|
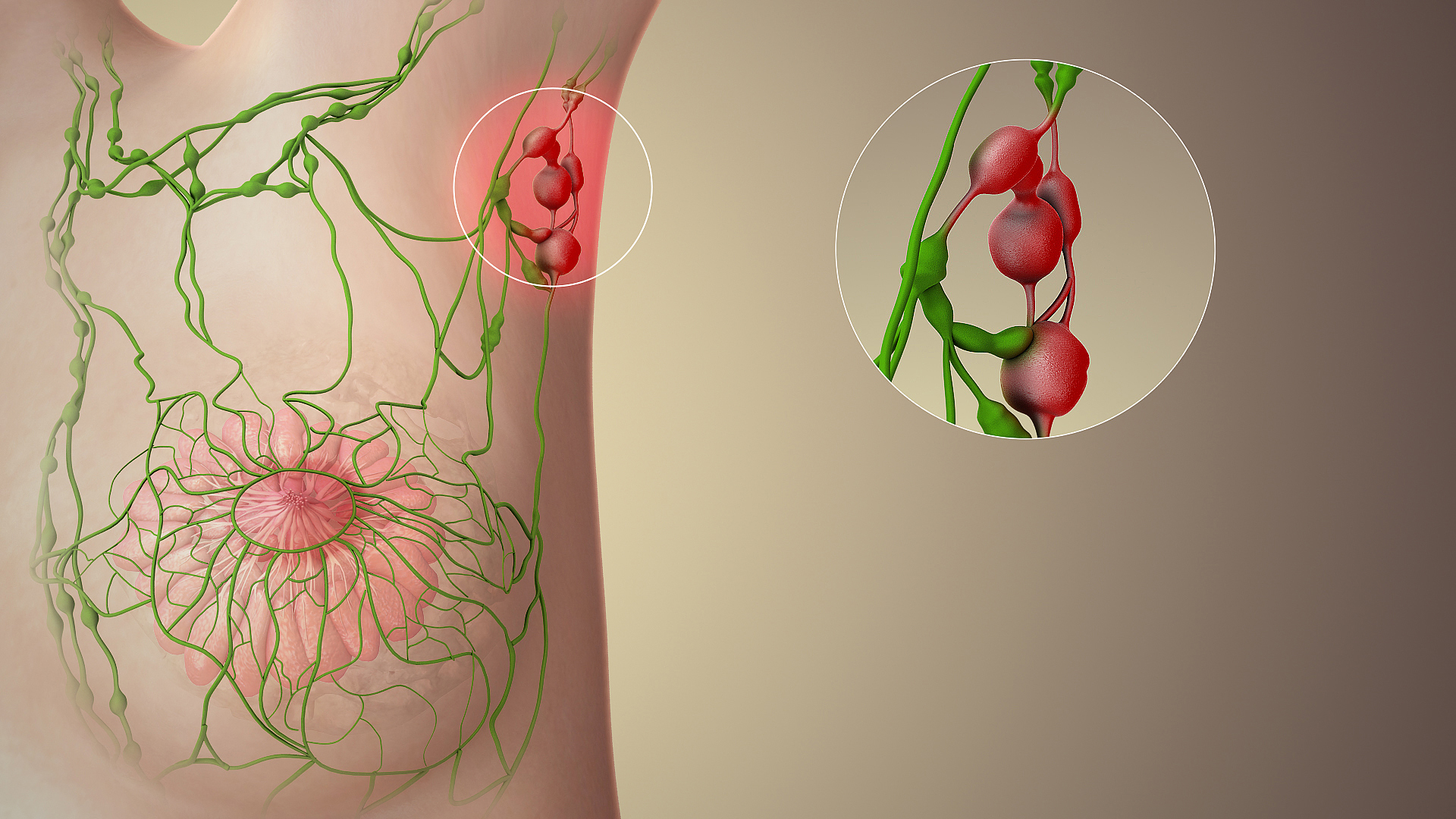
Superficial Inguinal Lymph Nodes
Inguinal lymph nodes are lymph nodes in the human groin. Located in the femoral triangle of the inguinal region, they are grouped into superficial and deep lymph nodes. The superficial have three divisions: the superomedial, superolateral, and inferior superficial. Superficial inguinal lymph nodes * The superficial inguinal lymph nodes are the inguinal lymph nodes that form a chain immediately below the inguinal ligament. They lie deep to the fascia of Camper that overlies the femoral vessels at the medial aspect of the thigh. They are bounded superiorly by the inguinal ligament in the femoral triangle; laterally by the border of the sartorius muscle, and medially by the adductor longus muscle. They are divided into three groups: * inferior – inferior of the saphenous opening of the leg, receive drainage from lower legs * superolateral – on the side of the saphenous opening, receive drainage from the side buttocks and the lower abdominal wall. * superomedial – located at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lymph Node
A lymph node, or lymph gland, is a kidney-shaped organ of the lymphatic system and the adaptive immune system. A large number of lymph nodes are linked throughout the body by the lymphatic vessels. They are major sites of lymphocytes that include B and T cells. Lymph nodes are important for the proper functioning of the immune system, acting as filters for foreign particles including cancer cells, but have no detoxification function. In the lymphatic system a lymph node is a secondary lymphoid organ. A lymph node is enclosed in a fibrous capsule and is made up of an outer cortex and an inner medulla. Lymph nodes become inflamed or enlarged in various diseases, which may range from trivial throat infections to life-threatening cancers. The condition of lymph nodes is very important in cancer staging, which decides the treatment to be used and determines the prognosis. Lymphadenopathy refers to glands that are enlarged or swollen. When inflamed or enlarged, lymph nodes can be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buttock
The buttocks (singular: buttock) are two rounded portions of the exterior anatomy of most mammals, located on the posterior of the pelvic region. In humans, the buttocks are located between the lower back and the perineum. They are composed of a layer of exterior skin and underlying subcutaneous fat superimposed on a left and right gluteus maximus and gluteus medius muscles. The two gluteus maximus muscles are the largest muscles in the human body. They are responsible for movements such as straightening the body into the upright (standing) posture when it is bent at the waist; maintaining the body in the upright posture by keeping the hip joints extended; and propelling the body forward via further leg (hip) extension when walking or running. In the seated position, the buttocks bear the weight of the upper body and take that weight off the feet. In many cultures, the buttocks play a role in sexual attraction. Many cultures have also used the buttocks as a primary target ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sentinel Lymph Node
The sentinel lymph node is the hypothetical first lymph node or group of nodes draining a cancer. In case of established cancerous dissemination it is postulated that the sentinel lymph nodes are the target organs primarily reached by metastasizing cancer cells from the tumor. The sentinel node procedure (also termed sentinel lymph node biopsy or SLNB) is the identification, removal and analysis of the sentinel lymph nodes of a particular tumour. Physiology The spread of some forms of cancer usually follows an orderly progression, spreading first to regional lymph nodes, then the next echelon of lymph nodes, and so on, since the flow of lymph is directional, meaning that some cancers spread in a predictable fashion from where the cancer started. In these cases, if the cancer spreads it will spread first to lymph nodes (lymph glands) close to the tumor before it spreads to other parts of the body. The concept of sentinel lymph node surgery is to determine if the cancer has sprea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
External Iliac Lymph Nodes
The external iliac lymph nodes are lymph nodes, from eight to ten in number, that lie along the external iliac vessels. They are arranged in three groups, one on the lateral, another on the medial, and a third on the anterior aspect of the vessels; the third group is, however, sometimes absent. Their principal afferents are derived from the inguinal lymph nodes, the deep lymphatics of the abdominal wall below the umbilicus and of the adductor region of the thigh, and the lymphatics from the glans penis, glans clitoridis, the membranous urethra, the prostate, the fundus of the urinary bladder, the cervix uteri, and upper part of the vagina. Additional images File:Lymph_node_regions.svg, Regional lymph tissue File:Gray611.png , The parietal lymph glands of the pelvis. File:Gray612.png , Iliopelvic glands (lateral view). File:Lymphatics of the prostate-Gray619.png , Lymphatics of the prostate. File:Gray621.png, Deep lymph nodes and vessels of the thorax and abdomen. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Christian Rosenmüller
Johann Christian Rosenmüller (May 25, 1771 – February 28, 1820) was a German anatomist born near Hildburghausen, Thuringia. He was the son of theologian Johann Georg Rosenmüller (1736-1815). He received his education at the Universities of Leipzig and Erlangen, and in 1794 was appointed prosector at the anatomical institute at Leipzig. In 1797 he earned his doctorate, and from 1802 until his death was a professor of anatomy and surgery at the University of Leipzig. An avid speleologist, in 1794 he provided the binomial name of '' Ursus spelaeus'' for the extinct cave bear from his analysis of bones found near the village of Muggendorf. He was the author of several treatises on anatomy and surgery, and has the following anatomical terms named after him: * Rosenmüller's fossa: The lateral nasopharyngeal recess. * Rosenmüller's gland: The palpebral portion of the lacrimal gland. * Rosenmüller's organ: Also known as the parovarium. Selected works * "Quaedam de ossibu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jules Germain Cloquet
Jules Germain Cloquet (18 December 1790 – 23 February 1883) was a French physician and surgeon who was born and practiced medicine in Paris. His older brother, Hippolyte Cloquet (1787-1840) and his younger nephew Ernest Cloquet (1818-1855) were also physicians. In 1821 Jules Cloquet became one of the earliest members elected to the Académie Nationale de Médecine in Paris. In 1836, he was elected Fellowship of the Royal College of Surgeons, Honorary Fellow of the Royal College of Surgeons in Ireland. Cloquet was known for his expertise as a surgeon, especially his work with hernial disorders. He was also the first to describe and identify the remnant of the embryonic hyaloid artery. This vestige was to become known as Cloquet's canal. Cloquet's name is associated with three anatomical terms regarding the femoral canal: * "Cloquet's hernia": a hernia of the femoral canal * "Cloquet's septum": a fibrous membrane bounding the femoral ring, annulus femoralis at the base of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cribriform Fascia
The cribriform fascia, fascia cribrosa also Hesselbach's fascia is the portion of fascia covering the saphenous opening in the thigh. It is perforated by the great saphenous vein and by numerous blood and lymphatic vessels. (A structure in anatomy that is pierced by several small holes is referred to as ''cribriform'' from Latin ''cribrum'' meaning sieve). Clinical significance The cribriform fascia has been proposed for use in preventing new vascularization when surgery is performed at the join between the great saphenous vein and the femoral vein. Eponym When the eponym is used, it is named for Franz Kaspar Hesselbach Franz Kaspar Hesselbach (27 January 1759 – 24 July 1816) was a German surgeon and anatomist who was a native of Hammelburg. He was a pupil, and later Prosector under Carl Caspar von Siebold (1736–1807) at Würzburg. Later Hesselbach was a lec ....F. K. Hesselbach. Anatomisch-chirurgische Abhandlung über den Urspurng der Leistenbrüche. Würzburg, Baumgärt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Femoral Vein
In the human body, the femoral vein is a blood vessel that accompanies the femoral artery in the femoral sheath. It begins at the adductor hiatus (an opening in the adductor magnus muscle) as the continuation of the popliteal vein. It ends at the inferior margin of the inguinal ligament where it becomes the external iliac vein. The femoral vein bears valves which are mostly bicuspid and whose number is variable between individuals and often between left and right leg. Structure Segments *The common femoral vein is the segment of the femoral vein between the branching point of the deep femoral vein and the inferior margin of the inguinal ligament.Page 590 in: *The subsartorial vein or superficial femoral vein are designations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pectinate Line
The pectinate line (dentate line) is a line which divides the upper two-thirds and lower third of the anal canal. Developmentally, this line represents the hindgut-proctodeum A proctodeum is the back ectodermal part of an alimentary canal. It is created during embryogenesis by a folding of the outer body wall. It will form the lower part of the anal canal The anal canal is the part that connects the rectum to the ... junction. It is an important anatomical landmark in humans, and several distinctions can be made based upon the location of a structure relative to this line: Additional images File:Rectoanal jxn.JPG, Microscopic cross section of the anorectal junction. File:Anorectum-en.svg , Anatomy of the anus and rectum File:Gray1078.png, Coronal section of rectum and anal canal. References External links * () {{Authority control Digestive system Anatomic Landmarks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anus
The anus (Latin, 'ring' or 'circle') is an opening at the opposite end of an animal's digestive tract from the mouth. Its function is to control the expulsion of feces, the residual semi-solid waste that remains after food digestion, which, depending on the type of animal, includes: matter which the animal cannot digest, such as bones; Summary at food material after the nutrients have been extracted, for example cellulose or lignin; ingested matter which would be toxic if it remained in the digestive tract; and dead or excess gut bacteria and other endosymbionts. Amphibians, reptiles, and birds use the same orifice (known as the cloaca) for excreting liquid and solid wastes, for copulation and egg-laying. Monotreme mammals also have a cloaca, which is thought to be a feature inherited from the earliest amniotes via the therapsids. Marsupials have a single orifice for excreting both solids and liquids and, in females, a separate vagina for reproduction. Female placental mamm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
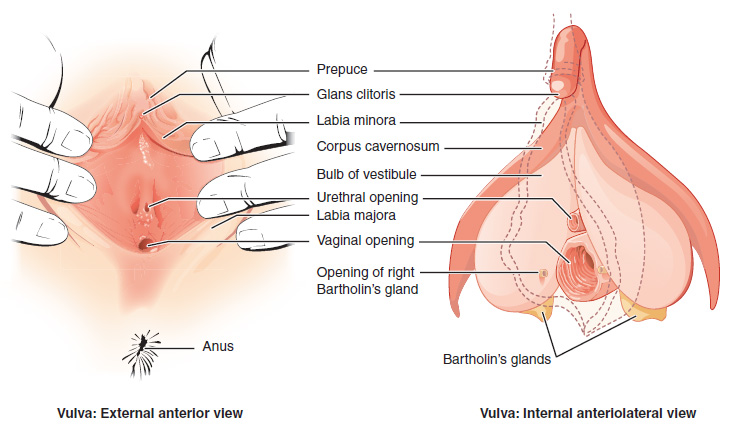
Vulva
The vulva (plural: vulvas or vulvae; derived from Latin for wrapper or covering) consists of the external sex organ, female sex organs. The vulva includes the mons pubis (or mons veneris), labia majora, labia minora, clitoris, bulb of vestibule, vestibular bulbs, vulval vestibule, urinary meatus, the Vagina#Vaginal opening and hymen, vaginal opening, hymen, and Bartholin's gland, Bartholin's and Skene's gland, Skene's vestibular glands. The urinary meatus is also included as it opens into the vulval vestibule. Other features of the vulva include the pudendal cleft, sebaceous glands, the urogenital triangle (anterior part of the perineum), and pubic hair. The vulva includes the entrance to the vagina, which leads to the uterus, and provides a double layer of protection for this by the folds of the outer and inner labia. Pelvic floor muscles support the structures of the vulva. Other muscles of the urogenital triangle also give support. Blood supply to the vulva comes from the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iliac Crest
The crest of the ilium (or iliac crest) is the superior border of the wing of ilium and the superiolateral margin of the greater pelvis. Structure The iliac crest stretches posteriorly from the anterior superior iliac spine (ASIS) to the posterior superior iliac spine (PSIS). Behind the ASIS, it divides into an outer and inner lip separated by the intermediate zone. The outer lip bulges laterally into the iliac tubercle. Platzer (2004), p 186 Palpable in its entire length, the crest is convex superiorly but is sinuously curved, being concave inward in front, concave outward behind. Palastanga (2006), p 243 It is thinner at the center than at the extremities. Development The iliac crest is derived from endochondral bone. Function To the external lip are attached the ''Tensor fasciae latae'', '' Obliquus externus abdominis'', and '' Latissimus dorsi'', and along its whole length the '' fascia lata''; to the intermediate line, the '' Obliquus internus abdominis''. To the inter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)