sentinel lymph node on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
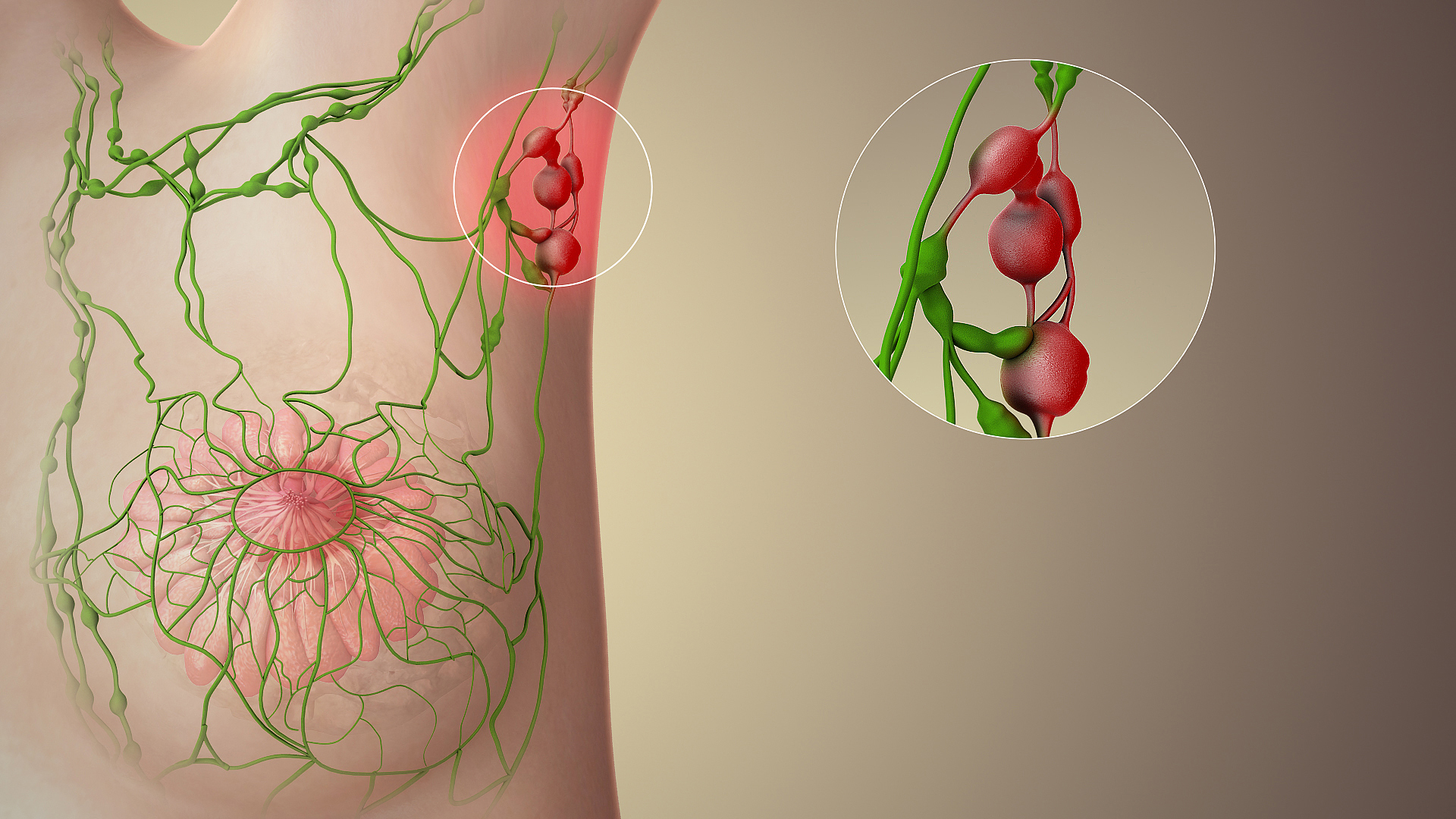 The sentinel lymph node is the hypothetical first
The sentinel lymph node is the hypothetical first
 The sentinel lymph node is the hypothetical first
The sentinel lymph node is the hypothetical first lymph node
A lymph node, or lymph gland, is a kidney-shaped organ of the lymphatic system and the adaptive immune system. A large number of lymph nodes are linked throughout the body by the lymphatic vessels. They are major sites of lymphocytes that includ ...
or group of nodes draining a cancer. In case of established cancerous dissemination it is postulated that the sentinel lymph nodes are the target organs primarily reached by metastasizing cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving Cell growth#Disorders, abnormal cell growth with the potential to Invasion (cancer), invade or Metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Po ...
cells from the tumor
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists ...
.
The sentinel node procedure (also termed sentinel lymph node biopsy or SLNB) is the identification, removal and analysis of the sentinel lymph nodes of a particular tumour.
Physiology
The spread of some forms of cancer usually follows an orderly progression, spreading first to regional lymph nodes, then the next echelon of lymph nodes, and so on, since the flow of lymph is directional, meaning that some cancers spread in a predictable fashion from where the cancer started. In these cases, if the cancer spreads it will spread first to lymph nodes (lymph glands) close to the tumor before it spreads to other parts of the body. The concept of sentinel lymph node surgery is to determine if the cancer has spread to the very first draining lymph node (called the "sentinel lymph node") or not. If the sentinel lymph node does not contain cancer, then there is a high likelihood that the cancer has not spread to any other area of the body.Uses
The concept of the sentinel lymph node is important because of the advent of the sentinel lymph node biopsy technique, also known as a sentinel node procedure. This technique is used in the staging of certain types of cancer to see if they have spread to any lymph nodes, since lymph node metastasis is one of the most important prognostic signs. It can also guide the surgeon to the appropriate therapy. There are various procedures entailing the sentinel node detection: * Preoperative planar lymphoscintigraphy * Preoperative planar lymphoscintigraphy in conjunction with SPECT/CT ingle photonemission CT (SPECT) with a low-dose CT* Intraoperative visual blue dye detection * Intraoperative fluorescence detection ( fluorescence image-guided surgery) * Intraoperativegamma probe
A gamma probe is a handheld device containing a scintillation counter for intraoperative use following Injection (medicine), injection of a radionuclide to locate sentinel lymph nodes by their radioactivity. It is used primarily for sentinel lymph ...
/Geiger meter-detection
*Preoperative or intraoperative super paramagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles injection, detection by using Sentimag instrument
* Postoperative scintigraphy of main specimen with planar acquisition
In everyday clinical activity, entailing sentinel node detection and sentinel lymph node biopsy
A biopsy is a medical test commonly performed by a surgeon, interventional radiologist, an interventional radiologist, or an interventional cardiology, interventional cardiologist. The process involves the extraction of sampling (medicine), sample ...
, it is not required to include all different techniques listed above. In skilled hands and in a center with sound routines, one, two or three of the listed methods can be considered sufficient.
To perform a sentinel lymph node biopsy, the physician performs a lymphoscintigraphy, wherein a low-activity radioactive substance is injected near the tumor. The injected substance, filtered sulfur colloid, is tagged with the radionuclide technetium-99m
Technetium-99m (99mTc) is a metastable nuclear isomer of technetium-99 (itself an isotope of technetium), symbolized as 99mTc, that is used in tens of millions of medical diagnostic procedures annually, making it the most commonly used Radiophar ...
. The injection protocols differ by doctor but the most common is a 500 μCi dose divided among 5 tuberculin syringes with 1/2 inch, 24 gauge needles. In the UK 20 megabecquerels of nanocolloid is recommended. The sulphur colloid is slightly acidic and causes minor stinging. A gentle massage of the injection sites spreads the sulphur colloid, relieving the pain and speeding up the lymph uptake. Scintigraphic imaging is usually started within 5 minutes of injection and the node appears from 5 min to 1 hour. This is usually done several hours before the actual biopsy. About 15 minutes before the biopsy the physician injects a blue dye in the same manner. Then, during the biopsy, the physician visually inspects the lymph nodes for staining and uses a gamma probe
A gamma probe is a handheld device containing a scintillation counter for intraoperative use following Injection (medicine), injection of a radionuclide to locate sentinel lymph nodes by their radioactivity. It is used primarily for sentinel lymph ...
or a Geiger counter to assess which lymph nodes have taken up the radionuclide. One or several nodes may take up the dye and radioactive tracer, and these nodes are designated the ''sentinel lymph nodes''. The surgeon then removes these lymph nodes and sends them to a pathologist for rapid examination under a microscope
A microscope () is a laboratory equipment, laboratory instrument used to examine objects that are too small to be seen by the naked eye. Microscopy is the science of investigating small objects and structures using a microscope. Microscopic ...
to look for the presence of cancer.
A frozen section procedure is commonly employed (which takes less than 20 minutes), so if neoplasia is detected in the lymph node a further lymph node dissection may be performed. With malignant melanoma, many pathologists eschew frozen sections for more accurate "permanent" specimen preparation due to the increased instances of false-negative with melanocytic staining.
Clinical advantages
There are various advantages to the sentinel node procedure. First and foremost, it decreases lymph node dissections where unnecessary, thereby reducing the risk of lymphedema, a common complication of this procedure. Increased attention on the node(s) identified to most likely contain metastasis is also more likely to detect micrometastasis and result in staging and treatment changes. Its main uses are inbreast cancer
Breast cancer is a cancer that develops from breast tissue. Signs of breast cancer may include a Breast lump, lump in the breast, a change in breast shape, dimpling of the skin, Milk-rejection sign, milk rejection, fluid coming from the nipp ...
and malignant melanoma surgery
Surgery is a medical specialty that uses manual and instrumental techniques to diagnose or treat pathological conditions (e.g., trauma, disease, injury, malignancy), to alter bodily functions (e.g., malabsorption created by bariatric surgery s ...
, although it has been used in other tumor types ( colon cancer) with a degree of success. Other cancers which have been investigated with this technique are penile cancer
Penile cancer, or penile carcinoma, is a cancer that develops in the skin or tissues of the penis. Symptoms may include abnormal growth, an ulcer or sore on the skin of the penis, and bleeding or foul smelling discharge.
Risk factors include phimo ...
, urinary bladder cancer
Bladder cancer is the abnormal growth of cells in the bladder. These cells can grow to form a tumor, which eventually spreads, damaging the bladder and other organs. Most people with bladder cancer are diagnosed after noticing blood in thei ...
, prostate cancer
Prostate cancer is the neoplasm, uncontrolled growth of cells in the prostate, a gland in the male reproductive system below the bladder. Abnormal growth of the prostate tissue is usually detected through Screening (medicine), screening tests, ...
, testicular cancer
Testicular cancer is cancer that develops in the testicles, a part of the male reproductive system. Symptoms may include a lump in the testicle or swelling or pain in the scrotum. Treatment may result in infertility.
Risk factors include an c ...
and renal cell cancer.
Research advantages
As a bridge to translational medicine, various aspects of cancer dissemination can be studied using sentinel node detection and ensuing sentinel node biopsy. Tumor biology pertaining to metastatic capacity, mechanisms of dissemination, the EMT-MET-process ( epithelial–mesenchymal transition) and cancer immunology are some subjects which can be more distinctly investigated.Disadvantages
However, the technique is not without drawbacks, particularly when used for melanoma patients. This technique only has therapeutic value in patients with positive nodes. Failure to detect cancer cells in the sentinel node can lead to a false negative result—there may still be cancerous cells in the lymph node basin. In addition, there is no compelling evidence that patients who have a full lymph node dissection as a result of a positive sentinel lymph node result have improved survival compared to those who do not have a full dissection until later in their disease, when the lymph nodes can be felt by a physician. Such patients may be having an unnecessary full dissection, with the attendant risk of lymphedema.History
The concept of a sentinel node was first described by Gould et al. 1960 in a patient with cancer of the parotid gland and was implemented clinically on a broad scale by Cabanas in penile cancer. The technique of sentinel node radiolocalization was co-founded by James C. Alex, MD, FACS and David N. Krag MD (University of Vermont Medical Center) and they were the first ones to pioneer this method for the use of cutaneous melanoma, breast cancer, head and neck cancer and Merkel cell carcinoma. Confirmative trials followed soon after. Studies were also conducted at the Moffitt Cancer Center with Charles Cox, MD, Cristina Wofter, MD, Douglas Reintgen, MD and James Norman, MD. Following validation of the sentinel node biopsy technique, a number of randomised controlled trials were initiated to establish whether the technique could safely be used to avoid unnecessary axillary dissection among women with early breast cancer. The first such trial, led byUmberto Veronesi
Umberto Veronesi (; 28 November 1925 – 8 November 2016) was an Italian oncologist, physician, scientist, and politician, internationally known for his contributions on prevention and treatment of breast cancer throughout a career spanning ove ...
at the European Institute of Oncology, showed that women with breast tumours of 2 cm or less could safely forgo axillary dissection if their sentinel lymph nodes were found to be cancer-free on biopsy. The benefits included less pain, greater arm mobility and less swelling in the arm.Veronesi, Umberto et al. (2003) A Randomized Comparison of Sentinel-Node Biopsy with Routine Axillary Dissection in Breast Cancer. ''N Engl J Med'' 349:546-553 DOI:10.1056/NEJMoa012782
See also
*ALMANAC
An almanac (also spelled almanack and almanach) is a regularly published listing of a set of current information about one or multiple subjects. It includes information like weather forecasting, weather forecasts, farmers' sowing, planting dates ...
, Axillary Lymphatic Mapping Against Nodal Axillary Clearance trial
References
Further reading
* * * * * * *External links
* * * * {{Authority control Lymphology Oncology Breast cancer