|
The Story Of Mel
The Story of Mel is an archetypical piece of computer programming folklore. Its subject, Melvin Kaye, is an exemplary " Real Programmer" whose subtle techniques fascinate his colleagues. Story Ed Nather's ''The Story of Mel'' details the extraordinary programming prowess of a former colleague of his, "Mel", at Royal McBee Computer Corporation. Although originally written in prose, Nather's story was modified by someone into a "free verse" form which has become widespread. Little is known about Mel Kaye, beyond the fact that he was credited with doing the "bulk of the programming" on the 1959 ACT-1 compiler for the Royal McBee LGP-30 computer. In Nather's story, Kaye is portrayed as being prone to avoiding optimizing assemblers in favor of crafting code to take advantage of hardware quirks, for example taking advantage of the rotation of the LGP-30's drum memory to avoid writing delay loops into the code. The story, as written by Nather, involved Kaye's work on rewriting a bl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Programming
Computer programming or coding is the composition of sequences of instructions, called computer program, programs, that computers can follow to perform tasks. It involves designing and implementing algorithms, step-by-step specifications of procedures, by writing source code, code in one or more programming languages. Programmers typically use high-level programming languages that are more easily intelligible to humans than machine code, which is directly executed by the central processing unit. Proficient programming usually requires expertise in several different subjects, including knowledge of the Domain (software engineering), application domain, details of programming languages and generic code library (computing), libraries, specialized algorithms, and Logic#Formal logic, formal logic. Auxiliary tasks accompanying and related to programming include Requirements analysis, analyzing requirements, Software testing, testing, debugging (investigating and fixing problems), imple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integer Overflow
In computer programming, an integer overflow occurs when an arithmetic operation on integers attempts to create a numeric value that is outside of the range that can be represented with a given number of digits – either higher than the maximum or lower than the minimum representable value. The most common result of an overflow is that the least significant representable digits of the result are stored; the result is said to ''wrap'' around the maximum (i.e. modulo a power of the radix, usually two in modern computers, but sometimes ten or other number). On some processors like graphics processing units (GPUs) and digital signal processors (DSPs) which support saturation arithmetic, overflowed results would be ''clamped'', i.e. set to the minimum value in the representable range if the result is below the minimum and set to the maximum value in the representable range if the result is above the maximum, rather than wrapped around. An overflow condition may give results lead ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free On-line Dictionary Of Computing
The Free On-line Dictionary of Computing (FOLDOC) is an online, searchable, encyclopedic dictionary of computing subjects. History FOLDOC was founded in 1985 by Denis Howe and was hosted by Imperial College London. In May 2015, the site was updated to state that it was "no longer supported by Imperial College Department of Computing". Howe has served as the editor-in-chief since the dictionary's inception, with visitors to the website able to make suggestions for additions or corrections to articles. Open sourcing The dictionary incorporates the text of other free resources, such as the Jargon File, as well as covering many other computing-related topics. Due to its availability under the GNU Free Documentation License, a copyleft license, it has in turn been incorporated in whole or part into other free content projects, such as Wikipedia. Recognition * This site's brief 2001 review by a Ziff Davis Ziff Davis, Inc. is an American digital media and internet company. F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Real Programmers Don't Use Pascal
"Real Programmers Don't Use Pascal" (a parody of the bestselling 1982 tongue-in-cheek book on stereotypes about masculinity ''Real Men Don't Eat Quiche'') is an essay about computer programming written by Ed Post of Tektronix, Inc., and published in July 1983 as a reader's contribution in ''Datamation''.Volume 29 number 7 History Widely circulated on Usenet in its day, and well known in the computer software industry, the article compares and contrasts ''real programmers'', who use punch cards and write programs in FORTRAN or assembly language, with modern-day "quiche eaters" who use programming languages such as Pascal which support structured programming and impose restrictions meant to prevent or minimize common bugs due to inadvertent programming logic errors. Also mentioned are feats such as Seymour Cray, the inventor of the Cray-1 supercomputer, using manual control switches to load the first operating system for the CDC 7600 without notes. The next year Ed Nather’s ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Librascope
Librascope was a Glendale, California, division of General Precision, Inc. (GPI). It was founded in 1937 by Lewis W. Imm to build and operate theater equipment, and acquired by General Precision in 1941. During World War II it worked on improving aircraft load balancing. Later, Librascope became a manufacturer of early digital computers sold in both the business and defense markets. It hired Stan Frankel, a Manhattan Project veteran and early ENIAC programmer, to design the LGP-30 desk computer in 1956. In 1964 Librascope's Avionic Equipment Division at San Marcos has been shifted to the Aerospace Group, GPI as the West Coast facility of the Kearfott Division. Librascope was eventually purchased by Singer Corporation and moved into the manufacture of marine systems and land-based C3 (Command, Control, Communication) systems for the international defense industry. The company specialized in fire control systems for torpedoes, though they continued to work on a variety o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UUCP
UUCP (Unix-to-Unix Copy) is a suite of computer programs and communications protocol, protocols allowing remote execution of commands and transfer of computer file, files, email and netnews between computers. A command named is one of the programs in the suite; it provides a user interface for requesting file copy operations. The UUCP suite also includes (user interface for remote command execution), (the communication program that performs the file transfers), (reports statistics on recent activity), (execute commands sent from remote machines), and (reports the UUCP name of the local system). Some versions of the suite include uuencoding, / (convert 8-bit binary files to 7-bit text format and vice versa). Although UUCP was originally developed on Unix in the 1970s and 1980s, and is most closely associated with Unix-like systems, UUCP implementations exist for several non-Unix-like operating systems, including DOS, OS/2, OpenVMS (for VAX hardware only), AmigaOS, classic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
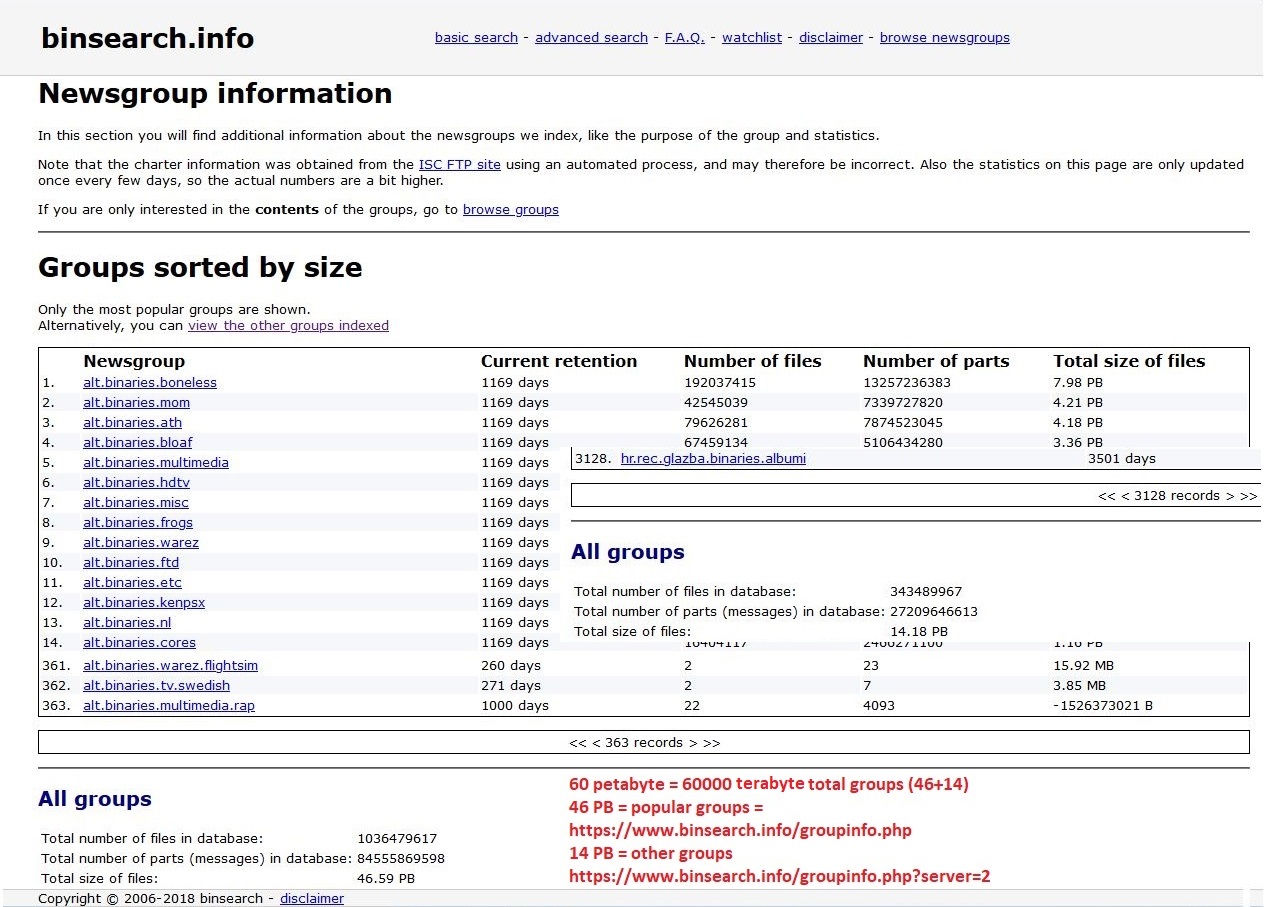
News Group
A Usenet newsgroup is a repository usually within the Usenet system for messages posted from users in different locations using the Internet. They are not only discussion groups or conversations, but also a repository to publish articles, start developing tasks like creating Linux, sustain mailing lists and file uploading. That’s thank to the protocol that poses no article size limit, but are to the providers to decide. In the late 1980s, Usenet articles were often limited by the providers to 60,000 characters, but in time, Usenet groups have been split into two types: ''text'' for mainly discussions, conversations, articles, limited by most providers to about 32,000 characters, and ''binary'' for file transfer, with providers setting limits ranging from less than 1 MB to about 4 MB. Newsgroups are technically distinct from, but functionally similar to, discussion forums on the World Wide Web. Newsreader software is used to read the content of newsgroups. Before the adoption ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Usenet
Usenet (), a portmanteau of User's Network, is a worldwide distributed discussion system available on computers. It was developed from the general-purpose UUCP, Unix-to-Unix Copy (UUCP) dial-up network architecture. Tom Truscott and Jim Ellis (computing), Jim Ellis conceived the idea in 1979, and it was established in 1980.''From Usenet to CoWebs: interacting with social information spaces'', Christopher Lueg, Danyel Fisher, Springer (2003), , Users read and post messages (called ''articles'' or ''posts'', and collectively termed ''news'') to one or more topic categories, known as Usenet newsgroup, newsgroups. Usenet resembles a bulletin board system (BBS) in many respects and is the precursor to the Internet forums that have become widely used. Discussions are Threaded discussion, threaded, as with web forums and BBSes, though posts are stored on the server sequentially. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IAS Machine
The IAS machine was the first electronic computer built at the Institute for Advanced Study (IAS) in Princeton, New Jersey. It is sometimes called the von Neumann machine, since the paper describing its design was edited by John von Neumann, a mathematics professor at both Princeton University and IAS. The computer was built under his direction, starting in 1946 and finished in 1951. The general organization is called von Neumann architecture, even though it was both conceived and implemented by others. The computer is in the collection of the Smithsonian National Museum of American History but is not currently on display. History Julian Bigelow was hired as chief engineer in May 1946. Ralph J. Slutz, Hewitt Crane, Herman Goldstine, Gerald Estrin, Arthur Burks, George W. Brown and Willis Ware also worked on the project. The machine was in limited operation in the summer of 1951 and fully operational on June 10, 1952. It was in operation until July 15, 1958. Descripti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opcode
In computing, an opcode (abbreviated from operation code) is an enumerated value that specifies the operation to be performed. Opcodes are employed in hardware devices such as arithmetic logic units (ALUs), central processing units (CPUs), and software instruction sets. In ALUs, the opcode is directly applied to circuitry via an input signal bus. In contrast, in CPUs, the opcode is the portion of a machine language instruction that specifies the operation to be performed. CPUs Opcodes are found in the machine language instructions of CPUs as well as in some abstract computing machines. In CPUs, an opcode may be referred to as an instruction machine code, instruction code, instruction syllable, instruction parcel, or opstring. For any particular processor (which may be a general CPU or a more specialized processing unit), the opcodes are defined by the processor's instruction set architecture (ISA). They can be described using an opcode table. The types of operations may in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Self-modifying Code
In computer science, self-modifying code (SMC or SMoC) is source code, code that alters its own instruction (computer science), instructions while it is execution (computing), executing – usually to reduce the instruction path length and improve computer performance, performance or simply to reduce otherwise duplicate code, repetitively similar code, thus simplifying software maintenance, maintenance. The term is usually only applied to code where the self-modification is intentional, not in situations where code accidentally modifies itself due to an error such as a buffer overflow. Self-modifying code can involve overwriting existing instructions or generating new code at run time and transferring control to that code. Self-modification can be used as an alternative to the method of "flag setting" and conditional program branching, used primarily to reduce the number of times a condition needs to be tested. The method is frequently used for conditionally invoking test/deb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |