence of pain in a specific location of the body without a loss of consciousness, as opposed to a general anesthetic. When it is used on specific nerve pathways (local anesthetic nerve block), paralysis (loss of muscle power) also can be achieved. Examples Short Duration & Low Potency Procaine Chloroprocaine Medium Duration & Potency Lidocaine Prilocaine High Duration & Potency Tetracaine Bupivacaine Cinchocaine Ropivacaine Clinical LAs belong to one of two classes: aminoamide and aminoester local anesthetics. Synthetic LAs are structurally related to cocaine. They differ from cocaine mainly in that they have a very low abuse potential and do not produce hypertension or (with few exceptions) vasoconstriction. They are used in various techniques of local anesthesia such as: * Topical anesthetic, Topical anesthesia (surface) * Topi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
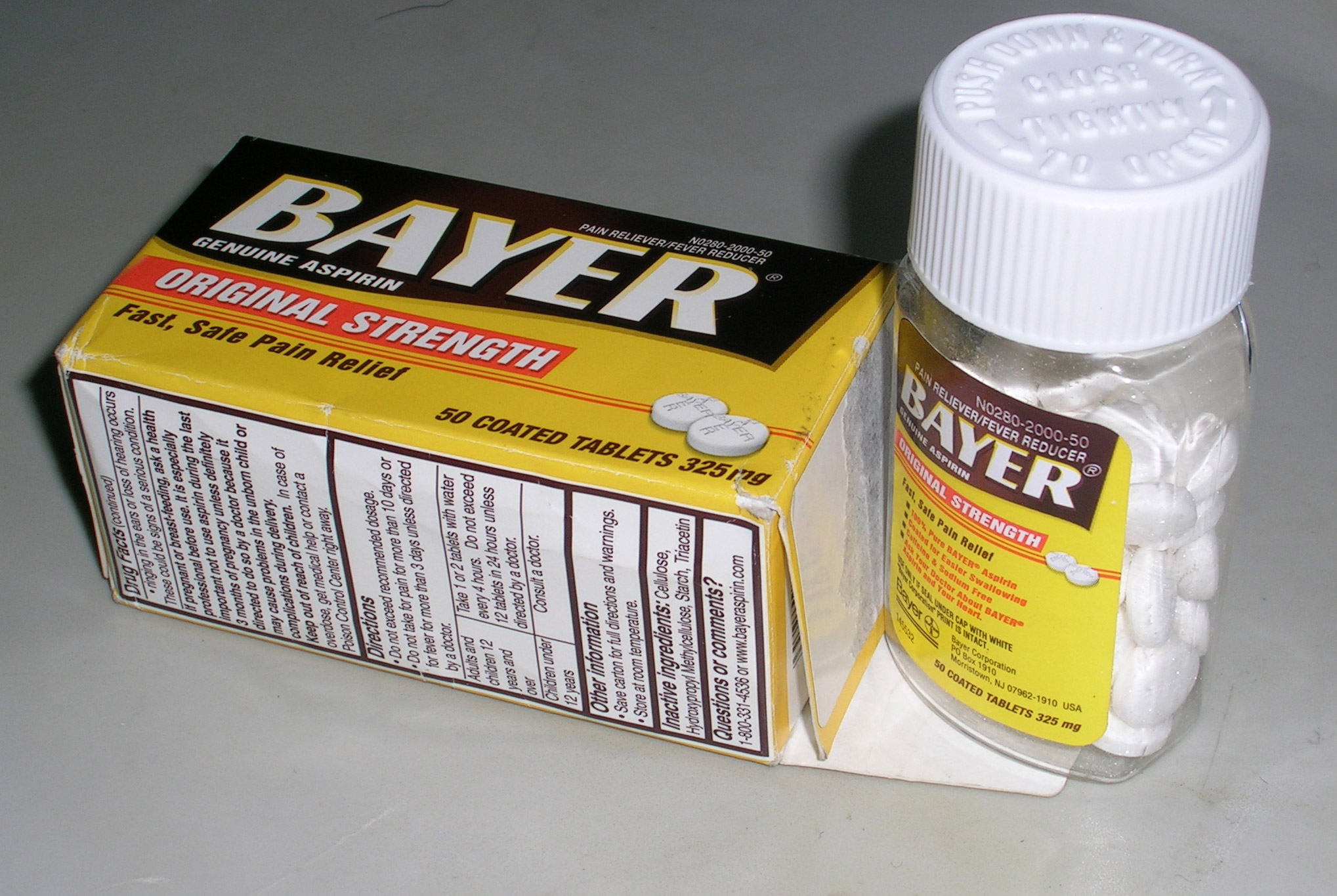
Over-the-counter Drug
Over-the-counter (OTC) drugs are medicines sold directly to a consumer without a requirement for a prescription from a healthcare professional, as opposed to prescription drugs, which may be supplied only to consumers possessing a valid prescription. In many countries, OTC drugs are selected by a regulatory agency to ensure that they contain ingredients that are safe and effective when used without a physician's care. OTC drugs are usually regulated according to their active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) rather than final products. By regulating APIs instead of specific drug formulations, governments allow manufacturers the freedom to formulate ingredients, or combinations of ingredients, into proprietary mixtures. The term ''over-the-counter'' (''OTC'') refers to a medication that can be purchased without a medical prescription. In contrast, prescription drugs require a prescription from a doctor or other health care professional and should only be used by the prescri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otolaryngology
Otorhinolaryngology ( , abbreviated ORL and also known as otolaryngology, otolaryngology–head and neck surgery (ORL–H&N or OHNS), or ear, nose, and throat (ENT)) is a surgical subspeciality within medicine that deals with the surgical and medical management of conditions of the head and neck. Doctors who specialize in this area are called otorhinolaryngologists, otolaryngologists, head and neck surgeons, or ENT surgeons or physicians. Patients seek treatment from an otorhinolaryngologist for diseases of the ear, nose, throat, base of the skull, head, and neck. These commonly include functional diseases that affect the senses and activities of eating, drinking, speaking, breathing, swallowing, and hearing. In addition, ENT surgery encompasses the surgical management of cancers and benign tumors and reconstruction of the head and neck as well as plastic surgery of the face and neck. Etymology The term is a combination of New Latin combining forms ('' oto-'' + '' rhino-'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dentistry
Dentistry, also known as dental medicine and oral medicine, is the branch of medicine focused on the teeth, gums, and mouth. It consists of the study, diagnosis, prevention, management, and treatment of diseases, disorders, and conditions of the mouth, most commonly focused on dentition (the development and arrangement of teeth) as well as the oral mucosa. Dentistry may also encompass other aspects of the craniofacial complex including the temporomandibular joint. The practitioner is called a dentist. The history of dentistry is almost as ancient as the history of humanity and civilization with the earliest evidence dating from 7000 BC to 5500 BC. Dentistry is thought to have been the first specialization in medicine which have gone on to develop its own accredited degree with its own specializations. Dentistry is often also understood to subsume the now largely defunct medical specialty of stomatology (the study of the mouth and its disorders and diseases) for which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Topical
A topical medication is a medication that is applied to a particular place on or in the body. Most often topical medication means application to body surfaces such as the skin or mucous membranes to treat ailments via a large range of classes including creams, foams, gels, lotions, and ointments. Many topical medications are epicutaneous, meaning that they are applied directly to the skin. Topical medications may also be inhalational, such as asthma medications, or applied to the surface of tissues other than the skin, such as eye drops applied to the conjunctiva, or ear drops placed in the ear, or medications applied to the surface of a tooth. The word ''topical'' derives from Greek τοπικός ''topikos'', "of a place". Justification Topical drug delivery is a route of administering drugs via the skin to provide topical therapeutic effects. As skin is one of the largest and most superficial organs in the human body, pharmacists utilise it to deliver vari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schirmer's Test
Schirmer's test determines whether the eye produces enough tears to keep it moist. This test is used when a person experiences very dry eyes or excessive watering of the eyes. It poses no risk to the subject. A negative (more than 10 mm of moisture on the filter paper in 5 minutes) test result is normal. Both eyes normally secrete the same amount of tears. It is named for Otto Schirmer. Test procedure The test works by the principle of capillary action, which allows the water in tears to travel along the length of a paper test strip in an identical fashion as a horizontal capillary tube. The rate of travel along the test strip is proportional to the rate of tear production. The patient is instructed to look upward, and the patient’s eyelid is pulled down. The bent end of the test strip is placed in the eye such that it rests between the palpebral conjunctiva of the lower eyelid and the bulbar conjunctiva of the eye. Schirmer's test uses paper strips inserted into the eye fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tonometry
Tonometry is the procedure eye care professionals perform to determine the intraocular pressure (IOP), the fluid pressure inside the eye. It is an important test in the evaluation of patients at risk from glaucoma. Most tonometers are calibrated to measure pressure in millimeters of mercury ( mmHg), with the normal eye pressure range between . Methods Applanation tonometry In applanation tonometry the intraocular pressure (IOP) is inferred from the force required to flatten (applanate) a constant area of the cornea, for the Imbert-Fick law. The Maklakoff tonometer was an early example of this method, while the Goldmann tonometer is the most widely used version in current practice. Because the probe makes contact with the cornea, a topical anesthetic, such as proxymetacaine, is introduced on to the surface of the eye in the form of an eye drop. Goldmann tonometry Goldmann tonometry is considered to be the gold standard IOP test and is the most widely accepted method. A spe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conjunctiva
The conjunctiva is a thin mucous membrane that lines the inside of the eyelids and covers the sclera (the white of the eye). It is composed of non-keratinized, stratified squamous epithelium with goblet cells, stratified columnar epithelium and stratified cuboidal epithelium (depending on the zone). The conjunctiva is highly vascularised, with many microvessels easily accessible for imaging studies. Structure The conjunctiva is typically divided into three parts: Blood supply Blood to the bulbar conjunctiva is primarily derived from the ophthalmic artery. The blood supply to the palpebral conjunctiva (the eyelid) is derived from the external carotid artery. However, the circulations of the bulbar conjunctiva and palpebral conjunctiva are linked, so both bulbar conjunctival and palpebral conjunctival vessels are supplied by both the ophthalmic artery and the external carotid artery, to varying extents. Nerve supply Sensory innervation of the conjunctiva is divided i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cornea
The cornea is the transparent front part of the eye that covers the iris, pupil, and anterior chamber. Along with the anterior chamber and lens, the cornea refracts light, accounting for approximately two-thirds of the eye's total optical power. In humans, the refractive power of the cornea is approximately 43 dioptres. The cornea can be reshaped by surgical procedures such as LASIK. While the cornea contributes most of the eye's focusing power, its focus is fixed. Accommodation (the refocusing of light to better view near objects) is accomplished by changing the geometry of the lens. Medical terms related to the cornea often start with the prefix "'' kerat-''" from the Greek word κέρας, ''horn''. Structure The cornea has unmyelinated nerve endings sensitive to touch, temperature and chemicals; a touch of the cornea causes an involuntary reflex to close the eyelid. Because transparency is of prime importance, the healthy cornea does not have or need blood vess ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Eye
The human eye is a sensory organ, part of the sensory nervous system, that reacts to visible light and allows humans to use visual information for various purposes including seeing things, keeping balance, and maintaining circadian rhythm. The eye can be considered as a living optical device. It is approximately spherical in shape, with its outer layers, such as the outermost, white part of the eye (the sclera) and one of its inner layers (the pigmented choroid) keeping the eye essentially light tight except on the eye's optic axis. In order, along the optic axis, the optical components consist of a first lens (the cornea—the clear part of the eye) that accomplishes most of the focussing of light from the outside world; then an aperture (the pupil) in a diaphragm (the iris—the coloured part of the eye) that controls the amount of light entering the interior of the eye; then another lens (the crystalline lens) that accomplishes the remaining focussing of light in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optometry
Optometry is a specialized health care profession that involves examining the eyes and related structures for defects or abnormalities. Optometrists are health care professionals who typically provide comprehensive primary eye care. In the United States and Canada, optometrists are those that hold a Doctor of Optometry degree. They are trained and licensed to practice medicine for eye related conditions, in addition to providing refractive (optical) eye care. In the United Kingdom, optometrists may also practice medicine (and provide refractive care) for eye related conditions. The Doctor of Optometry title can also be used in the UK for those that hold the postgraduate O.D. degree. Within their scope of practice, optometrists are considered physicians and bill medical insurance(s) (example: Medicare) accordingly. Moreover, many participate in academic research for eye related conditions and disease. Optometrists are the only health care professionals with a first professional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |