|
Time-variant System
A time-variant system is a system whose output response depends on moment of observation as well as moment of input signal application. In other words, a time delay or time advance of input not only shifts the output signal in time but also changes other parameters and behavior. Time variant systems respond differently to the same input at different times. The opposite is true for time invariant systems (TIV). Overview There are many well developed techniques for dealing with the response of linear time invariant systems, such as Laplace and Fourier transforms. However, these techniques are not strictly valid for time-varying systems. A system undergoing slow time variation in comparison to its time constants can usually be considered to be time invariant: they are close to time invariant on a small scale. An example of this is the aging and wear of electronic components, which happens on a scale of years, and thus does not result in any behaviour qualitatively different from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
System
A system is a group of interacting or interrelated elements that act according to a set of rules to form a unified whole. A system, surrounded and influenced by its open system (systems theory), environment, is described by its boundaries, structure and purpose and is expressed in its functioning. Systems are the subjects of study of systems theory and other systems sciences. Systems have several common properties and characteristics, including structure, function(s), behavior and interconnectivity. Etymology The term ''system'' comes from the Latin word ''systēma'', in turn from Greek language, Greek ''systēma'': "whole concept made of several parts or members, system", literary "composition"."σύστημα" , Henry George Liddell, Robert Scott, ''A Greek–English Lexicon'', on Pers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
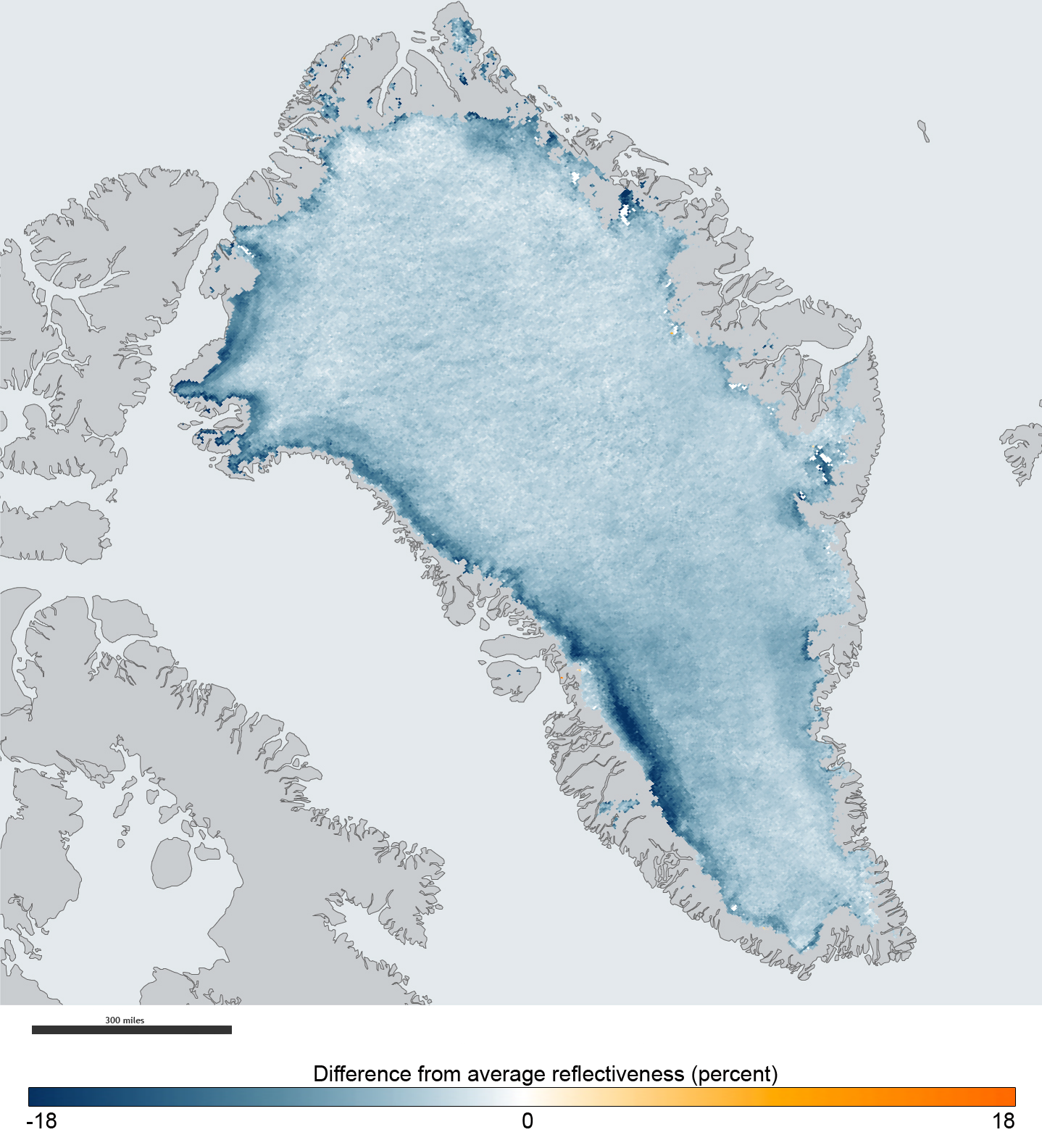
Albedo
Albedo ( ; ) is the fraction of sunlight that is Diffuse reflection, diffusely reflected by a body. It is measured on a scale from 0 (corresponding to a black body that absorbs all incident radiation) to 1 (corresponding to a body that reflects all incident radiation). ''Surface albedo'' is defined as the ratio of Radiosity (radiometry), radiosity ''J''e to the irradiance ''E''e (flux per unit area) received by a surface. The proportion reflected is not only determined by properties of the surface itself, but also by the spectral and angular distribution of solar radiation reaching the Earth's surface. These factors vary with atmospheric composition, geographic location, and time (see position of the Sun). While directional-hemispherical reflectance factor is calculated for a single angle of incidence (i.e., for a given position of the Sun), albedo is the directional integration of reflectance over all solar angles in a given period. The temporal resolution may range from seconds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
System Analysis
System analysis in the field of electrical engineering characterizes electrical systems and their properties. System analysis can be used to represent almost anything from population growth to audio speakers; electrical engineers often use it because of its direct relevance to many areas of their discipline, most notably signal processing, communication systems and control systems. Characterization of systems A system is characterized by how it responds to input signals. In general, a system has one or more input signals and one or more output signals. Therefore, one natural characterization of systems is by how many inputs and outputs they have: * '' SISO''Single input, single output * ''SIMO''Single input, multiple outputs * ''MISO''Multiple inputs, single output * ''MIMO''Multiple inputs, multiple outputs It is often useful (or necessary) to break up a system into smaller pieces for analysis. Therefore, we can regard a SIMO system as multiple SISO systems (one for eac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Control Theory
Control theory is a field of control engineering and applied mathematics that deals with the control system, control of dynamical systems in engineered processes and machines. The objective is to develop a model or algorithm governing the application of system inputs to drive the system to a desired state, while minimizing any ''delay'', ''overshoot'', or ''steady-state error'' and ensuring a level of control Stability theory, stability; often with the aim to achieve a degree of Optimal control, optimality. To do this, a controller with the requisite corrective behavior is required. This controller monitors the controlled process variable (PV), and compares it with the reference or Setpoint (control system), set point (SP). The difference between actual and desired value of the process variable, called the ''error'' signal, or SP-PV error, is applied as feedback to generate a control action to bring the controlled process variable to the same value as the set point. Other aspects ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Control System
A control system manages, commands, directs, or regulates the behavior of other devices or systems using control loops. It can range from a single home heating controller using a thermostat controlling a domestic boiler to large industrial control systems which are used for controlling processes or machines. The control systems are designed via control engineering process. For continuously modulated control, a feedback controller is used to automatically control a process or operation. The control system compares the value or status of the process variable (PV) being controlled with the desired value or setpoint (SP), and applies the difference as a control signal to bring the process variable output of the plant to the same value as the setpoint. For sequential and combinational logic, software logic, such as in a programmable logic controller, is used. Open-loop and closed-loop control Feedback control systems Logic control Logic control systems for indus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decimation (signal Processing)
Decimation, Decimate, or variants may refer to: * Decimation (punishment), punitive discipline * Decimation (signal processing), reduction of digital signal's sampling rate * Decimation (comics), 2006 Marvel crossover spinoff ''House of M'' * Decimate (game show), ''Decimate'' (game show), 2015 BBC television * The Decimation, an event in the Marvel Cinematic Universe See also * Decimator (other) {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Discrete Wavelet Transform
In numerical analysis and functional analysis Functional analysis is a branch of mathematical analysis, the core of which is formed by the study of vector spaces endowed with some kind of limit-related structure (for example, Inner product space#Definition, inner product, Norm (mathematics ..., a discrete wavelet transform (DWT) is any wavelet transform for which the wavelets are discretely sampled. As with other wavelet transforms, a key advantage it has over Fourier transforms is temporal resolution: it captures both frequency ''and'' location information (location in time). Definition One level of the transform The DWT of a signal x is calculated by passing it through a series of filters. First the samples are passed through a low-pass filter with impulse response g resulting in a convolution of the two: :y[n] = (x * g)[n] = \sum\limits_^\infty The signal is also decomposed simultaneously using a high-pass filter h. The outputs give the detail coefficients (fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greenhouse Gas
Greenhouse gases (GHGs) are the gases in the atmosphere that raise the surface temperature of planets such as the Earth. Unlike other gases, greenhouse gases absorb the radiations that a planet emits, resulting in the greenhouse effect. The Earth is warmed by sunlight, causing its surface to radiate heat, which is then mostly absorbed by greenhouse gases. Without greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, the average temperature of Earth's surface would be about , rather than the present average of .Le Treut, H., R. Somerville, U. Cubasch, Y. Ding, C. Mauritzen, A. Mokssit, T. Peterson and M. Prather, 2007:Chapter 1: Historical Overview of Climate Change. In:Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. olomon, S., D. Qin, M. Manning, Z. Chen, M. Marquis, K.B. Averyt, M. Tignor and H.L. Miller (eds.) Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New Y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Irradiance
Solar irradiance is the power per unit area (surface power density) received from the Sun in the form of electromagnetic radiation in the wavelength range of the measuring instrument. Solar irradiance is measured in watts per square metre (W/m2) in SI units. Solar irradiance is often integrated over a given time period in order to report the radiant energy emitted into the surrounding environment (joule per square metre, J/m2) during that time period. This integrated solar irradiance is called solar irradiation, solar radiation, solar exposure, solar insolation, or insolation. Irradiance may be measured in space or at the Earth's surface after atmospheric absorption and scattering. Irradiance in space is a function of distance from the Sun, the solar cycle, and cross-cycle changes.Michael Boxwell, ''Solar Electricity Handbook: A Simple, Practical Guide to Solar Energy'' (2012), pp. 41–42. Irradiance on the Earth's surface additionally depends on the tilt of the measuri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Time-invariant System
In control theory, a time-invariant (TI) system has a time-dependent system function that is not a direct function of time. Such systems are regarded as a class of systems in the field of system analysis. The time-dependent system function is a function of the time-dependent input function. If this function depends ''only'' indirectly on the time-domain (via the input function, for example), then that is a system that would be considered time-invariant. Conversely, any direct dependence on the time-domain of the system function could be considered as a "time-varying system". Mathematically speaking, "time-invariance" of a system is the following property: :''Given a system with a time-dependent output function , and a time-dependent input function , the system will be considered time-invariant if a time-delay on the input directly equates to a time-delay of the output function. For example, if time is "elapsed time", then "time-invariance" implies that the relationship betwe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Control Systems/Time Variant System Solutions
Control may refer to: Basic meanings Economics and business * Control (management), an element of management * Control, an element of management accounting * Comptroller (or controller), a senior financial officer in an organization * Controlling interest, a percentage of voting stock shares sufficient to prevent opposition * Foreign exchange controls, regulations on trade * Internal control, a process to help achieve specific goals typically related to managing risk Mathematics and science * Control (optimal control theory), a variable for steering a controllable system of state variables toward a desired goal * Controlling for a variable in statistics * Scientific control, an experiment in which "confounding variables" are minimised to reduce error * Control variables, variables which are kept constant during an experiment * Biological pest control, a natural method of controlling pests * Control network in geodesy and surveying, a set of reference points of known geospatial c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stationarity (statistics)
In mathematics and statistics, a stationary process (also called a strict/strictly stationary process or strong/strongly stationary process) is a stochastic process whose statistical properties, such as mean and variance, do not change over time. More formally, the joint probability distribution of the process remains the same when shifted in time. This implies that the process is statistically consistent across different time periods. Because many statistical procedures in time series analysis assume stationarity, non-stationary data are frequently transformed to achieve stationarity before analysis. A common cause of non-stationarity is a trend in the mean, which can be due to either a unit root or a deterministic trend. In the case of a unit root, stochastic shocks have permanent effects, and the process is not mean-reverting. With a deterministic trend, the process is called trend-stationary, and shocks have only transitory effects, with the variable tending towards a determin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |