|
Social Cue
Social cues are verbal or non-verbal signals expressed through the face, body, voice, motion (and more) and guide conversations as well as other social interactions by influencing our impressions of and responses to others. These percepts are important communicative tools as they convey important social and contextual information and therefore facilitate social understanding. A few examples of social cues include: *eye gaze *facial expression * vocal tone *body language Social cues are part of social cognition and serve several purposes in navigating the social world. Due to their social nature, humans rely heavily on the ability to understand other peoples' mental states and make predictions about their behaviour. Especially in the view of evolution, this ability is critical in helping to determine potential threats and advantageous opportunities; and in helping to form and maintain relationships in order to fulfill safety and basic physiological needs. These cues allow us to pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-verbal Communication
Nonverbal communication (NVC) is the transmission of messages or signals through a nonverbal platform such as eye contact, facial expressions, gestures, posture, and body language. It includes the use of social cues, kinesics, distance (proxemics) and physical environments/appearance, of voice (paralanguage) and of touch ( haptics). A signal has three different parts to it, including the basic signal, what the signal is trying to convey, and how it is interpreted. These signals that are transmitted to the receiver depend highly on the knowledge and empathy that this individual has. It can also include the use of time (chronemics) and eye contact and the actions of looking while talking and listening, frequency of glances, patterns of fixation, pupil dilation, and blink rate (oculesics). The study of nonverbal communication started in 1872 with the publication of ''The Expression of the Emotions in Man and Animals'' by Charles Darwin. Darwin began to study nonverbal communication ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intuition
Intuition is the ability to acquire knowledge without recourse to conscious reasoning. Different fields use the word "intuition" in very different ways, including but not limited to: direct access to unconscious knowledge; unconscious cognition; gut feelings; inner sensing; inner insight to unconscious pattern-recognition; and the ability to understand something instinctively, without any need for conscious reasoning.Intuition and consciousness – Rosenblatt AD, Thickstun JT. Psychoanal Q. 1994 Oct;63(4):696-714. Intuitive knowledge tends to be approximate. The word ''intuition'' comes from the Latin verb ''intueri'' translated as "consider" or from the late middle English word ''intuit'', "to contemplate". Use of intuition is sometimes referred to as responding to a "gut feeling" or "trusting your gut".Wilding, M.How to Stop Overthinking and Start Trusting your Gut ''Harvard Business Review'', published 10 March 2022, accessed 21 September 2022 Psychology Freud According to Si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hippocampus
The hippocampus (via Latin from Greek , 'seahorse') is a major component of the brain of humans and other vertebrates. Humans and other mammals have two hippocampi, one in each side of the brain. The hippocampus is part of the limbic system, and plays important roles in the consolidation of information from short-term memory to long-term memory, and in spatial memory that enables navigation. The hippocampus is located in the allocortex, with neural projections into the neocortex in humans, as well as primates. The hippocampus, as the medial pallium, is a structure found in all vertebrates. In humans, it contains two main interlocking parts: the hippocampus proper (also called ''Ammon's horn''), and the dentate gyrus. In Alzheimer's disease (and other forms of dementia), the hippocampus is one of the first regions of the brain to suffer damage; short-term memory loss and disorientation are included among the early symptoms. Damage to the hippocampus can also result from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orbitofrontal Cortex
The orbitofrontal cortex (OFC) is a prefrontal cortex region in the frontal lobes of the brain which is involved in the cognitive process of decision-making. In non-human primates it consists of the association cortex areas Brodmann area 11, 12 and 13; in humans it consists of Brodmann area 10, 11 and 47. The OFC is functionally related to the ventromedial prefrontal cortex.Phillips, LH., MacPherson, SE. & Della Sala, S. (2002). 'Age, cognition and emotion: the role of anatomical segregation in the frontal lobes: the role of anatomical segregation in the frontal lobes'. in J Grafman (ed.), Handbook of Neuropsychology: the frontal lobes. Elsevier Science, Amsterdam, pp. 73-98. Therefore, the region is distinguished due to the distinct neural connections and the distinct functions it performs.Barbas H, Ghashghaei H, Rempel-Clower N, Xiao D (2002) Anatomic basis of functional specialization in prefrontal cortices in primates. In: Handbook of Neuropsychology (Grafman J, ed), pp 1- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inferior Temporal
The inferior temporal gyrus is one of three gyri of the temporal lobe and is located below the middle temporal gyrus, connected behind with the inferior occipital gyrus; it also extends around the infero-lateral border on to the inferior surface of the temporal lobe, where it is limited by the inferior sulcus. This region is one of the higher levels of the ventral stream of visual processing, associated with the representation of objects, places, faces, and colors. It may also be involved in face perception, and in the recognition of numbers and words. The inferior temporal gyrus is the anterior region of the temporal lobe located underneath the central temporal sulcus. The primary function of the occipital temporal gyrus – otherwise referenced as IT cortex – is associated with visual stimuli processing, namely visual object recognition, and has been suggested by recent experimental results as the final location of the ventral cortical visual system. The IT cortex in humans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insular Cortex
The insular cortex (also insula and insular lobe) is a portion of the cerebral cortex folded deep within the lateral sulcus (the fissure separating the temporal lobe from the parietal and frontal lobes) within each hemisphere of the mammalian brain. The insulae are believed to be involved in consciousness and play a role in diverse functions usually linked to emotion or the regulation of the body's homeostasis. These functions include compassion, empathy, taste, perception, motor control, self-awareness, cognitive functioning, interpersonal experience, and awareness of homeostatic emotions such as hunger, pain and fatigue. In relation to these, it is involved in psychopathology. The insular cortex is divided into two parts: the anterior insula and the posterior insula in which more than a dozen field areas have been identified. The cortical area overlying the insula toward the lateral surface of the brain is the operculum (meaning ''lid''). The opercula are formed from parts o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fusiform Gyrus
The fusiform gyrus, also known as the ''lateral occipitotemporal gyrus'','' ''is part of the temporal lobe and occipital lobe in Brodmann area 37. The fusiform gyrus is located between the lingual gyrus and parahippocampal gyrus above, and the inferior temporal gyrus below. Though the functionality of the fusiform gyrus is not fully understood, it has been linked with various neural pathways related to recognition. Additionally, it has been linked to various neurological phenomena such as synesthesia, dyslexia, and prosopagnosia. Anatomy Anatomically, the fusiform gyrus is the largest macro-anatomical structure within the ventral temporal cortex, which mainly includes structures involved in high-level vision. The term fusiform gyrus (lit. "spindle-shaped convolution") refers to the fact that the shape of the gyrus is wider at its centre than at its ends. This term is based on the description of the gyrus by Emil Huschke in 1854. (see also section on history). The fusiform gyrus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amygdala
The amygdala (; plural: amygdalae or amygdalas; also '; Latin from Greek, , ', 'almond', 'tonsil') is one of two almond-shaped clusters of nuclei located deep and medially within the temporal lobes of the brain's cerebrum in complex vertebrates, including humans. Shown to perform a primary role in the processing of memory, decision making, and emotional responses (including fear, anxiety, and aggression), the amygdalae are considered part of the limbic system. The term "amygdala" was first introduced by Karl Friedrich Burdach in 1822. Structure The regions described as amygdala nuclei encompass several structures of the cerebrum with distinct connectional and functional characteristics in humans and other animals. Among these nuclei are the basolateral complex, the cortical nucleus, the medial nucleus, the central nucleus, and the intercalated cell clusters. The basolateral complex can be further subdivided into the lateral, the basal, and the accessory basal nucle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parietal Cortex
The parietal lobe is one of the four major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The parietal lobe is positioned above the temporal lobe and behind the frontal lobe and central sulcus. The parietal lobe integrates sensory information among various modalities, including spatial sense and navigation (proprioception), the main sensory receptive area for the sense of touch in the somatosensory cortex which is just posterior to the central sulcus in the postcentral gyrus, and the dorsal stream of the visual system. The major sensory inputs from the skin (touch, temperature, and pain receptors), relay through the thalamus to the parietal lobe. Several areas of the parietal lobe are important in language processing. The somatosensory cortex can be illustrated as a distorted figure – the cortical homunculus (Latin: "little man") in which the body parts are rendered according to how much of the somatosensory cortex is devoted to them. The superior parietal lobule and in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
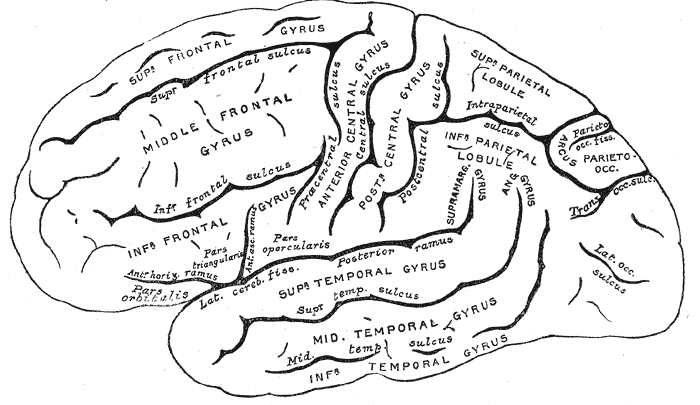
Gyrus
In neuroanatomy, a gyrus (pl. gyri) is a ridge on the cerebral cortex. It is generally surrounded by one or more sulci (depressions or furrows; sg. ''sulcus''). Gyri and sulci create the folded appearance of the brain in humans and other mammals. Structure The gyri are part of a system of folds and ridges that create a larger surface area for the human brain and other mammalian brains. Because the brain is confined to the skull, brain size is limited. Ridges and depressions create folds allowing a larger cortical surface area, and greater cognitive function, to exist in the confines of a smaller cranium. Development The human brain undergoes gyrification during fetal and neonatal development. In embryonic development, all mammalian brains begin as smooth structures derived from the neural tube. A cerebral cortex without surface convolutions is lissencephalic, meaning 'smooth-brained'. As development continues, gyri and sulci begin to take shape on the fetal brain, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Precuneus
In neuroanatomy, the precuneus is the portion of the superior parietal lobule on the medial surface of each brain hemisphere. It is located in front of the cuneus (the upper portion of the occipital lobe). The precuneus is bounded in front by the marginal branch of the cingulate sulcus, at the rear by the parieto-occipital sulcus, and underneath by the subparietal sulcus. It is involved with episodic memory, visuospatial processing, reflections upon self, and aspects of consciousness. The location of the precuneus makes it difficult to study. Furthermore, it is rarely subject to isolated injury due to strokes, or trauma such as gunshot wounds. This has resulted in it being "one of the less accurately mapped areas of the whole cortical surface". While originally described as homogeneous by Korbinian Brodmann, it is now appreciated to contain three subdivisions. It is also known after Achille-Louis Foville as the ''quadrate lobule of Foville''. The Latin form of was first used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medial Prefrontal Cortex
In mammalian brain anatomy, the prefrontal cortex (PFC) covers the front part of the frontal lobe of the cerebral cortex. The PFC contains the Brodmann areas BA8, BA9, BA10, BA11, BA12, BA13, BA14, BA24, BA25, BA32, BA44, BA45, BA46, and BA47. The basic activity of this brain region is considered to be orchestration of thoughts and actions in accordance with internal goals. Many authors have indicated an integral link between a person's will to live, personality, and the functions of the prefrontal cortex. This brain region has been implicated in executive functions, such as planning, decision making, short-term memory, personality expression, moderating social behavior and controlling certain aspects of speech and language. Executive function relates to abilities to differentiate among conflicting thoughts, determine good and bad, better and best, same and different, future consequences of current activities, working toward a defined goal, prediction of outcomes, e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |