|
Siege Of Saint-Omer
The siege of Saint-Omer (24 May – 16 July 1638) was a siege in the Thirty Years' War in which a French army under Gaspard III de Coligny, Maréchal de Châtillon, laid siege to the Flemish city of Saint-Omer, defended by a small garrison in command of Lancelot II Schetz, count of Grobbendonck. Despite several initial successes in the capture of the minor forts around Saint-Omer, on the night of 8/9 June a Spanish relief army under Thomas Francis, Prince of Carignano surprised Châtillon's troops and established a small fort in the middle of the French lines.Parrott p. 128 An entire army corps under Maréchal de La Force was ordered to move towards Saint-Omer to support Châtillon siege, but on 12 July a further Imperial-Spanish force commanded by Ottavio Piccolomini entered Saint-Omer, resolving the French marshals to withdraw. Background In June 1635 the allied armies of the Dutch Republic and France invaded the Spanish Netherlands from two sides and joined forces in the val ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War was one of the longest and most destructive conflicts in European history The history of Europe is traditionally divided into four time periods: prehistoric Europe (prior to about 800 BC), classical antiquity (800 BC to AD 500), the Middle Ages (AD 500 to AD 1500), and the modern era (since AD 1500). The first early ..., lasting from 1618 to 1648. Fought primarily in Central Europe, an estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians died as a result of battle, famine, and disease, while some areas of what is now modern Germany experienced population declines of over 50%. Related conflicts include the Eighty Years' War, the War of the Mantuan Succession, the Franco-Spanish War (1635–1659), Franco-Spanish War, and the Portuguese Restoration War. Until the 20th century, historians generally viewed it as a continuation of the religious struggle initiated by the 16th-century Reformation within the Holy Roman Empire. The 1555 Peace of Augsburg atte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meuse
The Meuse ( , , , ; wa, Moûze ) or Maas ( , ; li, Maos or ) is a major European river, rising in France and flowing through Belgium and the Netherlands before draining into the North Sea from the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta. It has a total length of . History From 1301 the upper Meuse roughly marked the western border of the Holy Roman Empire with the Kingdom of France, after Count Henry III of Bar had to receive the western part of the County of Bar (''Barrois mouvant'') as a French fief from the hands of King Philip IV. In 1408, a Burgundian army led by John the Fearless went to the aid of John III against the citizens of Liège, who were in open revolt. After the battle which saw the men from Liège defeated, John ordered the drowning in the Meuse of suspicious burghers and noblemen in Liège. The border remained stable until the annexation of the Three Bishoprics Metz, Toul and Verdun by King Henry II in 1552 and the occupation of the Duchy of Lorraine by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avesnes
Avesnes () is a commune in the Pas-de-Calais department in northern France. Geography The commune is a very small village situated some 12 miles (19 km) northeast of Montreuil-sur-Mer, on the D 129 E 1. Population See also *Communes of the Pas-de-Calais department The following is a list of the 890 communes of the Pas-de-Calais department of France. The communes cooperate in the following intercommunalities (as of 2020):Communes of Pas-de-Calais {{PasdeCalais-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peace Of Prague (1635)
The Peace of Prague (, ), signed on 30 May 1635, ended Saxony's participation in the Thirty Years War. Other German princes subsequently joined the treaty and although the Thirty Years War continued, it is generally agreed Prague ended it as a war of religion within the Holy Roman Empire. Thereafter, the conflict was largely driven by foreign powers, including Spain, Sweden, and France. Some scholars regard the treaty merely as a step towards the terms of the 1648 Peace of Westphalia, but others recognise it as an important treaty in its own right that marked the boundaries between two historical eras. European historians generally pay more attention to the Peace of Prague than their non-European colleagues, who are more focused on Westphalia. Background The Thirty Years' War began in 1618 when Frederick, the Protestant ruler of the Palatinate, accepted the crown of Bohemia. Many Germans remained neutral and viewed it as an inheritance dispute. With Bavarian support, Emper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
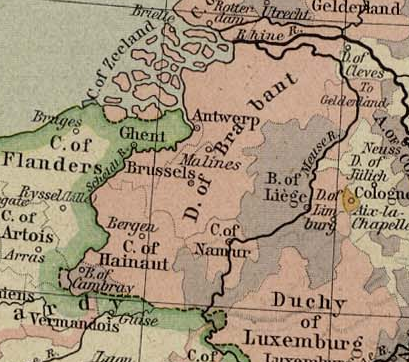
Duchy Of Brabant
The Duchy of Brabant was a State of the Holy Roman Empire established in 1183. It developed from the Landgraviate of Brabant and formed the heart of the historic Low Countries, part of the Burgundian Netherlands from 1430 and of the Habsburg Netherlands from 1482, until it was partitioned after the Dutch revolt. Present-day North Brabant (''Noord-Brabant'') was ceded to the Generality Lands of the Dutch Republic according to the 1648 Peace of Westphalia, while the reduced duchy remained part of the Habsburg Netherlands until it was conquered by French Revolutionary forces in 1794, which was recognized by treaty in 1797. Today all the duchy's former territories, apart from exclaves, are in Belgium except for the Dutch province of North Brabant. Geography The Duchy of Brabant (adjective: ''Brabantian'' or '' Brabantine'') was historically divided into four parts, each with its own capital. The four capitals were Leuven, Brussels, Antwerp and 's-Hertogenbosch. Before 's-Hertogenb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Rhine
The Lower Rhine (german: Niederrhein; kilometres 660 to 1,033 of the river Rhine) flows from Bonn, Germany, to the North Sea at Hook of Holland, Netherlands (including the Nederrijn or "Nether Rhine" within the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta); alternatively, ''Lower Rhine'' may refer to the part upstream of Pannerdens Kop, excluding the Nederrijn. Almost immediately after entering the Netherlands, the Rhine splits into numerous branches. The main branch is called the Waal which flows from Nijmegen to meet the Meuse; after which it is called Merwede. Near Rotterdam the river is known as Nieuwe Maas, and becomes the Nieuwe Waterweg flowing into the North Sea at Hook of Holland. The downstream Lower Rhine is a low lying land. Up to the beginning of industrialization roughly one fifth of the land area could only be used as pasture: an endless meadow, which could not be farmed because of flooding and a high ground-water level. However, the remaining soils of the Lower Rhine were alwa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matthias Gallas
Matthias Gallas, Graf von Campo und Herzog von Lucera (Count of Campo, Duke of Lucera) (Matteo Gallasso; 17 October 1588 in Trento – 25 April 1647 in Vienna) was an Austrian professional soldier during the Thirty Years' War. He distinguished himself in the first half of the war in service of the Catholic League, in the War of the Mantuan Succession, and as one of Albrecht von Wallenstein's Generals. After carrying out the dismissal and elimination of Wallenstein, Gallas became acting supreme commander of the Imperial Army three times between 1634 and 1647 but he never held the function or authority of a Generalissimo. He was a principal architect of the victory of Nördlingen 1634 but his following campaigns were less successful. After leading ineffective offensives against France, he managed to end Swedish attacks on Saxony and to drive them back to the Baltic coast in 1637. Unable to eliminate them or sustain his own forces in the devastated Pomerania, Gallas retreated with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles IV, Duke Of Lorraine
Charles IV (5 April 1604, Nancy – 18 September 1675, Allenbach) was Duke of Lorraine from 1624 until his death in 1675, with a brief interruption in 1634, when he abdicated under French pressure in favor of his younger brother, Nicholas Francis. Life He came to lose his duchy because of his notionally anti-French policy; in 1633, French troops invaded Lorraine in retaliation for Charles's support of Gaston d'Orléans—who repeatedly plotted against Richelieu's governance of France under the childless Louis XIII and treated dangerously with its enemies as a young heir presumptive—and Richelieu's policies were always anti-Habsburg so as to increase the strength and prestige of France at the expense of the two dynasties. Gaston d'Orléans, frequently sided with either branch of the Habsburg family against Richelieu, who was ''de facto'' ruler of France as its Chief Minister, and had to flee several times to avoid charges and trial for treason. His allies and confederates gene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Justus Sustermans 043
Justus (died on 10 November between 627 and 631) was the fourth Archbishop of Canterbury. He was sent from Italy to England by Pope Gregory the Great, on a mission to Christianize the Anglo-Saxons from their native paganism, probably arriving with the second group of missionaries despatched in 601. Justus became the first Bishop of Rochester in 604, and attended a church council in Paris in 614. Following the death of King Æthelberht of Kent in 616, Justus was forced to flee to Gaul, but was reinstated in his diocese the following year. In 624 Justus became Archbishop of Canterbury, overseeing the despatch of missionaries to Northumbria. After his death he was revered as a saint, and had a shrine in St Augustine's Abbey, Canterbury. Arrival in Britain Justus was a member of the Gregorian mission sent to England by Pope Gregory I. Almost everything known about Justus and his career is derived from the early 8th-century ''Historia ecclesiastica gentis Anglorum'' o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Schenkenschans
The siege of Schenkenschans (30 July 1635 – 30 April 1636) was a major siege of the Eighty Years' War. In a successful campaign the Army of Flanders, commanded by Spanish general Cardinal-Infante Ferdinand of Austria, captured Schenkenschans along with a number of important towns, reversing recent Dutch gains and opening the Dutch Republic to a possible invasion. The Dutch Stadtholder, Fredrick Henry, pushed the republic's military efforts to their limit to recapture the fortress of Schenkenschans to counter the threat to the exposed Dutch heartland. He succeeded in doing so after a costly nine month siege. Background The fortress with the name ''Schenkenschans'' ( en, Schenk's Sconce, es, Esquenque) was founded by the German mercenary commander Maarten Schenk van Nydeggen on the orders of stadtholder Adolf van Nieuwenaar in 1586. Its location was strategically chosen, because it dominated the place where in 1586 the Rhine and the Waal River forked (currently these river ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duchy Of Cleves
The Duchy of Cleves (german: Herzogtum Kleve; nl, Hertogdom Kleef) was a State of the Holy Roman Empire which emerged from the medieval . It was situated in the northern Rhineland on both sides of the Lower Rhine, around its capital Cleves and the towns of Wesel, Kalkar, Xanten, Emmerich, Rees and Duisburg bordering the lands of the Prince-Bishopric of Münster in the east and the Duchy of Brabant in the west. Its history is closely related to that of its southern neighbours: the Duchies of Jülich and Berg, as well as Guelders and the Westphalian county of Mark. The Duchy was archaically known as ''Cleveland'' in English. The duchy's territory roughly covered the present-day German districts of Cleves (northern part), Wesel and the city of Duisburg, as well as adjacent parts of the Limburg, North Brabant and Gelderland provinces in the Netherlands. History In the early 11th century Emperor Henry II entrusted the administration of the ''Klever Reichswald'', a large fores ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tienen
Tienen (; french: Tirlemont ) is a city and municipality in the province of Flemish Brabant, in Flanders, Belgium. The municipality comprises Tienen itself and the towns of Bost, Goetsenhoven, Hakendover, Kumtich, Oorbeek, Oplinter, Sint-Margriete-Houtem and Vissenaken. On 1 January 2017, Tienen had a total population of 34,365. The total area is which gives a population density of . History In the early Middle Ages, the town was probably ruled by an old German family Thienen. During the 1635 to 1659 Franco-Spanish War, Tienen was part of the Spanish Netherlands and was captured by a combined Franco-Dutch army in May 1635. Its capture resulted in one of the most serious atrocities of the Dutch Revolt; the town was sacked, over 200 civilians killed and many buildings damaged, including Catholic churches and monasteries. This ended Dutch prospects of winning over the predominantly Catholic population of the Southern Netherlands. After the 1714 Treaty of Utrecht, the town ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)


.jpg)