|
Tetrahedrane
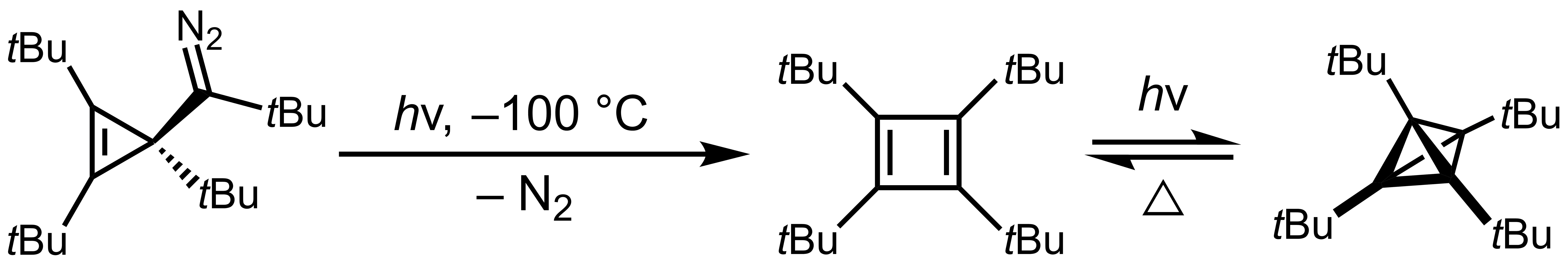
Tetrahedrane is a hypothetical platonic hydrocarbon with chemical formula and a tetrahedral structure. The molecule would be subject to considerable angle strain and has not been synthesized as of 2021. However, a number of derivatives have been prepared. In a more general sense, the term ''tetrahedranes'' is used to describe a class of molecules and ions with related structure, e.g. white phosphorus. Organic tetrahedranes In 1978, Günther Maier prepared tetra- ''tert''-butyl-tetrahedrane. These bulky substituents envelop the tetrahedrane core. Maier suggested that bonds in the core are prevented from breaking because this would force the substituents closer together (corset effect) resulting in Van der Waals strain. Tetrahedrane is one of the possible platonic hydrocarbons and has the IUPAC name tricyclo .1.0.02,4utane. Unsubstituted tetrahedrane () remains elusive, although it is predicted to be kinetically stable. One strategy that has been explored (but thus far failed) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrahedrane From Diazo
Tetrahedrane is a hypothetical platonic hydrocarbon with chemical formula and a tetrahedral structure. The molecule would be subject to considerable angle strain and has not been synthesized as of 2021. However, a number of derivatives have been prepared. In a more general sense, the term ''tetrahedranes'' is used to describe a class of molecules and ions with related structure, e.g. white phosphorus. Organic tetrahedranes In 1978, Günther Maier prepared tetra- ''tert''-butyl-tetrahedrane. These bulky substituents envelop the tetrahedrane core. Maier suggested that bonds in the core are prevented from breaking because this would force the substituents closer together (corset effect) resulting in Van der Waals strain. Tetrahedrane is one of the possible platonic hydrocarbons and has the IUPAC name tricyclo .1.0.02,4utane. Unsubstituted tetrahedrane () remains elusive, although it is predicted to be kinetically stable. One strategy that has been explored (but thus far fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Platonic Hydrocarbon
In organic chemistry, a Platonic hydrocarbon is a hydrocarbon (molecule) whose structure matches one of the five Platonic solids, with carbon atoms replacing its vertices, carbon–carbon bonds replacing its edges, and hydrogen atoms as needed. Not all Platonic solids have molecular hydrocarbon counterparts; those that do are the tetrahedron (tetrahedrane), the cube ( cubane), and the dodecahedron (dodecahedrane). Tetrahedrane Tetrahedrane (C4H4) is a hypothetical compound. It has not yet been synthesized without substituents, but it is predicted to be kinetically stable in spite of its angle strain. Some stable derivatives, including tetra( ''tert''-butyl)tetrahedrane (a hydrocarbon) and tetra(trimethylsilyl)tetrahedrane, have been produced. Cubane Cubane (C8H8) has been synthesized. Although it has high angle strain, cubane is kinetically stable, due to a lack of readily available decomposition paths. Octahedrane Angle strain would make an octahedron highly unstable due ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkyne
\ce \ce Acetylene \ce \ce \ce Propyne \ce \ce \ce \ce 1-Butyne In organic chemistry, an alkyne is an unsaturated hydrocarbon containing at least one carbon—carbon triple bond. The simplest acyclic alkynes with only one triple bond and no other functional groups form a homologous series with the general chemical formula . Alkynes are traditionally known as acetylenes, although the name ''acetylene'' also refers specifically to , known formally as ethyne using IUPAC nomenclature. Like other hydrocarbons, alkynes are generally hydrophobic. Structure and bonding In acetylene, the H–C≡C bond angles are 180°. By virtue of this bond angle, alkynes are rod-like. Correspondingly, cyclic alkynes are rare. Benzyne cannot be isolated. The C≡C bond distance of 121 picometers is much shorter than the C=C distance in alkenes (134 pm) or the C–C bond in alkanes (153 pm). : The triple bond is very strong with a bond strength of 839 kJ/mol. The sigma bond contri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
S-orbital
In atomic theory and quantum mechanics, an atomic orbital is a function describing the location and wave-like behavior of an electron in an atom. This function can be used to calculate the probability of finding any electron of an atom in any specific region around the atom's nucleus. The term ''atomic orbital'' may also refer to the physical region or space where the electron can be calculated to be present, as predicted by the particular mathematical form of the orbital. Each orbital in an atom is characterized by a set of values of the three quantum numbers , , and , which respectively correspond to the electron's energy, angular momentum, and an angular momentum vector component (magnetic quantum number). Alternative to the magnetic quantum number, the orbitals are often labeled by the associated harmonic polynomials (e.g., ''xy'', ). Each such orbital can be occupied by a maximum of two electrons, each with its own projection of spin m_s. The simple names s orbital, p orbit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
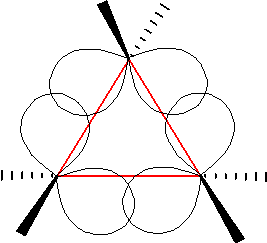
Banana Bond
In organic chemistry, a bent bond, also known as a banana bond, is a type of covalent chemical bond with a geometry somewhat reminiscent of a banana. The term itself is a general representation of electron density or configuration resembling a similar "bent" structure within small ring molecules, such as cyclopropane (C3H6) or as a representation of double or triple bonds within a compound that is an alternative to the sigma and pi bond model. Small cyclic molecules Bent bonds are a special type of chemical bonding in which the ordinary hybridization state of two atoms making up a chemical bond are modified with increased or decreased s-orbital character in order to accommodate a particular molecular geometry. Bent bonds are found in strained organic compounds such as cyclopropane, oxirane and aziridine. In these compounds, it is not possible for the carbon atoms to assume the 109.5° bond angles with standard sp3 hybridization. Increasing the p-character to sp5 (i.e. s-dens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Covalent Bond
A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electrons to form electron pairs between atoms. These electron pairs are known as shared pairs or bonding pairs. The stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atoms, when they share electrons, is known as covalent bonding. For many molecules, the sharing of electrons allows each atom to attain the equivalent of a full valence shell, corresponding to a stable electronic configuration. In organic chemistry, covalent bonding is much more common than ionic bonding. Covalent bonding also includes many kinds of interactions, including σ-bonding, π-bonding, metal-to-metal bonding, agostic interactions, bent bonds, three-center two-electron bonds and three-center four-electron bonds. The term ''covalent bond'' dates from 1939. The prefix ''co-'' means ''jointly, associated in action, partnered to a lesser degree, '' etc.; thus a "co-valent bond", in essence, means that the atoms share "valence" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tris(pentafluorophenyl)borane
Tris(pentafluorophenyl)borane, sometimes referred to as "BCF", is the chemical compound . It is a white, volatile solid. The molecule consists of three pentafluorophenyl groups attached in a "paddle-wheel" manner to a central boron atom; the core is planar. It has been described as the “ideal Lewis acid” because of its high thermal stability and the relative inertness of the B-C bonds. Related fluoro-substituted boron compounds, such as those containing groups, decompose with formation of B-F bonds. Tris(pentafluorophenyl)borane is thermally stable at temperatures well over 200 °C, resistant to oxygen, and water-tolerant. Preparation Tris(pentafluorophenyl)borane is prepared using a Grignard reagent derived from bromopentafluorobenzene: : The synthesis originally employed , but this reagent can detonate with elimination of . Structure The structure of tris(pentafluorophenyl)borane (BCF) was determined by gas electron diffraction. It has a propeller-like arrangement of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
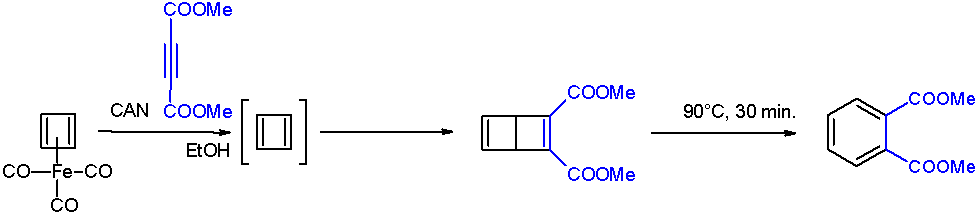
Cyclobutadiene
Cyclobutadiene is an organic compound with the formula . It is very reactive owing to its tendency to dimerize. Although the parent compound has not been isolated, some substituted derivatives are robust and a single molecule of cyclobutadiene is quite stable. Since the compound degrades by a bimolecular process, the species can be observed by matrix isolation techniques at temperatures below 35 K. It is thought to adopt a rectangular structure. Structure and reactivity The compound is the prototypical antiaromatic hydrocarbon with 4 π-electrons. It is the smallest 'n'' annulene ( annulene). Its rectangular structure is the result of the Jahn–Teller effect, which distorts the molecule and lowers its symmetry, converting the triplet to a singlet ground state. The electronic states of cyclobutadiene have been explored with a variety of computational methods. The rectangular structure is consistent with the existence of two different 1,2-dideutero-1,3-cyclobutadiene valence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Monoxide
Carbon monoxide ( chemical formula CO) is a colorless, poisonous, odorless, tasteless, flammable gas that is slightly less dense than air. Carbon monoxide consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom connected by a triple bond. It is the simplest molecule of the oxocarbon family. In coordination complexes the carbon monoxide ligand is called carbonyl. It is a key ingredient in many processes in industrial chemistry. The most common source of carbon monoxide is the partial combustion of carbon-containing compounds, when insufficient oxygen or heat is present to produce carbon dioxide. There are also numerous environmental and biological sources that generate and emit a significant amount of carbon monoxide. It is important in the production of many compounds, including drugs, fragrances, and fuels. Upon emission into the atmosphere, carbon monoxide affects several processes that contribute to climate change. Carbon monoxide has important biological roles across phylog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |