|
Temple Treasury
The temple treasury was a storehouse (Hebrew אוצר 'otsar) first of the tabernacle then of the Jerusalem Temples mentioned in the Hebrew Bible. The term "storehouse" is generic, and also occurs later in accounts of life in Roman Palestine where the ''otzar'' was a tax-collector's grainhouse. The first mention of the "treasury of the " occurs in Joshua 6:19 where all the silver and gold vessels are consecrated to a "storehouse" which travelled with the tabernacle. Later, this was made permanent in the First Temple, till the treasury was pillaged by Nebuchadnezzar's army. In the Second Temple, the treasury was used for storing the grain for the Levites. In Nehemiah and Zechariah, this became the subject of contention when Eliashib, grandson of Joshua the high priest, leased the storehouse to Tobiah the Ammonite. In the deutero-canonical , reference is made to "untold sums of money" held at the treasury in Jerusalem. A related term, the ''korbanas'', is found in the New Te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tabernacle
According to the Hebrew Bible, the tabernacle (), also known as the Tent of the Congregation (, also Tent of Meeting), was the portable earthly dwelling of God used by the Israelites from the Exodus until the conquest of Canaan. Moses was instructed at biblical Mount Sinai, Mount Sinai to construct and transport the tabernacle with the Israelites on their journey through the wilderness and their subsequent conquest of the Promised Land. After 440 years, Solomon's Temple in Jerusalem superseded it as the dwelling-place of God. The main source describing the tabernacle is the biblical Book of Exodus, specifically Exodus 25–31 and 35–40. Those passages describe an inner sanctuary, the Holy of Holies, created by the veil suspended by four pillars. This sanctuary contained the Ark of the Covenant, with its cherubim-covered mercy seat. An outer sanctuary (the "Holy Place") contained a gold lamp-stand or candlestick. On the north side stood a table, on which lay the showbread. On th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Judas Iscariot
Judas Iscariot (; ; died AD) was, according to Christianity's four canonical gospels, one of the original Twelve Apostles of Jesus Christ. Judas betrayed Jesus to the Sanhedrin in the Garden of Gethsemane, in exchange for thirty pieces of silver, by kiss of Judas, kissing him on the cheek and addressing him as "names and titles of Jesus in the New Testament#Master, master" to reveal his identity in the darkness to the crowd who had come to arrest him. In modern times, his name is often used synonymously with betrayal or treason. The Gospel of Mark gives no motive for Judas's betrayal but does present Jesus predicts his betrayal, Jesus predicting it at the Last Supper, an event also described in all the other gospels. The Gospel of Matthew states that Judas committed the betrayal in exchange for thirty pieces of silver. The Gospel of Luke and the Gospel of John suggest that he was Spirit possession, possessed by Satan. According to , after learning that Jesus Crucifixion of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
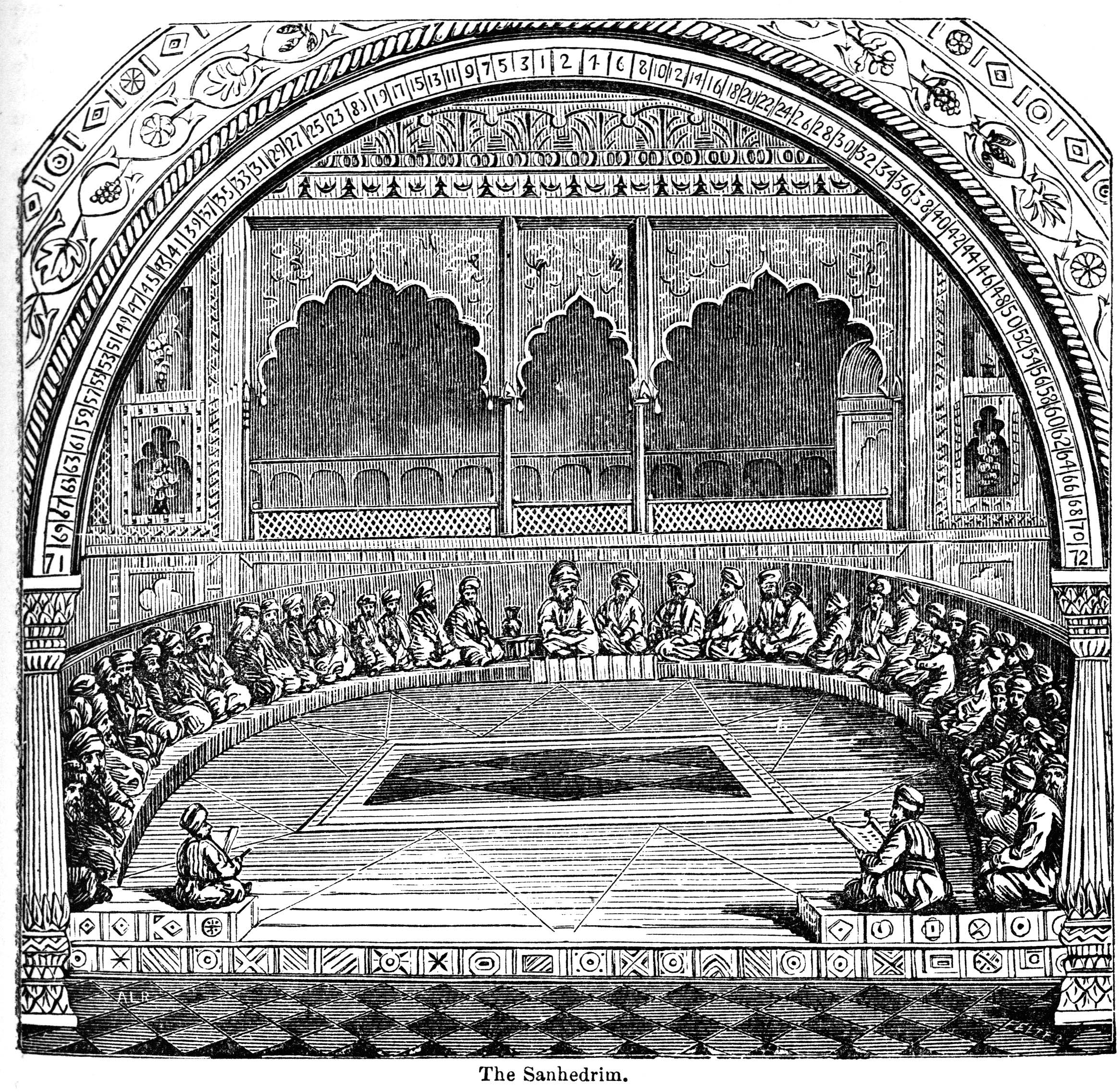
Sanhedrin
The Sanhedrin (Hebrew and Middle Aramaic , a loanword from , 'assembly,' 'sitting together,' hence ' assembly' or 'council') was a Jewish legislative and judicial assembly of either 23 or 70 elders, existing at both a local and central level in the ancient Land of Israel. There were two classes of Rabbinite courts called sanhedrins: Greater and Lesser. A lesser Sanhedrin of 23 judges was appointed to sit as a tribunal in each city. There was only one Great Sanhedrin of 70 judges, which, among other roles, acted as a supreme court, taking appeals from cases that lesser courts decided. In general usage, ''the Sanhedrin'' without qualifier usually refers to the Great Sanhedrin, which was presided over by the Nasi, who functioned as its head or representing president, and was a member of the court; the Av Beit Din or the chief of the court, who was second to the Nasi and 69 general members. In the Second Temple period, the Great Sanhedrin met in the Temple in Jerusalem, in a bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chanuyot
The temple shops or Hebrew plural ''hanuyot'' (חנויות) were buildings near the Temple in Jerusalem mentioned in the Babylonian Talmud (B.Shabbat 15a, B.Rosh Hashanah 31a; B.Avodah Zarah 8b). According to the Talmud the Sanhedrin relocated to the temple shops, ''hanuyot'', at some point before the destruction of the Temple in 70 CE. The plural ''hanuyot'' is also the word for "shops" in modern Hebrew. The hanuyot are to be distinguished from the temple treasury or grain storehouse (אוצר 'otsar) for the Temple in Jerusalem mentioned in the Hebrew Bible. The Talmud indicates that the hanuyot were where the Priests and Levites stored the accoutrements for the daily functioning of the Temple. The ''hanuyot'' consisted of a single room along the southern edge of the Mount, almost long and wide. Its single story was high. Mazar (1975) identifies the ''hanuyot'' with the Royal Stoa, a basilica erected by Herod the Great at the southern end of his expansion of the Temple Mount. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Jewish War
''The Jewish War'' is a work of Jewish history written by Josephus, a first-century Roman-Jewish historian. It has been described by the biblical historian Steve Mason as "perhaps the most influential non-biblical text of Western history". Content Divided into seven books, it opens with a summary of Jewish history from the capture of Jerusalem by the Seleucid emperor Antiochus IV Epiphanes in 168 BC to the first stages of the First Jewish–Roman War, books I and II. The next five books detail the unfolding of the war, under Roman generals Vespasian and Titus, to the death of the last Sicarii. The book was written about 75 AD, originally in Josephus' "paternal tongue" – either Aramaic or Hebrew – though this version has not survived. It was later translated into Greek, probably under the supervision of Josephus himself. Buth and Pierce wrote, "The current Greek edition does not appear to be a translation, but must be considered a new edition, a complete re-working of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pontius Pilate
Pontius Pilate (; ) was the Roman administration of Judaea (AD 6–135), fifth governor of the Judaea (Roman province), Roman province of Judaea, serving under Emperor Tiberius from 26/27 to 36/37 AD. He is best known for being the official who presided over Pilate's court, the trial of Jesus and ultimately ordered crucifixion of Jesus, his crucifixion. Pilate's importance in Christianity is underscored by his prominent place in both the Apostles' Creed, Apostles' and Nicene Creeds. Because the gospels portray Pilate as reluctant to execute Jesus, the Ethiopian Orthodox Tewahedo Church believes that Pilate became a Christian and venerates him as both a martyr and a saint, a belief which is historically shared by the Coptic Orthodox Church, Coptic Church, with a Calendar of saints, feast day on 19 or 25 June, respectively. Pontius Pilate is the best-attested figure to hold the position of Roman governor, though few sources about his rule have survived. Virtually nothing is known ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raymond E
Raymond is a male given name of Germanic origin. It was borrowed into English from French (older French spellings were Reimund and Raimund, whereas the modern English and French spellings are identical). It originated as the Germanic ᚱᚨᚷᛁᚾᛗᚢᚾᛞ (''Raginmund'') or ᚱᛖᚷᛁᚾᛗᚢᚾᛞ (''Reginmund''). ''Ragin'' ( Gothic) and ''regin'' ( Old German) meant "counsel". The Old High German ''mund'' originally meant "hand", but came to mean "protection". This etymology suggests that the name originated in the Early Middle Ages, possibly from Latin. Alternatively, the name can also be derived from Germanic Hraidmund, the first element being ''Hraid'', possibly meaning "fame" (compare ''Hrod'', found in names such as Robert, Roderick, Rudolph, Roland, Rodney and Roger) and ''mund'' meaning "protector". Despite the German and French origins of the English name, some of its early uses in English documents appear in Latinized form. As a surname, its first recorde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
War Of The Jews
''The Jewish War'' is a work of Jewish history written by Josephus, a first-century Roman-Jewish historian. It has been described by the biblical historian Steve Mason as "perhaps the most influential non-biblical text of Western history". Content Divided into seven books, it opens with a summary of Jewish history from the capture of Jerusalem by the Seleucid emperor Antiochus IV Epiphanes in 168 BC to the first stages of the First Jewish–Roman War, books I and II. The next five books detail the unfolding of the war, under Roman generals Vespasian and Titus, to the death of the last Sicarii. The book was written about 75 AD, originally in Josephus' "paternal tongue" – either Aramaic or Hebrew – though this version has not survived. It was later translated into Greek, probably under the supervision of Josephus himself. Buth and Pierce wrote, "The current Greek edition does not appear to be a translation, but must be considered a new edition, a complete re-working of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Josephus
Flavius Josephus (; , ; ), born Yosef ben Mattityahu (), was a Roman–Jewish historian and military leader. Best known for writing '' The Jewish War'', he was born in Jerusalem—then part of the Roman province of Judea—to a father of priestly descent and a mother who claimed Hasmonean royal ancestry. He initially fought against the Roman Empire during the First Jewish–Roman War as general of the Jewish forces in Galilee, until surrendering in AD 67 to the Roman army led by military commander Vespasian after the six-week siege of Yodfat. Josephus claimed the Jewish messianic prophecies that initiated the First Jewish–Roman War made reference to Vespasian becoming Roman emperor. In response, Vespasian decided to keep him as a slave and presumably interpreter. After Vespasian became emperor in AD 69, he granted Josephus his freedom, at which time Josephus assumed the Emperor's family name of '' Flavius''. Flavius Josephus fully defected to the Roman s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thirty Pieces Of Silver
Thirty pieces of silver was the price for which Judas Iscariot betrayed Jesus, according to an account in the Gospel of Matthew 26:15 in the New Testament. Before the Last Supper, Judas is said to have gone to the chief priests and agreed to hand over Jesus in exchange for 30 silver coins and to have attempted to return the money afterwards, filled with remorse. The Gospel of Matthew claims that the subsequent purchase of the potter's field was fulfilment by Jesus of a prophecy of Zechariah. The image has often been used in artwork depicting the Passion of Christ. The phrase is used in literature and common speech to refer to people "selling out", compromising a trust, friendship, or loyalty for personal gain. Biblical narrative According to the Gospel of Matthew, Judas Iscariot was a disciple of Jesus. Before the Last Supper, Judas went to the chief priests and agreed to hand over Jesus in exchange for 30 silver coins. Jesus was then arrested in Gethsemane, where Judas re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Testament
The New Testament (NT) is the second division of the Christian biblical canon. It discusses the teachings and person of Jesus in Christianity, Jesus, as well as events relating to Christianity in the 1st century, first-century Christianity. The New Testament's background, the first division of the Christian Bible, is called the Old Testament, which is based primarily upon the Hebrew Bible; together they are regarded as Sacred Scripture by Christians. The New Testament is a collection of 27 Christianity, Christian texts written in Koine Greek by various authors, forming the second major division of the Christian Bible. It includes four Gospel, gospels, the Acts of the Apostles, epistles attributed to Paul the Apostle, Paul and other authors, and the Book of Revelation. The Development of the New Testament canon, New Testament canon developed gradually over the first few centuries of Christianity through a complex process of debate, rejection of Heresy, heretical texts, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jerusalem Temple
The Temple in Jerusalem, or alternatively the Holy Temple (; , ), refers to the two religious structures that served as the central places of worship for Israelites and Jews on the modern-day Temple Mount in the Old City of Jerusalem. According to the Hebrew Bible, the First Temple was built in the 10th century BCE, during the reign of Solomon over the United Kingdom of Israel. It stood until , when it was destroyed during the Babylonian siege of Jerusalem. Almost a century later, the First Temple was replaced by the Second Temple, which was built after the Neo-Babylonian Empire was conquered by the Achaemenid Persian Empire. While the Second Temple stood for a longer period of time than the First Temple, it was likewise destroyed during the Roman siege of Jerusalem in 70 CE. Projects to build the hypothetical "Third Temple" have not come to fruition in the modern era, though the Temple in Jerusalem still features prominently in Judaism. As an object of longing and a sym ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |