|
Chromium(III) Oxide
Chromium(III) oxide (or chromia) is an inorganic compound with the formula . It is one of the principal oxides of chromium and is used as a pigment. In nature, it occurs as the rare mineral eskolaite. Structure and properties has the corundum structure, consisting of a hexagonal close packed array of oxide anions with two thirds of the octahedral holes occupied by chromium. Similar to corundum, is a hard, brittle material (Mohs hardness 8 to 8.5). It is antiferromagnetic up to , the Néel temperature. It is not readily attacked by acids. Occurrence occurs naturally as the mineral eskolaite, which is found in chromium-rich tremolite skarns, metaquartzites, and chlorite veins. Eskolaite is also a rare component of chondrite meteorites. The mineral is named after Finnish geologist Pentti Eskola. Production The Parisians Pannetier and Binet first prepared the transparent hydrated form of in 1838 via a secret process, sold as a pigment. It is derived from the mineral chromi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eskolaite
Eskolaite is a rare chromium oxide mineral (chromium(III) oxide Cr2O3). Discovery and occurrence It was first described in 1958 for an occurrence in the Outokumpu, Finland, Outokumpu ore deposit of eastern Finland. It occurs in chromium bearing tremolite skarns, metamorphosed quartzites and Chlorite group, chlorite bearing Vein (geology), veins in Finland; in Glacier, glacial boulder clays in Ireland and in stream pebbles in the Merume River of Guyana. It has also been recognized as a rare component in chondrite meteorites. The mineral is named after the Finnish geologist Pentti Eskola (1883–1964). Structure and physical properties Eskolaite crystallizes with trigonal symmetry in the List of space groups, space group ''R'c'' and has the lattice parameters a = 4.95 Å and c = 13.58 Å at standard conditions. The unit cell contains six formula units. The lattice is analogous to that of corundum, with Cr3+ replacing Al3+. See also * List of minerals named after people Reference ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pentti Eskola
Pentti Elias Eskola (8 January 1883 – 6 December 1964) was a Finland, Finnish geologist who specialised in the petrology of granites and developed the concept of metamorphic facies. He won the Wollaston Medal in 1958, the Vetlesen Prize in 1964, and was given a state funeral upon his death. The mineral eskolaite is named in his honor. Eskola was born in Lellainen, the son of a farmer. He graduated from the University of Helsinki in 1906 and received a doctorate in 1914 with a dissertation on the petrology of the Orijärvi Region. Eskola was a student of Wilhelm Ramsay. He visited Norway and the US in 1920–21 working at the Geophysical Laboratory in Washington, D.C., and with the Geological Survey of Canada during which time he examined eclogites. He became a geologist for the Finnish Survey in 1922 and joined as a professor of geology at Helsinki in 1924 working there until 1954. Eskola's major work on metamorphism was influenced by the work of Jakob Sederholm, J.J. Sederho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
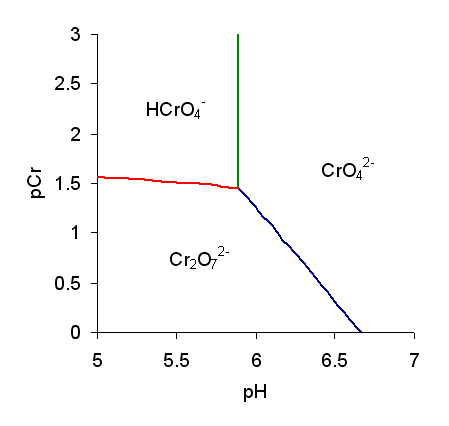
Chromate And Dichromate
Chromate salts contain the chromate anion, . Dichromate salts contain the dichromate anion, . They are oxyanions of chromium in the +6 oxidation state and are moderately strong oxidizing agents. In an aqueous solution, chromate and dichromate ions can be interconvertible. Chemical properties Potassium-chromate-sample.jpg, Potassium chromate Potassium-dichromate-sample.jpg, Potassium dichromate Chromates react with hydrogen peroxide, giving products in which peroxide, , replaces one or more oxygen atoms. In acid solution the unstable blue peroxo complex Chromium(VI) oxide peroxide, , is formed; it is an uncharged covalent molecule, which may be extracted into ether. Addition of pyridine results in the formation of the more stable complex . Acid–base properties In aqueous solution, chromate and dichromate anions exist in a chemical equilibrium. : The predominance diagram shows that the position of the equilibrium depends on both pH and the analytical concentration o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Monoxide
Carbon monoxide (chemical formula CO) is a poisonous, flammable gas that is colorless, odorless, tasteless, and slightly less dense than air. Carbon monoxide consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom connected by a triple bond. It is the simplest oxocarbon, carbon oxide. In coordination complexes, the carbon monoxide ligand is called ''metal carbonyl, carbonyl''. It is a key ingredient in many processes in industrial chemistry. The most common source of carbon monoxide is the partial combustion of carbon-containing compounds. Numerous environmental and biological sources generate carbon monoxide. In industry, carbon monoxide is important in the production of many compounds, including drugs, fragrances, and fuels. Indoors CO is one of the most acutely toxic contaminants affecting indoor air quality. CO may be emitted from tobacco smoke and generated from malfunctioning fuel-burning stoves (wood, kerosene, natural gas, propane) and fuel-burning heating systems (wood, oil, n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromium(III) Chloride
Chromium(III) chloride (also called chromic chloride) is an inorganic chemical compound with the chemical formula . This crystalline salt forms several hydrates with the formula , among which are hydrates where ''n'' can be 5 (chromium(III) chloride pentahydrate ) or 6 (chromium(III) chloride hexahydrate ). The anhydrous compound with the formula are violet crystals, while the most common form of the chromium(III) chloride are the dark green crystals of hexahydrate, . Chromium chlorides find use as catalysts and as precursors to dyes for wool. Structure Anhydrous chromium(III) chloride adopts the structure, with occupying one third of the octahedral interstices in alternating layers of a pseudo- cubic close packed lattice of ions. The absence of cations in alternate layers leads to weak bonding between adjacent layers. For this reason, crystals of cleave easily along the planes between layers, which results in the flaky (micaceous) appearance of samples of chromium(III) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlorine
Chlorine is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Cl and atomic number 17. The second-lightest of the halogens, it appears between fluorine and bromine in the periodic table and its properties are mostly intermediate between them. Chlorine is a yellow-green gas at room temperature. It is an extremely reactive element and a strong oxidizing agent, oxidising agent: among the elements, it has the highest electron affinity and the third-highest electronegativity on the revised Electronegativity#Pauling electronegativity, Pauling scale, behind only oxygen and fluorine. Chlorine played an important role in the experiments conducted by medieval Alchemy, alchemists, which commonly involved the heating of chloride Salt (chemistry), salts like ammonium chloride (sal ammoniac) and sodium chloride (common salt), producing various chemical substances containing chlorine such as hydrogen chloride, mercury(II) chloride (corrosive sublimate), and . However, the nature of fre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
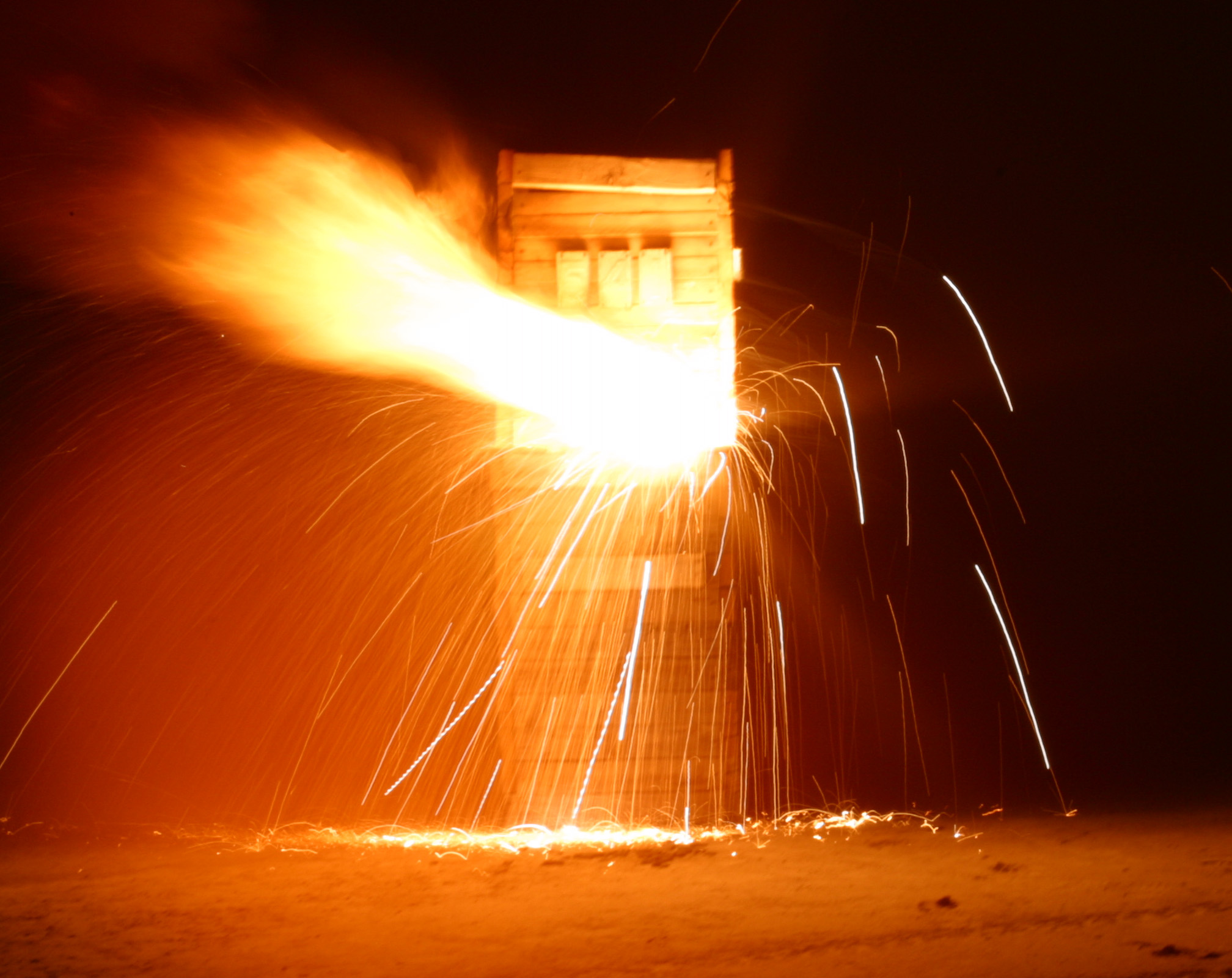
Thermite Reaction
Thermite () is a pyrotechnic composition of metal powder and metal oxide. When ignited by heat or chemical reaction, thermite undergoes an exothermic reduction-oxidation (redox) reaction. Most varieties are not explosive, but can create brief bursts of heat and high temperature in a small area. Its form of action is similar to that of other fuel-oxidizer mixtures, such as black powder. Thermites have diverse compositions. Fuels include aluminum, magnesium, titanium, zinc, silicon, and boron. Aluminum is common because of its high boiling point and low cost. Oxidizers include bismuth(III) oxide, boron(III) oxide, silicon(IV) oxide, chromium(III) oxide, manganese(IV) oxide, iron(III) oxide, iron(II,III) oxide, copper(II) oxide, and lead(II,IV) oxide. In a thermochemical survey comprising twenty-five metals and thirty-two metal oxides, 288 out of 800 binary combinations were characterized by adiabatic temperatures greater than 2000 K. Combinations like these, which possess th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphoteric
In chemistry, an amphoteric compound () is a molecule or ion that can react both as an acid and as a base. What exactly this can mean depends on which definitions of acids and bases are being used. Etymology and terminology Amphoteric is derived from the Greek word () meaning "both". Related words in acid-base chemistry are amphichromatic and amphichroic, both describing substances such as acid-base indicators which give one colour on reaction with an acid and another colour on reaction with a base. Amphiprotism Amphiprotism is exhibited by compounds with both Brønsted acidic and basic properties. A prime example is H2O. Amphiprotic molecules can either donate or accept a proton (). Amino acids (and proteins) are amphiprotic molecules because of their amine () and carboxylic acid () groups. Ampholytes Ampholytes are zwitterions ‒ molecules or ions that contain both acidic and basic functional groups. Amino acids have both a basic group and an acidic group . Of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Refractory
In materials science, a refractory (or refractory material) is a material that is resistant to decomposition by heat or chemical attack and that retains its strength and rigidity at high temperatures. They are inorganic, non-metallic compounds that may be porous or non-porous, and their crystallinity varies widely: they may be crystalline, polycrystalline, amorphous, or composite. They are typically composed of oxides, carbides or nitrides of the following elements: silicon, aluminium, magnesium, calcium, boron, chromium and zirconium. Many refractories are ceramics, but some such as graphite are not, and some ceramics such as clay pottery are not considered refractory. Refractories are distinguished from the '' refractory metals'', which are elemental metals and their alloys that have high melting temperatures. Refractories are defined by ASTM C71 as "non-metallic materials having those chemical and physical properties that make them applicable for structures, o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Razor Strop
A razor strop or simply a strop (sometimes called a razor strap or strap) is a flexible strip of leather, canvas, denim fabric, balsa wood, or other soft material, used to straighten and polish the blade of a straight razor, a knife, or a woodworking tool such as a chisel. In many cases stropping re-aligns parts of the blade edge that have been bent out of alignment. In other cases, especially when an abrasive polishing compound is used, stropping may remove a small amount of metal (functionally equivalent to lapping). Stropping can also burnish (i.e., push metal around on) the blade. The strop may be a hanging strop or a hand-held paddle. Various abrasive compounds may be applied to the strop to aid in polishing the blade while stropping to obtain a mirror-like finish. Common abrasive compounds include half-micron diamonds, green chromium(III) oxide, white rouge (aluminum oxide), and jeweller's rouge (iron(III) oxide). Use Stropping is traditionally associated with straig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromium(IV) Oxide
Chromium dioxide or chromium(IV) oxide is an inorganic compound with the formula CrO2. It is a black synthetic magnetic solid. It once was widely used in magnetic tape emulsion. With the increase in popularity of CDs and DVDs and more recently digital media, the use of chromium(IV) oxide has declined. However, it is still used in data tape applications for enterprise-class storage systems. It is still considered by many oxide and tape manufacturers to have been one of the best magnetic recording particulates ever invented. Preparation and basic properties CrO2 was first prepared by Friedrich Wöhler by decomposition of chromyl chloride. Acicular chromium dioxide was first synthesized in 1956 by Norman L. Cox, a chemist at E.I. DuPont, by decomposing chromium trioxide in the presence of water at a temperature of and a pressure of 200 MPa. The balanced equation for the hydrothermal synthesis is: :3 CrO3 + Cr2O3 → 5 CrO2 + O2 The magnetic crystal that forms is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viridian
Viridian is a blue-green pigment, a hydrated chromium(III) oxide, of medium saturation and relatively dark in value. It is composed of a majority of green, followed by blue. The first recorded use of ''viridian'' as a color name in English was in the 1860s. Viridian takes its name from the Latin , meaning "green". The pigment was first prepared in mid-19th-century Paris and remains available from several US manufacturers as prepared artists' colors in all media. History Viridian pigment was first prepared in 1838 in Paris by Parisian color chemist and painter Pannetier alongside his assistant Binet as a hydrated form of chromium oxide. The preparation process was demanding, expensive, and shrouded in secrecy. The French chemist C. E. Guignet developed and patented a cheaper manufacturing method in 1859 that enabled larger distribution and use of the pigment. This method involved calcining a combination of boric acid and potassium bichromate, then washing the material. Win ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |