|
Submental Triangle
The submental triangle (or suprahyoid triangle) is a division of the anterior triangle of the neck. Boundaries It is limited to: * Lateral (away from the midline), formed by the anterior belly of the digastricus * Medial (towards the midline), formed by the midline of the neck between the mandible and the hyoid bone * Inferior Inferior may refer to: * Inferiority complex * An Anatomical terms of location#Superior and inferior, anatomical term of location * Inferior angle of the scapula, in the human skeleton *Inferior (book), ''Inferior'' (book), by Angela Saini * ''The ... (below), formed by the body of the hyoid bone *Floor is formed by the mylohyoideus *Roof is formed by Investing layer of deep cervical fascia Contents It contains one or two lymph glands, the submental lymph nodes (three or four in number) and Submental veins and commencement of anterior jugular veins. (The contents of the triangle actually lie in the superficial fascia over the roof of submental t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anterior Triangle Of The Neck
The anterior triangle is a region of the neck. Structure The triangle is inverted with its apex inferior to its base which is under the chin. Investing fascia covers the roof of the triangle while visceral fascia covers the floor. Anatomy Muscles: * Suprahyoid muscles - Digastric (Ant and Post Belly), mylohyoid, geniohyoid and Stylohyoid. * Infrahyoid muscles - Omohyoid, Sternohyoid, Sternothyroid, and Thyrohyoid. Nerve supply 2 Bellies of Digastric * Anterior: Mylohyoid nerve * Posterior: Facial nerve Stylohyoid: by the facial nerve, by a branch from that to the posterior belly of digastric. Mylohyoid: by its own nerve, a branch of the inferior alveolar ( from the mandibular division of trigeminal nerve), which arises just before the parent nerve enters the mandibular foramen, pierces the sphenomandibular ligament, and runs forward on the inferior surface of the mylohyoid, supplying it and the anterior belly of the digastric. Geniohyoid: by a branch from the hypoglossal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatomical Terms Of Location
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to unambiguously describe the anatomy of animals, including humans. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position provides a definition of what is at the front ("anterior"), behind ("posterior") and so on. As part of defining and describing terms, the body is described through the use of anatomical planes and anatomical axes. The meaning of terms that are used can change depending on whether an organism is bipedal or quadrupedal. Additionally, for some animals such as invertebrates, some terms may not have any meaning at all; for example, an animal that is radially symmetrical will have no anterior surface, but can still have a description that a part is close to the middle ("proximal") or further from the middle ("distal"). International organisations have determined vocabularies that are often used as standard vocabularies for subdisciplines o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digastricus
The digastric muscle (also digastricus) (named ''digastric'' as it has two 'bellies') is a small muscle located under the jaw. The term "digastric muscle" refers to this specific muscle. However, other muscles that have two separate muscle bellies include the suspensory muscle of duodenum, omohyoid, occipitofrontalis. It lies below the body of the mandible, and extends, in a curved form, from the mastoid notch to the mandibular symphysis. It belongs to the suprahyoid muscles group. A broad aponeurotic layer is given off from the tendon of the digastric muscle on either side, to be attached to the body and greater cornu of the hyoid bone; this is termed the suprahyoid aponeurosis. Structure The digastricus (digastric muscle) consists of two muscular bellies united by an intermediate rounded tendon. The two bellies of the digastric muscle have different embryological origins, and are supplied by different cranial nerves. Each person has a right and left digastric muscle. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
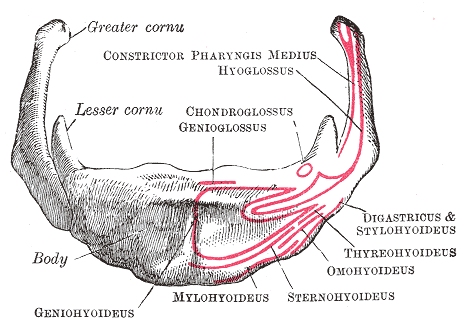
Human Mandible
In anatomy, the mandible, lower jaw or jawbone is the largest, strongest and lowest bone in the human facial skeleton. It forms the lower jaw and holds the lower teeth in place. The mandible sits beneath the maxilla. It is the only movable bone of the skull (discounting the ossicles of the middle ear). It is connected to the temporal bones by the temporomandibular joints. The bone is formed in the fetus from a fusion of the left and right mandibular prominences, and the point where these sides join, the mandibular symphysis, is still visible as a faint ridge in the midline. Like other symphyses in the body, this is a midline articulation where the bones are joined by fibrocartilage, but this articulation fuses together in early childhood.Illustrated Anatomy of the Head and Neck, Fehrenbach and Herring, Elsevier, 2012, p. 59 The word "mandible" derives from the Latin word ''mandibula'', "jawbone" (literally "one used for chewing"), from '' mandere'' "to chew" and ''-bula' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyoid Bone
The hyoid bone (lingual bone or tongue-bone) () is a horseshoe-shaped bone situated in the anterior midline of the neck between the chin and the thyroid cartilage. At rest, it lies between the base of the mandible and the third cervical vertebra. Unlike other bones, the hyoid is only distantly articulated to other bones by muscles or ligaments. It is the only bone in the human body that is not connected to any other bones nearby. The hyoid is anchored by muscles from the anterior, posterior and inferior directions, and aids in tongue movement and swallowing. The hyoid bone provides attachment to the muscles of the floor of the mouth and the tongue above, the larynx below, and the epiglottis and pharynx behind. Its name is derived . Structure The hyoid bone is classed as an irregular bone and consists of a central part called the body, and two pairs of horns, the greater and lesser horns. Body The body of the hyoid bone is the central part of the hyoid bone. *At the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Body Of Hyoid Bone
The hyoid bone (lingual bone or tongue-bone) () is a horseshoe-shaped bone situated in the anterior midline of the neck between the chin and the thyroid cartilage. At rest, it lies between the base of the mandible and the third cervical vertebra. Unlike other bones, the hyoid is only distantly articulated to other bones by muscles or ligaments. It is the only bone in the human body that is not connected to any other bones nearby. The hyoid is anchored by muscles from the anterior, posterior and inferior directions, and aids in tongue movement and swallowing. The hyoid bone provides attachment to the muscles of the floor of the mouth and the tongue above, the larynx below, and the epiglottis and pharynx behind. Its name is derived . Structure The hyoid bone is classed as an irregular bone and consists of a central part called the body, and two pairs of horns, the greater and lesser horns. Body The body of the hyoid bone is the central part of the hyoid bone. *At the front ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mylohyoid Muscle
The mylohyoid muscle or diaphragma oris is a paired muscle of the neck. It runs from the mandible to the hyoid bone, forming the floor of the oral cavity of the mouth. It is named after its two attachments near the molar teeth. It forms the floor of the submental triangle. It elevates the hyoid bone and the tongue, important during swallowing and speaking. Structure The mylohyoid muscle is flat and triangular, and is situated immediately superior to the anterior belly of the digastric muscle. It is a pharyngeal muscle (derived from the first pharyngeal arch) and classified as one of the suprahyoid muscles. Together, the paired mylohyoid muscles form a muscular floor for the oral cavity of the mouth. The two mylohyoid muscles arise from the mandible at the mylohyoid line, which extends from the mandibular symphysis in front to the last molar tooth behind. The posterior fibers pass inferomedially and insert at anterior surface of the hyoid bone. The medial fibres of the two m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Investing Layer Of Deep Cervical Fascia
The investing layer of deep cervical fascia is the most superficial part of the deep cervical fascia, and encloses the whole neck. It is considered by some sources to be incomplete or nonexistent. Attachments It surrounds the neck like a collar, it splits around the sternocleidomastoid muscle and the trapezius muscle. It is attached as; * Posteriorly - Ligamentum nuchae * Anteriorly - Attached to the hyoid bone * Superiorly - (from backwards to forwards); ** External occipital protuberance and Superior nuchal line of occipital bone ** Mastoid process of Temporal bone ** External acoustic meatus ** Lower margin of the zygomatic arch ** Lower border of body of mandible from the angle of mandible to the symphysis menti * Inferiorly - (from backwards to forwards); ** Spine and acromial process of scapula ** Upper surface of the clavicle **Suprasternal notch of manubrium sterni Tracings * Horizontal extent - From ligamentum nuchae when traced forward, the fascia splits and en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lymph Glands
A lymph node, or lymph gland, is a kidney-shaped organ of the lymphatic system and the adaptive immune system. A large number of lymph nodes are linked throughout the body by the lymphatic vessels. They are major sites of lymphocytes that include B and T cells. Lymph nodes are important for the proper functioning of the immune system, acting as filters for foreign particles including cancer cells, but have no detoxification function. In the lymphatic system a lymph node is a secondary lymphoid organ. A lymph node is enclosed in a fibrous capsule and is made up of an outer cortex and an inner medulla. Lymph nodes become inflamed or enlarged in various diseases, which may range from trivial throat infections to life-threatening cancers. The condition of lymph nodes is very important in cancer staging, which decides the treatment to be used and determines the prognosis. Lymphadenopathy refers to glands that are enlarged or swollen. When inflamed or enlarged, lymph nodes can be fir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Submental Lymph Nodes
The submental glands (or suprahyoid) are situated between the anterior bellies of the digastric muscle and the hyoid bone. Their '' afferents'' drain the central portions of the lower lip and floor of the mouth and the apex of the tongue. Their '' efferents'' pass partly to the submandibular lymph nodes and partly to a gland of the deep cervical group situated on the internal jugular vein at the level of the cricoid cartilage. See also * Submental triangle References External links * () Image at umich.edu - must rolloverat Baylor College of Medicine Baylor College of Medicine (BCM) is a medical school and research center in Houston, Texas, within the Texas Medical Center, the world's largest medical center. BCM is composed of four academic components: the School of Medicine, the Graduate Sc ... Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma , Symptoms and Types Lymphatics of the head and neck {{Portal bar, Anatomy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anterior Jugular Vein
The anterior jugular vein is a vein in the neck. Structure The anterior jugular vein lies lateral to the cricothyroid ligament. It begins near the hyoid bone by the confluence of several superficial veins from the submandibular region. Its tributaries are some laryngeal veins, and occasionally a small thyroid vein. It descends between the median line and the anterior border of the sternocleidomastoid muscle, and, at the lower part of the neck, passes beneath that muscle to open into the termination of the external jugular vein, or, in some instances, into the subclavian vein. Just above the sternum the two anterior jugular veins communicate by a transverse trunk, the venous jugular arch, which receive tributaries from the inferior thyroid veins; each also communicates with the internal jugular. There are no valves in this vein. The pretracheal lymph nodes follow the anterior jugular vein on each side of the midline. Variation The anterior jugular vein varies consider ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anterior Triangle Of The Neck
The anterior triangle is a region of the neck. Structure The triangle is inverted with its apex inferior to its base which is under the chin. Investing fascia covers the roof of the triangle while visceral fascia covers the floor. Anatomy Muscles: * Suprahyoid muscles - Digastric (Ant and Post Belly), mylohyoid, geniohyoid and Stylohyoid. * Infrahyoid muscles - Omohyoid, Sternohyoid, Sternothyroid, and Thyrohyoid. Nerve supply 2 Bellies of Digastric * Anterior: Mylohyoid nerve * Posterior: Facial nerve Stylohyoid: by the facial nerve, by a branch from that to the posterior belly of digastric. Mylohyoid: by its own nerve, a branch of the inferior alveolar ( from the mandibular division of trigeminal nerve), which arises just before the parent nerve enters the mandibular foramen, pierces the sphenomandibular ligament, and runs forward on the inferior surface of the mylohyoid, supplying it and the anterior belly of the digastric. Geniohyoid: by a branch from the hypoglossal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)