|
Tin(IV) Oxide
Tin(IV) oxide, also known as stannic oxide, is the inorganic compound with the formula SnO2. The mineral form of SnO2 is called cassiterite, and this is the main ore of tin. With many other names, this oxide of tin is an important material in tin chemistry. It is a colourless, diamagnetic, amphoteric solid. Structure Tin(IV) oxide crystallises with the rutile structure. As such the tin atoms are six coordinate and the oxygen atoms three coordinate. SnO2 is usually regarded as an oxygen-deficient n-type semiconductor. Hydrous forms of SnO2 have been described as stannic acid. Such materials appear to be hydrated particles of SnO2 where the composition reflects the particle size. Preparation Tin(IV) oxide occurs naturally. Synthetic tin(IV) oxide is produced by burning tin metal in air. Annual production is in the range of 10 kilotons. SnO2 is reduced industrially to the metal with carbon in a reverberatory furnace at 1200–1300 °C. Reactions The reaction from tin(IV) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cassiterite
Cassiterite is a tin oxide mineral, SnO2. It is generally opaque, but it is translucent in thin crystals. Its luster and multiple crystal faces produce a desirable gem. Cassiterite was the chief tin ore throughout ancient history and remains the most important source of tin today. Occurrence Most sources of cassiterite today are found in alluvial or placer deposits containing the weathering-resistant grains. The best sources of primary cassiterite are found in the tin mines of Bolivia, where it is found in crystallised hydrothermal veins. Rwanda has a nascent cassiterite mining industry. Fighting over cassiterite deposits (particularly in Walikale) is a major cause of the conflict waged in eastern parts of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. This has led to cassiterite being considered a conflict mineral. Cassiterite is a widespread minor constituent of igneous rocks. The Bolivian veins and the 4500 year old workings of Cornwall and Devon, England, are concentrate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
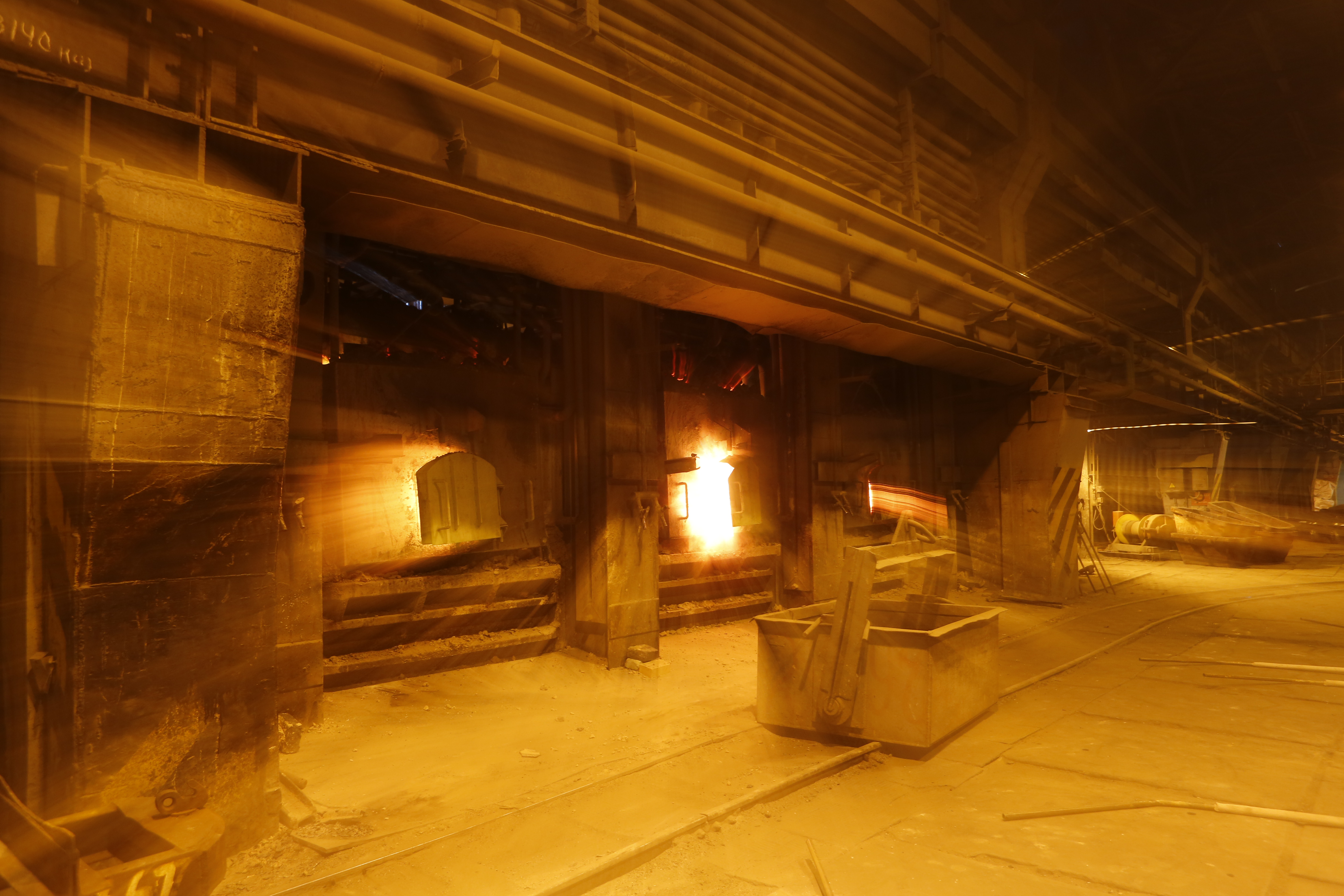
Reverberatory Furnace
A reverberatory furnace is a metallurgy, metallurgical or process Metallurgical furnace, furnace that isolates the material being processed from contact with the fuel, but not from contact with combustion gases. The term ''reverberation'' is used here in a generic sense of ''rebounding'' or ''Reflection (physics), reflecting'', not in the acoustics, acoustic sense of ''echoing''. Operation Chemistry determines the optimum relationship between the fuel and the material, among other variables. The reverberatory furnace can be contrasted on the one hand with the blast furnace, in which fuel and material are mixed in a single chamber, and, on the other hand, with crucible, Muffle furnace, muffling, or Retort, retort furnaces, in which the subject material is isolated from the fuel and all of the products of combustion including gases and flying ash. There are, however, a great many furnace designs, and the terminology of metallurgy has not been very consistently defined, so it is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tin-glazing
Tin-glazing is the process of giving tin-glazed pottery items a ceramic glaze that is white, glossy and opaque, which is normally applied to red or buff earthenware. Tin-glaze is plain lead glaze with a small amount of tin oxide added.Caiger-Smith, Alan, ''Tin-Glaze Pottery in Europe and the Islamic World: The Tradition of 1000 Years in Maiolica, Faience and Delftware'', London, Faber and Faber, 1973 The opacity and whiteness of tin glaze encourage its frequent decoration. Historically this has mostly been done before the single firing, when the colours blend into the glaze, but since the 17th century also using overglaze enamels, with a light second firing, allowing a wider range of colours. Majolica, maiolica, delftware and faience are among the terms used for common types of tin-glazed pottery. An alternative is lead-glazing, where the basic glaze is transparent; some types of pottery use both. However, when pieces are glazed only with lead, the glaze becomes fluid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earthenware
Earthenware is glazed or unglazed Vitrification#Ceramics, nonvitreous pottery that has normally been fired below . Basic earthenware, often called terracotta, absorbs liquids such as water. However, earthenware can be made impervious to liquids by coating it with a ceramic glaze, and such a process is used for the great majority of modern domestic earthenware. The main other important types of pottery are porcelain, bone china, and stoneware, all fired at high enough temperatures to vitrify. End applications include tableware and ceramic art, decorative ware such as figurines. Earthenware comprises "most building bricks, nearly all European pottery up to the seventeenth century, most of the wares of Egypt, Persia and the near East; Greek, Roman and Mediterranean, and some of the Chinese; and the fine earthenware which forms the greater part of our tableware today" ("today" being 1962).Dora Billington, ''The Technique of Pottery'', London: B.T.Batsford, 1962 Pit fired pottery, P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lead-tin-yellow
Lead-tin yellow is a yellow pigment, of historical importance in oil painting, sometimes called the "Yellow of the Old Masters" because of the frequency with which it was used by those famous painters. Nomenclature The name lead-tin yellow is a modern label. During the thirteenth to eighteenth centuries when it was in widest use, it was known by a variety of names. In Italy, it was ''giallorino'' or ''giallolino''. In other countries of Europe, it was massicot, (Spanish), (German), ''general'' (English) or (Portuguese). All of these names were often applied to other yellow pigments as well as lead-tin yellow. Composition Lead-tin yellow historically occurred in two varieties. The first and more common one, today known as "Type I", was a lead stannate, an oxide of lead and tin with the chemical formula Pb2SnO4. The second, "Type II", was a silicate with the formula .Hermann Kühn, 1967, "Blei-Zinn-Gelb und seine Verwendung in der Malerei", ''Farbe und Lack'' 73: 938-949 Le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antimony Pentoxide
Antimony pentoxide (molecular formula: Sb2O5) is a chemical compound of antimony and oxygen. It contains antimony in the +5 oxidation state. Structure Antimony pentoxide has the same structure as the ''B'' form of niobium pentoxide and can be derived from the rutile structure, with antimony coordinated by six oxygen atoms in a distorted octahedral arrangement. The SbO6 octahedra are corner- and edge-sharing. Preparation The hydrated oxide is prepared by hydrolysis of antimony pentachloride; or by acidification of potassium hexahydroxoantimonate(V). It may also be prepared by oxidation of antimony trioxide with nitric acid. Uses Antimony pentoxide finds use as a flame retardant in Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene, ABS and other plastics and as a clarifying agent, flocculant in the production of titanium dioxide, and is sometimes used in the production of glass, paint and adhesives. It is also used as an ion-exchange resin, ion exchange resin for a number of ion#Anions and cation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromium(III) Oxide
Chromium(III) oxide (or chromia) is an inorganic compound with the formula . It is one of the principal oxides of chromium and is used as a pigment. In nature, it occurs as the rare mineral eskolaite. Structure and properties has the corundum structure, consisting of a hexagonal close packed array of oxide anions with two thirds of the octahedral holes occupied by chromium. Similar to corundum, is a hard, brittle material (Mohs hardness 8 to 8.5). It is antiferromagnetic up to , the Néel temperature. It is not readily attacked by acids. Occurrence occurs naturally as the mineral eskolaite, which is found in chromium-rich tremolite skarns, metaquartzites, and chlorite veins. Eskolaite is also a rare component of chondrite meteorites. The mineral is named after Finnish geologist Pentti Eskola. Production The Parisians Pannetier and Binet first prepared the transparent hydrated form of in 1838 via a secret process, sold as a pigment. It is derived from the mineral chromi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vanadium(V) Oxide
Vanadium(V) oxide (''vanadia'') is the inorganic compound with the formula V2 O5. Commonly known as vanadium pentoxide, it is a dark yellow solid, although when freshly precipitated from aqueous solution, its colour is deep orange. Because of its high oxidation state, it is both an amphoteric oxide and an oxidizing agent. From the industrial perspective, it is the most important compound of vanadium, being the principal precursor to alloys of vanadium and is a widely used industrial catalyst. The mineral form of this compound, shcherbinaite, is extremely rare, almost always found among fumaroles. A mineral trihydrate, V2O5·3H2O, is also known under the name of navajoite. Chemical properties Reduction to lower oxides Upon heating a mixture of vanadium(V) oxide and vanadium(III) oxide, comproportionation occurs to give vanadium(IV) oxide, as a deep-blue solid: :V2O5 + V2O3 → 4 VO2 The reduction can also be effected by oxalic acid, carbon monoxide, and sulfur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ceramic Glaze
Ceramic glaze, or simply glaze, is a glassy coating on ceramics. It is used for decoration, to ensure the item is impermeable to liquids and to minimize the adherence of pollutants. Glazing renders earthenware impermeable to water, sealing the inherent porosity of earthenware. It also gives a tougher surface. Glaze is also used on stoneware and porcelain. In addition to their functionality, glazes can form a variety of surface finishes, including degrees of glossy or matte finish and color. Glazes may also enhance the underlying design or texture either unmodified or inscribed, carved or painted. Most pottery produced in recent centuries has been glazed, other than pieces in bisque porcelain, terracotta, and some other types. Tiles are often glazed on the surface face, and modern architectural terracotta is often glazed. Glazed brick is also common. Sanitaryware is invariably glazed, as are many ceramics used in industry, for example ceramic insulators for overhead power li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carboxylic Acid
In organic chemistry, a carboxylic acid is an organic acid that contains a carboxyl group () attached to an Substituent, R-group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is often written as or , sometimes as with R referring to an organyl group (e.g., alkyl, alkenyl, aryl), or hydrogen, or other groups. Carboxylic acids occur widely. Important examples include the amino acids and fatty acids. Deprotonation of a carboxylic acid gives a carboxylate anion. Examples and nomenclature Carboxylic acids are commonly identified by their trivial names. They often have the suffix ''-ic acid''. IUPAC-recommended names also exist; in this system, carboxylic acids have an ''-oic acid'' suffix. For example, butyric acid () is butanoic acid by IUPAC guidelines. For nomenclature of complex molecules containing a carboxylic acid, the carboxyl can be considered position one of the parent chain even if there are other substituents, such as 3-chloropropanoic acid. Alternately, it can be named ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium Stannate
Sodium stannate, formally sodium hexahydroxostannate(IV), is the inorganic compound with the formula Na2 n(OH)6 This colourless salt forms upon dissolving metallic tin or tin(IV) oxide in sodium hydroxide and is used as a stabiliser for hydrogen peroxide. In older literature, stannates are sometimes represented as having the simple oxyanion SnO32−, in which case this compound is sometimes named as sodium stannate–3–water and represented as Na2SnO3·3H2O, a hydrate with three waters of crystallisation. The anhydrous form of sodium stannate, Na2SnO3, is recognised as a distinct compound with its own CAS Registry Number, and a distinct material safety data sheet. Alkali metal stannate compounds are prepared by dissolving elemental tin in a suitable metal hydroxide, in the case of sodium stannate by the reaction: :Sn + 2 NaOH + 4 H2O → Na2 n(OH)6 + 2 H2 A similar reaction occurs when tin dioxid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stannate
In chemistry, the term stannate or tinnate refers to compounds of tin (Sn). Stannic acid (Sn(OH)4), the formal precursor to stannates, does not exist and is actually a hydrate of SnO2. The term is also used in naming conventions as a suffix; for example the hexachlorostannate ion is . In materials science, two kinds of tin oxyanions are distinguished: *''orthostannates'' contain discrete units (e.g. K4SnO4) or have a spinel structure (e.g. Mg2SnO4) *''metastannates'' with a stoichiometry MIISnO3, MSnO3 which may contain polymeric anions or may be sometimes better described as mixed oxides These materials are semiconductors."Preparation, characterization and structure of metal stannates: a new family of photocatalysts for organic pollutants degradation." ''Handbook of Photocatalysts'' (2010), pp. 493–510. Nova Science Publishers, Inc., Hauppauge, NY Examples * Barium stannate, BaSnO3 (a metastannate) * Cobalt stannate, Co2SnO4, primary constituent of the pigment cerulean bl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |