|
Gyrus
In neuroanatomy, a gyrus (pl. gyri) is a ridge on the cerebral cortex. It is generally surrounded by one or more sulci (depressions or furrows; sg. ''sulcus''). Gyri and sulci create the folded appearance of the brain in humans and other mammals. Structure The gyri are part of a system of folds and ridges that create a larger surface area for the human brain and other mammalian brains. Because the brain is confined to the skull, brain size is limited. Ridges and depressions create folds allowing a larger cortical surface area, and greater cognitive function, to exist in the confines of a smaller cranium. Development The human brain undergoes gyrification during fetal and neonatal development. In embryonic development, all mammalian brains begin as smooth structures derived from the neural tube. A cerebral cortex without surface convolutions is lissencephalic, meaning 'smooth-brained'. As development continues, gyri and sulci begin to take shape on the fetal brain, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gyri
In neuroanatomy, a gyrus (pl. gyri) is a ridge on the cerebral cortex. It is generally surrounded by one or more sulci (depressions or furrows; sg. ''sulcus''). Gyri and sulci create the folded appearance of the brain in humans and other mammals. Structure The gyri are part of a system of folds and ridges that create a larger surface area for the human brain and other mammalian brains. Because the brain is confined to the skull, brain size is limited. Ridges and depressions create folds allowing a larger cortical surface area, and greater cognitive function, to exist in the confines of a smaller cranium. Development The human brain undergoes gyrification during fetal and neonatal development. In embryonic development, all mammalian brains begin as smooth structures derived from the neural tube. A cerebral cortex without surface convolutions is lissencephalic, meaning 'smooth-brained'. As development continues, gyri and sulci begin to take shape on the fetal brain, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
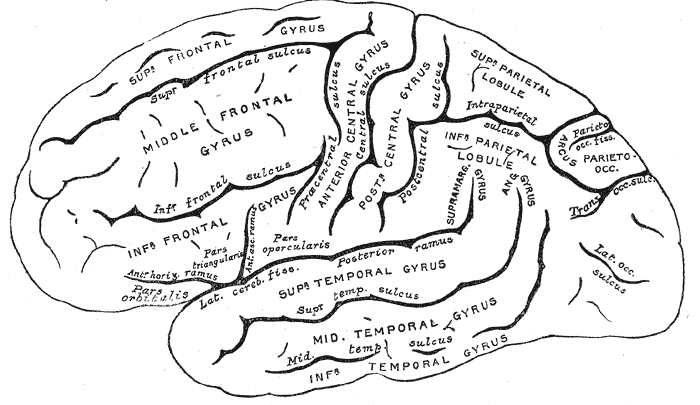
Superior Temporal Gyrus
The superior temporal gyrus (STG) is one of three (sometimes two) gyri in the temporal lobe of the human brain, which is located laterally to the head, situated somewhat above the external ear. The superior temporal gyrus is bounded by: * the lateral sulcus above; * the superior temporal sulcus (not always present or visible) below; * an imaginary line drawn from the preoccipital notch to the lateral sulcus posteriorly. The superior temporal gyrus contains several important structures of the brain, including: * Brodmann areas 41 and 42, marking the location of the auditory cortex, the cortical region responsible for the sensation of sound; * Wernicke's area, Brodmann 22p, an important region for the processing of speech so that it can be understood as language. The superior temporal gyrus contains the auditory cortex, which is responsible for processing sounds. Specific sound frequencies map precisely onto the auditory cortex. This auditory (or tonotopic) map is similar to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Frontal Gyrus
The middle frontal gyrus makes up about one-third of the frontal lobe of the human brain. (A ''gyrus'' is one of the prominent "bumps" or "ridges" on the surface of the human brain.) The middle frontal gyrus, like the inferior frontal gyrus and the superior frontal gyrus, is more of a region in the frontal gyrus than a true gyrus. The borders of the middle frontal gyrus are the ''inferior frontal sulcus'' below; the ''superior frontal sulcus'' above; and the precentral sulcus The precentral sulcus is a part of the human brain that lies parallel to, and in front of, the central sulcus. (A ''sulcus'' is one of the prominent grooves on the surface of the human brain.) The precentral sulcus divides the inferior, middl ... behind. Additional images File:Middle frontal gyrus animation small.gif, Position of middle frontal gyrus (shown in red). File:Gray725 middle frontal gyrus.png, Left cerebral hemisphere seen from above. File:Gray726 middle frontal gyrus.png, Lateral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gyrification
Gyrification is the process of forming the characteristic folds of the cerebral cortex. The peak of such a fold is called a ''gyrus'' (pl. ''gyri''), and its trough is called a '' sulcus'' (pl. ''sulci''). The neurons of the cerebral cortex reside in a thin layer of gray matter, only 2–4 mm thick, at the surface of the brain. Much of the interior volume is occupied by white matter, which consists of long axonal projections to and from the cortical neurons residing near the surface. Gyrification allows a larger cortical surface area and hence greater cognitive functionality to fit inside a smaller cranium. In most mammals, gyrification begins during fetal development. Primates, cetaceans, and ungulates have extensive cortical gyri, with a few species exceptions, while rodents generally have none. Gyrification in some animals, for example the ferret, continues well into postnatal life. Gyrification during human brain development As fetal development proceeds, gyri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orbital Part Of Inferior Frontal Gyrus
The orbital part of inferior frontal gyrus also known as the pars orbitalis is the orbital part of the inferior frontal gyrus. In humans, this region is bordered by the triangular part of the inferior frontal gyrus (pars triangularis) and, surrounding the anterior horizontal limb of the lateral sulcus, a portion of the opercular part of inferior frontal gyrus (pars opercularis). Bounded caudally by the anterior ascending limb of the lateral sulcus, it borders on the insula in the depth of the lateral sulcus. It is bordered anteriorly/inferiorly by the lateral orbital sulcus. Cytoarchitectonically it is most closely represented by Brodmann area 47 Brodmann is a German surname. Notable people with the surname include: *Ines Brodmann (birth date unknown), Swiss orienteer *Korbinian Brodmann (1868–1918), German neurologist *Mario Brodmann (born 1966), Swiss former ice hockey forward *René Br ... (BA47).Brodmann, K. (1909). Vergleichende Lokalisationslehre der Grosshirnrinde in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inferior Frontal Gyrus
The inferior frontal gyrus (IFG), (gyrus frontalis inferior), is the lowest positioned gyrus of the frontal gyri, of the frontal lobe, and is part of the prefrontal cortex. Its superior border is the inferior frontal sulcus (which divides it from the middle frontal gyrus), its inferior border is the lateral sulcus (which divides it from the superior temporal gyrus) and its posterior border is the inferior precentral sulcus. Above it is the middle frontal gyrus, behind it is the precentral gyrus. The inferior frontal gyrus contains Broca's area, which is involved in language processing and speech production. Structure The inferior frontal gyrus is highly convoluted and has three cytoarchitecturally diverse regions. The three subdivisions are an opercular part, a triangular part, and an orbital part. These divisions are marked by two rami arising from the lateral sulcus. The ascending ramus separates the opercular and triangular parts. The anterior (horizontal) ramus separates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polymicrogyria
Polymicrogyria (PMG) is a condition that affects the development of the human brain by multiple small gyri ( microgyri) creating excessive folding of the brain leading to an abnormally thick cortex. This abnormality can affect either one region of the brain or multiple regions. The time of onset has yet to be identified; however, it has been found to occur before birth in either the earlier or later stages of brain development. Early stages include impaired proliferation and migration of neuroblasts, while later stages show disordered post-migration development. The symptoms experienced differ depending on what part of the brain is affected. There is no specific treatment to get rid of this condition, but there are medications that can control the symptoms such as seizures, delayed development or weakened muscles as some of the noted effects. Syndromes Significant technological advances have been made within the past few decades that have allowed more extensive studies to be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuronal Migration Disorder
Neuronal migration disorder (NMD) refers to a heterogenous group of disorders that, it is supposed, share the same etiopathological mechanism: a variable degree of disruption in the migration of neuroblasts during neurogenesis. The neuronal migration disorders are termed cerebral dysgenesis disorders, brain malformations caused by primary alterations during neurogenesis; on the other hand, brain malformations are highly diverse and refer to any insult to the brain during its formation and maturation due to intrinsic or extrinsic causes that ultimately will alter the normal brain anatomy. However, there is some controversy in the terminology because virtually any malformation will involve neuroblast migration, either primarily or secondarily. Symptoms and signs Symptoms vary according to the abnormality, but often feature poor muscle tone and motor function, seizures, developmental delays, mental retardation Intellectual disability (ID), also known as general learning disabilit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuronal Migration Disorders
Neuronal migration disorder (NMD) refers to a heterogenous group of disorders that, it is supposed, share the same etiopathological mechanism: a variable degree of disruption in the migration of neuroblasts during neurogenesis. The neuronal migration disorders are termed cerebral dysgenesis disorders, brain malformations caused by primary alterations during neurogenesis; on the other hand, brain malformations are highly diverse and refer to any insult to the brain during its formation and maturation due to intrinsic or extrinsic causes that ultimately will alter the normal brain anatomy. However, there is some controversy in the terminology because virtually any malformation will involve neuroblast migration, either primarily or secondarily. Symptoms and signs Symptoms vary according to the abnormality, but often feature poor muscle tone and motor function, seizures, developmental delays, mental retardation, failure to grow and thrive, difficulties with feeding, swelling in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulcus (neuroanatomy)
In neuroanatomy, a sulcus (Latin: "furrow", pl. ''sulci'') is a depression or groove in the cerebral cortex. It surrounds a gyrus (pl. gyri), creating the characteristic folded appearance of the brain in humans and other mammals. The larger sulci are usually called fissures. Structure Sulci, the grooves, and gyri, the folds or ridges, make up the folded surface of the cerebral cortex. Larger or deeper sulci are termed fissures, and in many cases the two terms are interchangeable. The folded cortex creates a larger surface area for the brain in humans and other mammals. When looking at the human brain, two-thirds of the surface are hidden in the grooves. The sulci and fissures are both grooves in the cortex, but they are differentiated by size. A sulcus is a shallower groove that surrounds a gyrus. A fissure is a large furrow that divides the brain into lobes and also into the two hemispheres as the longitudinal fissure. Importance of expanded surface area As the surfac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulcus (neuroanatomy)
In neuroanatomy, a sulcus (Latin: "furrow", pl. ''sulci'') is a depression or groove in the cerebral cortex. It surrounds a gyrus (pl. gyri), creating the characteristic folded appearance of the brain in humans and other mammals. The larger sulci are usually called fissures. Structure Sulci, the grooves, and gyri, the folds or ridges, make up the folded surface of the cerebral cortex. Larger or deeper sulci are termed fissures, and in many cases the two terms are interchangeable. The folded cortex creates a larger surface area for the brain in humans and other mammals. When looking at the human brain, two-thirds of the surface are hidden in the grooves. The sulci and fissures are both grooves in the cortex, but they are differentiated by size. A sulcus is a shallower groove that surrounds a gyrus. A fissure is a large furrow that divides the brain into lobes and also into the two hemispheres as the longitudinal fissure. Importance of expanded surface area As the surfac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polymicrogyria
Polymicrogyria (PMG) is a condition that affects the development of the human brain by multiple small gyri ( microgyri) creating excessive folding of the brain leading to an abnormally thick cortex. This abnormality can affect either one region of the brain or multiple regions. The time of onset has yet to be identified; however, it has been found to occur before birth in either the earlier or later stages of brain development. Early stages include impaired proliferation and migration of neuroblasts, while later stages show disordered post-migration development. The symptoms experienced differ depending on what part of the brain is affected. There is no specific treatment to get rid of this condition, but there are medications that can control the symptoms such as seizures, delayed development or weakened muscles as some of the noted effects. Syndromes Significant technological advances have been made within the past few decades that have allowed more extensive studies to be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |