|
Spectral Density Estimation
In statistical signal processing, the goal of spectral density estimation (SDE) or simply spectral estimation is to estimate the spectral density (also known as the power spectral density) of a signal from a sequence of time samples of the signal. Intuitively speaking, the spectral density characterizes the frequency content of the signal. One purpose of estimating the spectral density is to detect any periodicities in the data, by observing peaks at the frequencies corresponding to these periodicities. Some SDE techniques assume that a signal is composed of a limited (usually small) number of generating frequencies plus noise and seek to find the location and intensity of the generated frequencies. Others make no assumption on the number of components and seek to estimate the whole generating spectrum. Overview Spectrum analysis, also referred to as frequency domain analysis or spectral density estimation, is the technical process of decomposing a complex signal into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statistical Signal Processing
Signal processing is an electrical engineering subfield that focuses on analyzing, modifying and synthesizing ''signals'', such as sound, images, and scientific measurements. Signal processing techniques are used to optimize transmissions, digital storage efficiency, correcting distorted signals, subjective video quality and to also detect or pinpoint components of interest in a measured signal. History According to Alan V. Oppenheim and Ronald W. Schafer, the principles of signal processing can be found in the classical numerical analysis techniques of the 17th century. They further state that the digital refinement of these techniques can be found in the digital control systems of the 1940s and 1950s. In 1948, Claude Shannon wrote the influential paper "A Mathematical Theory of Communication" which was published in the Bell System Technical Journal. The paper laid the groundwork for later development of information communication systems and the processing of signals fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polar Coordinates
In mathematics, the polar coordinate system is a two-dimensional coordinate system in which each point on a plane is determined by a distance from a reference point and an angle from a reference direction. The reference point (analogous to the origin of a Cartesian coordinate system) is called the ''pole'', and the ray from the pole in the reference direction is the ''polar axis''. The distance from the pole is called the ''radial coordinate'', ''radial distance'' or simply ''radius'', and the angle is called the ''angular coordinate'', ''polar angle'', or ''azimuth''. Angles in polar notation are generally expressed in either degrees or radians (2 rad being equal to 360°). Grégoire de Saint-Vincent and Bonaventura Cavalieri independently introduced the concepts in the mid-17th century, though the actual term "polar coordinates" has been attributed to Gregorio Fontana in the 18th century. The initial motivation for the introduction of the polar system was the study of circula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-parametric Statistics
Nonparametric statistics is the branch of statistics that is not based solely on parametrized families of probability distributions (common examples of parameters are the mean and variance). Nonparametric statistics is based on either being distribution-free or having a specified distribution but with the distribution's parameters unspecified. Nonparametric statistics includes both descriptive statistics and statistical inference. Nonparametric tests are often used when the assumptions of parametric tests are violated. Definitions The term "nonparametric statistics" has been imprecisely defined in the following two ways, among others: Applications and purpose Non-parametric methods are widely used for studying populations that take on a ranked order (such as movie reviews receiving one to four stars). The use of non-parametric methods may be necessary when data have a ranking but no clear numerical interpretation, such as when assessing preferences. In terms of levels of me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smoothing
In statistics and image processing, to smooth a data set is to create an approximating function (mathematics), function that attempts to capture important patterns in the data, while leaving out noise or other fine-scale structures/rapid phenomena. In smoothing, the data points of a signal are modified so individual points higher than the adjacent points (presumably because of noise) are reduced, and points that are lower than the adjacent points are increased leading to a smoother signal. Smoothing may be used in two important ways that can aid in data analysis (1) by being able to extract more information from the data as long as the assumption of smoothing is reasonable and (2) by being able to provide analyses that are both flexible and robust. Many different algorithms are used in smoothing. Smoothing may be distinguished from the related and partially overlapping concept of curve fitting in the following ways: * curve fitting often involves the use of an explicit function for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Welch's Method
Welch's method, named after Peter D. Welch, is an approach for spectral density estimation. It is used in physics, engineering, and applied mathematics for estimating the power of a signal at different frequencies. The method is based on the concept of using periodogram spectrum estimates, which are the result of converting a signal from the time domain to the frequency domain. Welch's method is an improvement on the standard periodogram spectrum estimating method and on Bartlett's method, in that it reduces noise in the estimated power spectra in exchange for reducing the frequency resolution. Due to the noise caused by imperfect and finite data, the noise reduction from Welch's method is often desired. Definition and procedure The Welch method is based on Bartlett's method and differs in two ways: # The signal is split up into overlapping segments: the original data segment is split up into L data segments of length M, overlapping by D points. ## If D = M / 2, the overlap is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Window Function
In signal processing and statistics, a window function (also known as an apodization function or tapering function) is a mathematical function that is zero-valued outside of some chosen interval, normally symmetric around the middle of the interval, usually near a maximum in the middle, and usually tapering away from the middle. Mathematically, when another function or waveform/data-sequence is "multiplied" by a window function, the product is also zero-valued outside the interval: all that is left is the part where they overlap, the "view through the window". Equivalently, and in actual practice, the segment of data within the window is first isolated, and then only that data is multiplied by the window function values. Thus, tapering, not segmentation, is the main purpose of window functions. The reasons for examining segments of a longer function include detection of transient events and time-averaging of frequency spectra. The duration of the segments is determined in ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Impulse Response
In signal processing and control theory, the impulse response, or impulse response function (IRF), of a dynamic system is its output when presented with a brief input signal, called an Dirac delta function, impulse (). More generally, an impulse response is the reaction of any dynamic system in response to some external change. In both cases, the impulse response describes the reaction of the system as a Function (mathematics), function of time (or possibly as a function of some other independent variable that parameterizes the dynamic behavior of the system). In all these cases, the dynamic system and its impulse response may be actual physical objects, or may be mathematical systems of equations describing such objects. Since the impulse function contains all frequencies (see Dirac delta function#Fourier transform, the Fourier transform of the Dirac delta function, showing infinite frequency bandwidth that the Dirac delta function has), the impulse response defines the response ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
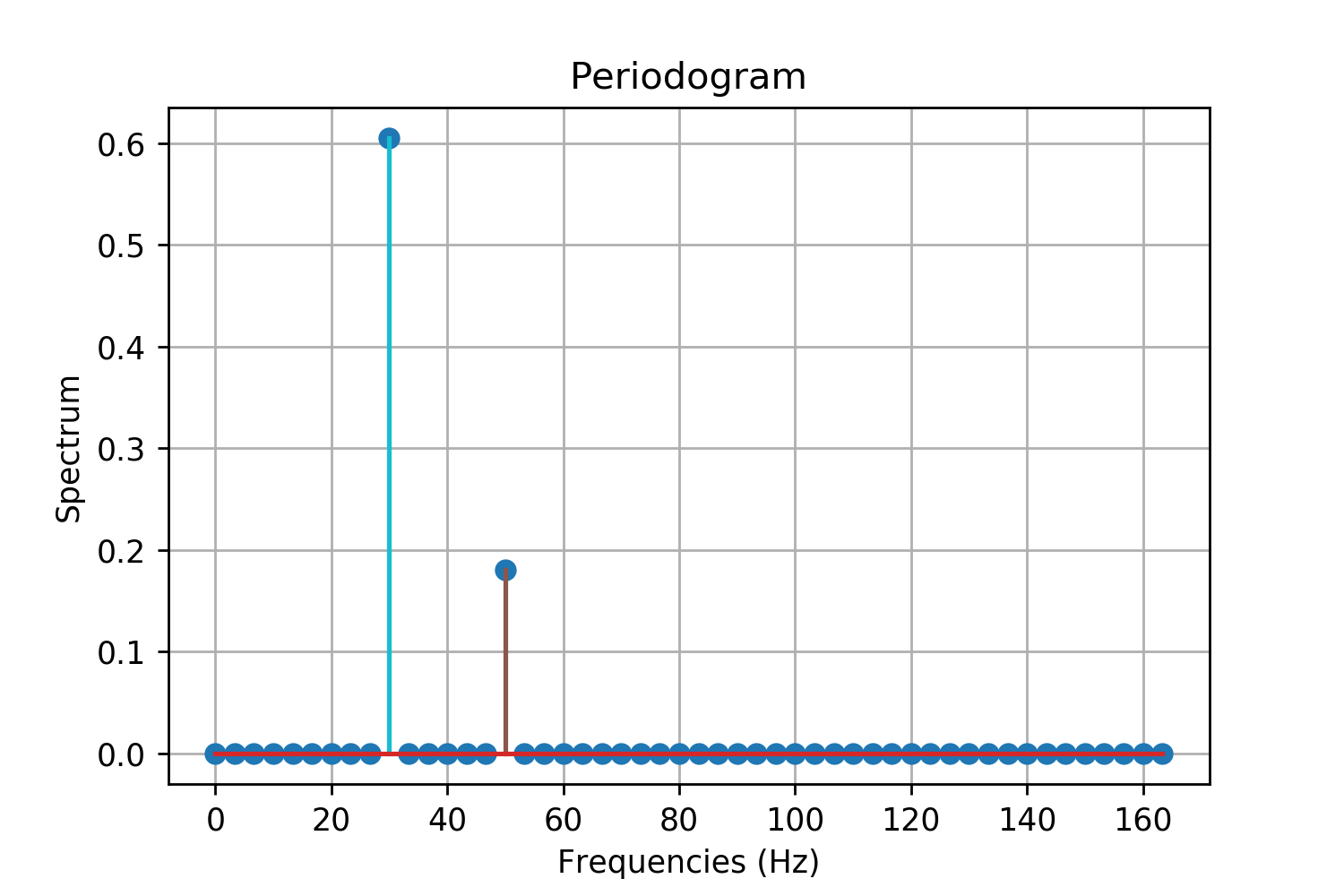
Periodogram
In signal processing, a periodogram is an estimate of the spectral density of a signal. The term was coined by Arthur Schuster in 1898. Today, the periodogram is a component of more sophisticated methods (see spectral estimation). It is the most common tool for examining the amplitude vs frequency characteristics of FIR filters and window functions. FFT spectrum analyzers are also implemented as a time-sequence of periodograms. Definition There are at least two different definitions in use today. One of them involves time-averaging, and one does not. Time-averaging is also the purview of other articles ( Bartlett's method and Welch's method). This article is not about time-averaging. The definition of interest here is that the power spectral density of a continuous function, x(t), is the Fourier transform of its auto-correlation function (see Cross-correlation theorem, Spectral density#Power spectral density, and Wiener–Khinchin theorem): :\mathcal\ = X(f)\cdot X^*(f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fast Fourier Transform
A fast Fourier transform (FFT) is an algorithm that computes the discrete Fourier transform (DFT) of a sequence, or its inverse (IDFT). Fourier analysis converts a signal from its original domain (often time or space) to a representation in the frequency domain and vice versa. The DFT is obtained by decomposing a sequence of values into components of different frequencies. This operation is useful in many fields, but computing it directly from the definition is often too slow to be practical. An FFT rapidly computes such transformations by factorizing the DFT matrix into a product of sparse (mostly zero) factors. As a result, it manages to reduce the complexity of computing the DFT from O\left(N^2\right), which arises if one simply applies the definition of DFT, to O(N \log N), where N is the data size. The difference in speed can be enormous, especially for long data sets where ''N'' may be in the thousands or millions. In the presence of round-off error, many FFT algorithm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sampling (signal Processing)
In signal processing, sampling is the reduction of a continuous-time signal to a discrete-time signal. A common example is the conversion of a sound wave to a sequence of "samples". A sample is a value of the signal at a point in time and/or space; this definition differs from the usage in statistics, which refers to a set of such values. A sampler is a subsystem or operation that extracts samples from a continuous signal. A theoretical ideal sampler produces samples equivalent to the instantaneous value of the continuous signal at the desired points. The original signal can be reconstructed from a sequence of samples, up to the Nyquist limit, by passing the sequence of samples through a type of low-pass filter called a reconstruction filter. Theory Functions of space, time, or any other dimension can be sampled, and similarly in two or more dimensions. For functions that vary with time, let ''S''(''t'') be a continuous function (or "signal") to be sampled, and let samp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Discrete Fourier Transform
In mathematics, the discrete Fourier transform (DFT) converts a finite sequence of equally-spaced samples of a function into a same-length sequence of equally-spaced samples of the discrete-time Fourier transform (DTFT), which is a complex-valued function of frequency. The interval at which the DTFT is sampled is the reciprocal of the duration of the input sequence. An inverse DFT is a Fourier series, using the DTFT samples as coefficients of complex sinusoids at the corresponding DTFT frequencies. It has the same sample-values as the original input sequence. The DFT is therefore said to be a frequency domain representation of the original input sequence. If the original sequence spans all the non-zero values of a function, its DTFT is continuous (and periodic), and the DFT provides discrete samples of one cycle. If the original sequence is one cycle of a periodic function, the DFT provides all the non-zero values of one DTFT cycle. The DFT is the most important discret ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Time-variant System
A time-variant system is a system whose output response depends on moment of observation as well as moment of input signal application. In other words, a time delay or time advance of input not only shifts the output signal in time but also changes other parameters and behavior. Time variant systems respond differently to the same input at different times. The opposite is true for time invariant systems (TIV). Overview There are many well developed techniques for dealing with the response of linear time invariant systems, such as Laplace and Fourier transforms. However, these techniques are not strictly valid for time-varying systems. A system undergoing slow time variation in comparison to its time constants can usually be considered to be time invariant: they are close to time invariant on a small scale. An example of this is the aging and wear of electronic components, which happens on a scale of years, and thus does not result in any behaviour qualitatively different from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |