
Solar irradiance is the
power per unit area (
surface power density
In physics and engineering, surface power density is power per unit area.
Applications
* The intensity of electromagnetic radiation can be expressed in W/m2. An example of such a quantity is the solar constant.
* Wind turbines are often compared ...
) received from the
Sun
The Sun is the star at the centre of the Solar System. It is a massive, nearly perfect sphere of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core, radiating the energy from its surface mainly as visible light a ...
in the form of
electromagnetic radiation
In physics, electromagnetic radiation (EMR) is a self-propagating wave of the electromagnetic field that carries momentum and radiant energy through space. It encompasses a broad spectrum, classified by frequency or its inverse, wavelength ...
in the
wavelength
In physics and mathematics, wavelength or spatial period of a wave or periodic function is the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.
In other words, it is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same ''phase (waves ...
range of the measuring instrument.
Solar
irradiance is measured in
watt
The watt (symbol: W) is the unit of Power (physics), power or radiant flux in the International System of Units (SI), equal to 1 joule per second or 1 kg⋅m2⋅s−3. It is used to quantification (science), quantify the rate of Work ...
s per
square metre
The square metre ( international spelling as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures) or square meter ( American spelling) is the unit of area in the International System of Units (SI) with symbol m2. It is the area of a square ...
(W/m
2) in
SI unit
The International System of Units, internationally known by the abbreviation SI (from French ), is the modern form of the metric system and the world's most widely used system of units of measurement, system of measurement. It is the only system ...
s.
Solar irradiance is often
integrated over a given time period in order to report the
radiant energy
In physics, and in particular as measured by radiometry, radiant energy is the energy of electromagnetic radiation, electromagnetic and gravitational radiation. As energy, its SI unit is the joule (J). The quantity of radiant energy may be calcul ...
emitted into the surrounding environment (
joule
The joule ( , or ; symbol: J) is the unit of energy in the International System of Units (SI). In terms of SI base units, one joule corresponds to one kilogram- metre squared per second squared One joule is equal to the amount of work d ...
per square metre, J/m
2) during that time period. This integrated solar irradiance is called solar irradiation, solar radiation, solar exposure, solar insolation, or insolation.
Irradiance may be measured in
space
Space is a three-dimensional continuum containing positions and directions. In classical physics, physical space is often conceived in three linear dimensions. Modern physicists usually consider it, with time, to be part of a boundless ...
or at the
Earth's surface
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to Planetary habitability, harbor life. This is enabled by Earth being an ocean world, the only one in the Solar System sustaining liquid surface water. Almost all ...
after
atmospheric
An atmosphere () is a layer of gases that envelop an astronomical object, held in place by the gravity of the object. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A stellar atmosphere ...
absorption and
scattering
In physics, scattering is a wide range of physical processes where moving particles or radiation of some form, such as light or sound, are forced to deviate from a straight trajectory by localized non-uniformities (including particles and radiat ...
. Irradiance in space is a
function of distance from the Sun, the
solar cycle
The Solar cycle, also known as the solar magnetic activity cycle, sunspot cycle, or Schwabe cycle, is a periodic 11-year change in the Sun's activity measured in terms of Modern Maximum, variations in the number of observed sunspots on the Sun ...
, and cross-cycle changes.
[Michael Boxwell, ''Solar Electricity Handbook: A Simple, Practical Guide to Solar Energy'' (2012), pp. 41–42.]
Irradiance on the Earth's surface additionally depends on the tilt of the measuring surface, the height of the Sun above the horizon, and atmospheric conditions.
Solar irradiance affects
plant metabolism and animal behavior.
The study and measurement of solar irradiance have several important applications, including the prediction of energy generation from
solar power plants, the heating and cooling loads of buildings, climate modeling and weather forecasting,
passive daytime radiative cooling
Passive daytime radiative cooling (PDRC) (also passive radiative cooling, daytime passive radiative cooling, radiative sky cooling, photonic radiative cooling, and terrestrial radiative cooling) is the use of unpowered, reflective/Emissivity, ther ...
applications, and space travel.
Types
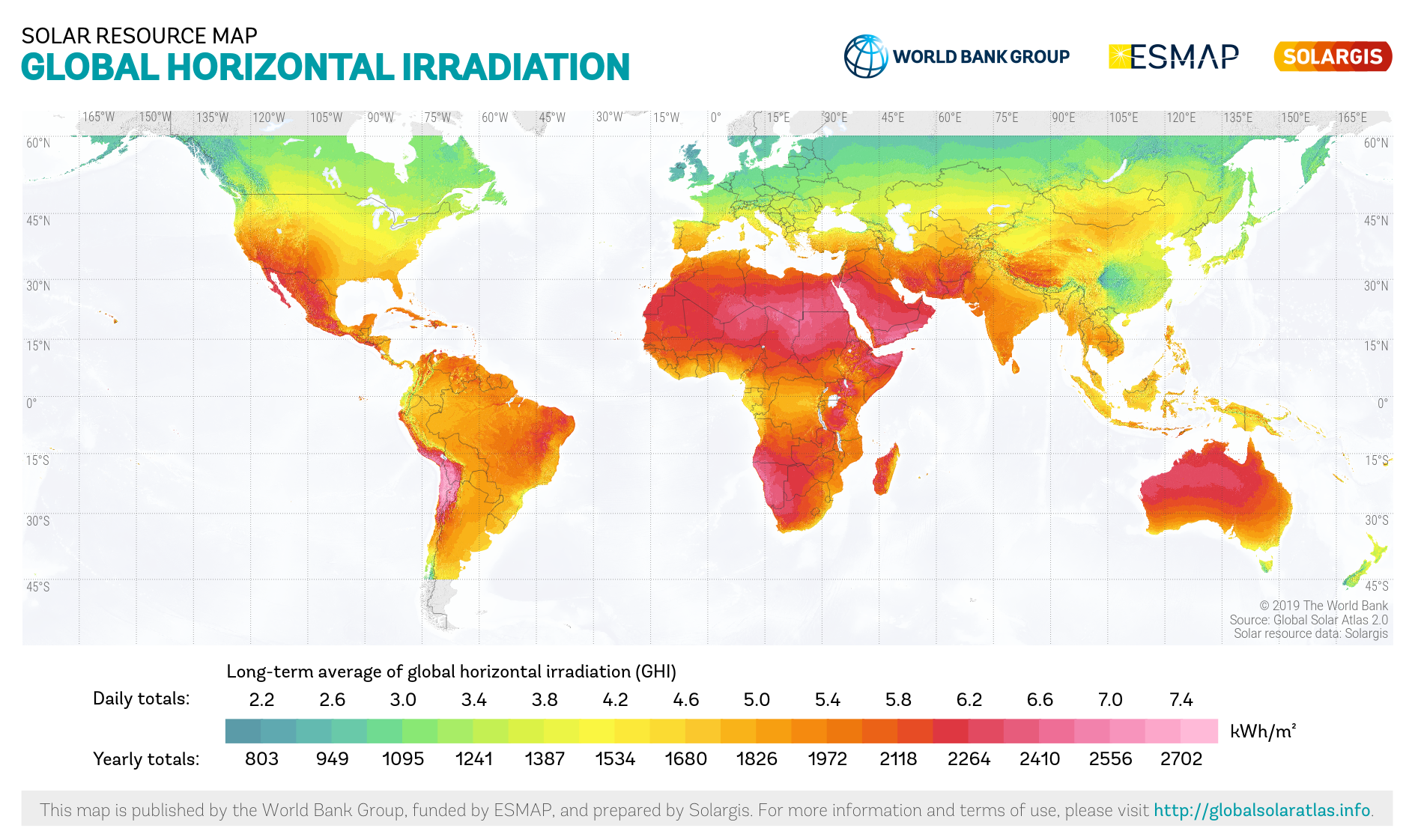

There are several measured types of solar irradiance.
* Total solar irradiance (TSI) is a measure of the
solar power
Solar power, also known as solar electricity, is the conversion of energy from sunlight into electricity, either directly using photovoltaics (PV) or indirectly using concentrated solar power. Solar panels use the photovoltaic effect to c ...
over all wavelengths per unit area incident on the Earth's
upper atmosphere
Upper atmosphere is a collective term that refers to various layers of the atmosphere of the Earth above the troposphere and corresponding regions of the atmospheres of other planets, and includes:
* The mesosphere, which on Earth lies between th ...
. It is measured facing (pointing at / parallel to) the incoming sunlight (i.e. the flux through a surface
perpendicular
In geometry, two geometric objects are perpendicular if they intersect at right angles, i.e. at an angle of 90 degrees or π/2 radians. The condition of perpendicularity may be represented graphically using the '' perpendicular symbol'', � ...
to the incoming sunlight; other angles would not be TSI and be reduced by the
dot product
In mathematics, the dot product or scalar productThe term ''scalar product'' means literally "product with a Scalar (mathematics), scalar as a result". It is also used for other symmetric bilinear forms, for example in a pseudo-Euclidean space. N ...
).
The
solar constant is a conventional measure of mean TSI at a distance of one
astronomical unit
The astronomical unit (symbol: au or AU) is a unit of length defined to be exactly equal to . Historically, the astronomical unit was conceived as the average Earth-Sun distance (the average of Earth's aphelion and perihelion), before its m ...
(AU).
*
Direct normal irradiance (DNI), or beam radiation, is measured at the surface of the Earth at a given location with a surface element perpendicular to the Sun direction.
It excludes diffuse solar radiation (radiation that is scattered or reflected by atmospheric components). Direct irradiance is equal to the extraterrestrial irradiance above the atmosphere minus the atmospheric losses due to
absorption and
scattering
In physics, scattering is a wide range of physical processes where moving particles or radiation of some form, such as light or sound, are forced to deviate from a straight trajectory by localized non-uniformities (including particles and radiat ...
. Losses depend on time of day (length of light's path through the atmosphere depending on the
solar elevation angle),
cloud cover,
moisture
Moisture is the presence of a liquid, especially water, often in trace amounts. Moisture is defined as water in the adsorbed or absorbed phase. Small amounts of water may be found, for example, in the air (humidity), in foods, and in some comme ...
content and other
contents
Content or contents may refer to:
Media
* Content (media), information or experience provided to audience or end-users by publishers or media producers
** Content industry, an umbrella term that encompasses companies owning and providing mass m ...
. The irradiance above the atmosphere also varies with time of year (because the distance to the Sun varies), although this effect is generally less significant compared to the effect of losses on DNI.
* Diffuse horizontal irradiance (DHI), or diffuse sky radiation is the radiation at the Earth's surface from light scattered by the atmosphere. It is measured on a horizontal surface with radiation coming from all points in the sky excluding ''circumsolar radiation'' (radiation coming from the sun disk).
There would be almost no DHI in the absence of atmosphere.
* Global horizontal irradiance (GHI) is the total irradiance from the Sun on a horizontal surface on Earth. It is the sum of direct irradiance (after accounting for the
solar zenith angle of the Sun ''z'') and diffuse horizontal irradiance:
* Global tilted irradiance (GTI) is the total radiation received on a surface with defined tilt and azimuth, fixed or Sun-tracking. GTI can be measured
or modeled from GHI, DNI, DHI. It is often a reference for
photovoltaic power plants, while photovoltaic modules are mounted on the fixed or tracking constructions.
* Global normal irradiance (GNI) is the total irradiance from the Sun at the surface of Earth at a given location with a surface element perpendicular to the Sun.
Spectral versions of the above irradiances (e.g. spectral TSI, spectral DNI, etc.) are any of the above with units divided either by meter or nanometer (for a spectral graph as function of wavelength), or per-
Hz (for a spectral function with an x-axis of frequency). When one plots such spectral distributions as a graph, the integral of the function (area under the curve) will be the (non-spectral) irradiance. e.g.: Say one had a solar cell on the surface of the earth facing straight up, and had DNI in units of Wmnm, graphed as a function of wavelength (in nm). Then, the unit of the integral (Wm) is the product of those two units.
Units
The SI unit of irradiance is
watt
The watt (symbol: W) is the unit of Power (physics), power or radiant flux in the International System of Units (SI), equal to 1 joule per second or 1 kg⋅m2⋅s−3. It is used to quantification (science), quantify the rate of Work ...
s per square
metre
The metre (or meter in US spelling; symbol: m) is the base unit of length in the International System of Units (SI). Since 2019, the metre has been defined as the length of the path travelled by light in vacuum during a time interval of of ...
(W/m
2 = Wm
−2). The unit of insolation often used in the
solar power
Solar power, also known as solar electricity, is the conversion of energy from sunlight into electricity, either directly using photovoltaics (PV) or indirectly using concentrated solar power. Solar panels use the photovoltaic effect to c ...
industry is kilowatt hours per square metre (kWh/m
2).
The
langley is an alternative unit of insolation. One langley is one
thermochemical calorie per square centimetre or 41,840J/m
2.
At the top of Earth's atmosphere

The average annual solar radiation arriving at the top of the Earth's atmosphere is about 1361W/m
2. This represents the power per unit area of solar irradiance across the spherical surface surrounding the Sun with a radius equal to the distance to the Earth (1
AU). This means that the approximately circular disc of the Earth, as viewed from the Sun, receives a roughly stable 1361W/m
2 at all times. The area of this circular disc is , in which is the radius of the Earth. Because
the Earth is approximately spherical, it has total area
, meaning that the solar radiation arriving at the top of the atmosphere, averaged over the entire surface of the Earth, is simply divided by four to get 340W/m
2. In other words, averaged over the year and the day, the Earth's atmosphere receives 340W/m
2 from the Sun. This figure is important in
radiative forcing
Radiative forcing (or climate forcing) is a concept used to quantify a change to the balance of energy flowing through a planetary atmosphere. Various factors contribute to this change in energy balance, such as concentrations of greenhouse gases ...
.
Derivation
The distribution of solar radiation at the top of the atmosphere is determined by
Earth's sphericity and orbital parameters.
This applies to any unidirectional beam incident to a rotating sphere.
Insolation is essential for
numerical weather prediction
Numerical weather prediction (NWP) uses mathematical models of the atmosphere and oceans to weather forecasting, predict the weather based on current weather conditions. Though first attempted in the 1920s, it was not until the advent of comput ...
and understanding
seasons
A season is a division of the year based on changes in weather, ecology, and the number of daylight hours in a given region. On Earth, seasons are the result of the axial parallelism of Earth's axial tilt, tilted orbit around the Sun. In temperat ...
and
climatic change. Application to
ice ages
An ice age is a long period of reduction in the temperature of Earth's surface and atmosphere, resulting in the presence or expansion of continental and polar ice sheets and alpine glaciers. Earth's climate alternates between ice ages, and Gre ...
is known as
Milankovitch cycles
Milankovitch cycles describe the collective effects of changes in the Earth's movements on its climate over thousands of years. The term was coined and named after the Serbian geophysicist and astronomer Milutin Milanković. In the 1920s, he pr ...
.
Distribution is based on a fundamental identity from
spherical trigonometry
Spherical trigonometry is the branch of spherical geometry that deals with the metrical relationships between the edge (geometry), sides and angles of spherical triangles, traditionally expressed using trigonometric functions. On the sphere, ge ...
, the
spherical law of cosines:
where , and are arc lengths, in radians, of the sides of a spherical triangle. is the angle in the vertex opposite the side which has arc length . Applied to the calculation of
solar zenith angle , the following applies to the spherical law of cosines:
This equation can be also derived from a more general formula:
where is an angle from the horizontal and is an
azimuth angle.

The separation of Earth from the Sun can be denoted and the mean distance can be denoted , approximately The
solar constant is denoted . The solar flux density (insolation) onto a plane tangent to the sphere of the Earth, but above the bulk of the atmosphere (elevation 100 km or greater) is:
The average of over a day is the average of over one rotation, or the
hour angle
In astronomy and celestial navigation, the hour angle is the dihedral angle between the '' meridian plane'' (containing Earth's axis and the zenith) and the '' hour circle'' (containing Earth's axis and a given point of interest).
It may be ...
progressing from to :
Let be the hour angle when becomes positive. This could occur at sunrise when
, or for as a solution of
or
If , then the sun does not set and the sun is already risen at , so . If , the sun does not rise and
.
is nearly constant over the course of a day, and can be taken outside the integral
Therefore:
 Solar irradiance is the power per unit area (
Solar irradiance is the power per unit area (
 There are several measured types of solar irradiance.
* Total solar irradiance (TSI) is a measure of the
There are several measured types of solar irradiance.
* Total solar irradiance (TSI) is a measure of the  The average annual solar radiation arriving at the top of the Earth's atmosphere is about 1361W/m2. This represents the power per unit area of solar irradiance across the spherical surface surrounding the Sun with a radius equal to the distance to the Earth (1 AU). This means that the approximately circular disc of the Earth, as viewed from the Sun, receives a roughly stable 1361W/m2 at all times. The area of this circular disc is , in which is the radius of the Earth. Because the Earth is approximately spherical, it has total area , meaning that the solar radiation arriving at the top of the atmosphere, averaged over the entire surface of the Earth, is simply divided by four to get 340W/m2. In other words, averaged over the year and the day, the Earth's atmosphere receives 340W/m2 from the Sun. This figure is important in
The average annual solar radiation arriving at the top of the Earth's atmosphere is about 1361W/m2. This represents the power per unit area of solar irradiance across the spherical surface surrounding the Sun with a radius equal to the distance to the Earth (1 AU). This means that the approximately circular disc of the Earth, as viewed from the Sun, receives a roughly stable 1361W/m2 at all times. The area of this circular disc is , in which is the radius of the Earth. Because the Earth is approximately spherical, it has total area , meaning that the solar radiation arriving at the top of the atmosphere, averaged over the entire surface of the Earth, is simply divided by four to get 340W/m2. In other words, averaged over the year and the day, the Earth's atmosphere receives 340W/m2 from the Sun. This figure is important in  The separation of Earth from the Sun can be denoted and the mean distance can be denoted , approximately The solar constant is denoted . The solar flux density (insolation) onto a plane tangent to the sphere of the Earth, but above the bulk of the atmosphere (elevation 100 km or greater) is:
The average of over a day is the average of over one rotation, or the
The separation of Earth from the Sun can be denoted and the mean distance can be denoted , approximately The solar constant is denoted . The solar flux density (insolation) onto a plane tangent to the sphere of the Earth, but above the bulk of the atmosphere (elevation 100 km or greater) is:
The average of over a day is the average of over one rotation, or the
 Solar irradiance is the power per unit area (
Solar irradiance is the power per unit area (
 There are several measured types of solar irradiance.
* Total solar irradiance (TSI) is a measure of the
There are several measured types of solar irradiance.
* Total solar irradiance (TSI) is a measure of the  The average annual solar radiation arriving at the top of the Earth's atmosphere is about 1361W/m2. This represents the power per unit area of solar irradiance across the spherical surface surrounding the Sun with a radius equal to the distance to the Earth (1 AU). This means that the approximately circular disc of the Earth, as viewed from the Sun, receives a roughly stable 1361W/m2 at all times. The area of this circular disc is , in which is the radius of the Earth. Because the Earth is approximately spherical, it has total area , meaning that the solar radiation arriving at the top of the atmosphere, averaged over the entire surface of the Earth, is simply divided by four to get 340W/m2. In other words, averaged over the year and the day, the Earth's atmosphere receives 340W/m2 from the Sun. This figure is important in
The average annual solar radiation arriving at the top of the Earth's atmosphere is about 1361W/m2. This represents the power per unit area of solar irradiance across the spherical surface surrounding the Sun with a radius equal to the distance to the Earth (1 AU). This means that the approximately circular disc of the Earth, as viewed from the Sun, receives a roughly stable 1361W/m2 at all times. The area of this circular disc is , in which is the radius of the Earth. Because the Earth is approximately spherical, it has total area , meaning that the solar radiation arriving at the top of the atmosphere, averaged over the entire surface of the Earth, is simply divided by four to get 340W/m2. In other words, averaged over the year and the day, the Earth's atmosphere receives 340W/m2 from the Sun. This figure is important in  The separation of Earth from the Sun can be denoted and the mean distance can be denoted , approximately The solar constant is denoted . The solar flux density (insolation) onto a plane tangent to the sphere of the Earth, but above the bulk of the atmosphere (elevation 100 km or greater) is:
The average of over a day is the average of over one rotation, or the
The separation of Earth from the Sun can be denoted and the mean distance can be denoted , approximately The solar constant is denoted . The solar flux density (insolation) onto a plane tangent to the sphere of the Earth, but above the bulk of the atmosphere (elevation 100 km or greater) is:
The average of over a day is the average of over one rotation, or the