|
Sigma Complex
In chemistry, a sigma complex or σ-complex usually refers to a family of coordination complexes where one or more ligand interacts with the metal using the bonding electrons in a sigma bond. Dihydrogen complexes are examples. Transition metal silane complexes are often especially stable sigma complexes. A subset of sigma complexes are agostic complexes, where a C-H sigma bond functions as the donor ligand. In some cases, even C-C bonds function as sigma ligands. Sigma complexes are of great mechanistic significance, despite their frequent fragility. They represent an initial interaction between the metal center and saturated substrates. Sigma complexes are generally assumed to be intermediates prior to full oxidative addition Oxidative addition and reductive elimination are two important and related classes of reactions in organometallic chemistry. Oxidative addition is a process that increases both the oxidation state and coordination number of a metal centre. Oxidat ... ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HFe H2 Dppe 2 , a solvent
{{disambiguation ...
HFE may refer to: * HFE (gene), a gene that encodes the Human hemochromatosis protein * H-parameter model (hFE), the current gain of a bipolar junction transistor * Health First Europe * Hefei Luogang International Airport, in Anhui, China, now defunct * Hefei Xinqiao International Airport, in Anhui, China * Hello from Earth, an interstellar radio message * Herschend Family Entertainment Corporation, an American entertainment company * Hertford East railway station, in England * Hidden Field Equations, a cryptosystem * Horizontal Fiscal Equalisation, in Australia * Human factors engineering * Hydrofluoroether Hydrofluoroethers (HFE) are a class of organic solvents. As non-ozone-depleting chemicals, they were developed originally as a replacement for CFCs, HFCs, HCFCs, and PFCs. They are typically colorless, odorless, tasteless, low toxicity, low visc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coordination Complex
A coordination complex consists of a central atom or ion, which is usually metallic and is called the ''coordination centre'', and a surrounding array of bound molecules or ions, that are in turn known as ''ligands'' or complexing agents. Many metal-containing compounds, especially those that include transition metals (elements like titanium that belong to the Periodic Table's d-block), are coordination complexes. Nomenclature and terminology Coordination complexes are so pervasive that their structures and reactions are described in many ways, sometimes confusingly. The atom within a ligand that is bonded to the central metal atom or ion is called the donor atom. In a typical complex, a metal ion is bonded to several donor atoms, which can be the same or different. A polydentate (multiple bonded) ligand is a molecule or ion that bonds to the central atom through several of the ligand's atoms; ligands with 2, 3, 4 or even 6 bonds to the central atom are common. These compl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dihydrogen Complex
Dihydrogen complexes are coordination complexes containing intact H2 as a ligand. They are a subset of sigma complexes. The prototypical complex is W(CO)3( PCy3)2(H2). This class of compounds represent intermediates in metal-catalyzed reactions involving hydrogen. Hundreds of dihydrogen complexes have been reported. Most examples are cationic transition metals complexes with octahedral geometry. Upon complexation, the H−H bond is extended to 0.81–0.82 Å as indicated by neutron diffraction, about a 10% extension relative to the H−H bond in free H2. Some complexes containing multiple hydrogen ligands, i.e. polyhydrides, also exhibit short H−H contacts. It has been suggested that distances 1 Å are better described as dihydride complexes (see figure). Characterization The usual method for characterization is 1H NMR spectroscopy. The magnitude of spin-spin coupling, ''J''HD, is a useful indicator of the strength of the bond between the hydrogen and deuterium in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
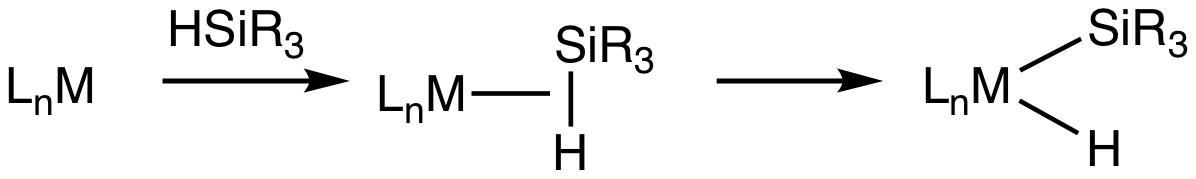
Transition Metal Silane Complexes
Transition metal silane complexes are coordination compounds containing hydrosilane ligands. An early example is (MeC5H4)Mn(CO)2(η2-HSiPh3) (Ph = C6H5). The bonding in silane sigma complexes is similar to that invoked in agostic interactions. The metal center engages the Si-H entity via a 3-center, 2-electron bond. It is widely assumed that these sigma complexes are intermediates in the oxidative addition of hydrosilanes to give metal silyl hydrides. This transformation is invoked in hydrosilylation catalysis. Evidence for sigma-silane complexes is provided by proton NMR spectroscopy. For (MeC5H4)Mn(CO)2(η2-HSiPh3), J(29Si,1H) = 65 Hz compared to 180 Hz in free diphenylsilane. In silyl hydride complexes, the coupling in about 6 Hz. Neutron diffraction Neutron diffraction or elastic neutron scattering is the application of neutron scattering to the determination of the atomic and/or magnetic structure of a material. A sample to be examined is placed in a beam of thermal o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agostic Complex
In organometallic chemistry, agostic interaction refers to the interaction of a coordinatively-unsaturated transition metal with a C−H bond, when the two electrons involved in the C−H bond enter the empty d-orbital of the transition metal, resulting in a three-center two-electron bond. Many catalytic transformations, e.g. oxidative addition and reductive elimination, are proposed to proceed via intermediates featuring agostic interactions. Agostic interactions are observed throughout organometallic chemistry in alkyl, alkylidene, and polyenyl ligands. History The term agostic, derived from the Ancient Greek word for "to hold close to oneself", was coined by Maurice Brookhart and Malcolm Green, on the suggestion of the classicist Jasper Griffin, to describe this and many other interactions between a transition metal and a C−H bond. Often such agostic interactions involve alkyl or aryl groups that are held close to the metal center through an additional σ-bond.. Short ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxidative Addition
Oxidative addition and reductive elimination are two important and related classes of reactions in organometallic chemistry. Oxidative addition is a process that increases both the oxidation state and coordination number of a metal centre. Oxidative addition is often a step in catalytic cycles, in conjunction with its reverse reaction, reductive elimination. Role in transition metal chemistry For transition metals, oxidative reaction results in the decrease in the d''n'' to a configuration with fewer electrons, often 2e fewer. Oxidative addition is favored for metals that are (i) basic and/or (ii) easily oxidized. Metals with a relatively low oxidation state often satisfy one of these requirements, but even high oxidation state metals undergo oxidative addition, as illustrated by the oxidation of Pt(II) with chlorine: : tCl4sup>2− + Cl2 → tCl6sup>2− In classical organometallic chemistry, the formal oxidation state of the metal and the electron count of the complex both in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transition Metals
In chemistry, a transition metal (or transition element) is a chemical element in the d-block of the periodic table (groups 3 to 12), though the elements of group 12 (and less often group 3) are sometimes excluded. They are the elements that can use d orbitals as valence orbitals to form chemical bonds. The lanthanide and actinide elements (the f-block) are called inner transition metals and are sometimes considered to be transition metals as well. Since they are metals, they are lustrous and have good electrical and thermal conductivity. Most (with the exception of group 11 and group 12) are hard and strong, and have high melting and boiling temperatures. They form compounds in any of two or more different oxidation states and bind to a variety of ligands to form coordination complexes that are often coloured. They form many useful alloys and are often employed as catalysts in elemental form or in compounds such as coordination complexes and oxides. Most are strongly paramagn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |