|
Serous Demilunes
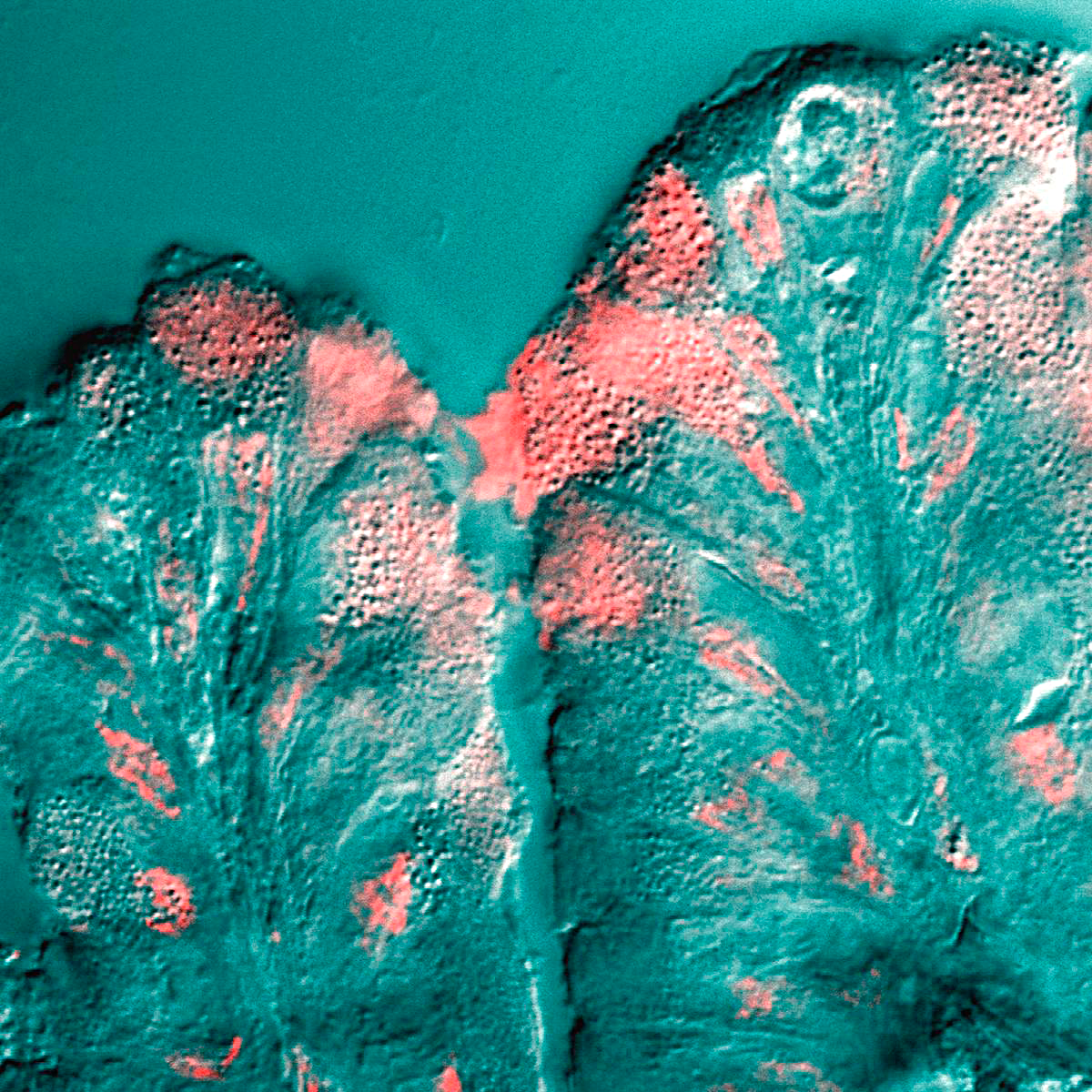
Serous demilunes, also known as Crescents of Giannuzzi or Demilunes of Heidenhain, are cellular formations in the shape of a half-moon (hence the name "demilune") on some salivary glands. Serous demilunes are the serous cells at the distal end of mucous tubuloalveolar secretory unit of certain salivary glands. These demilune cells secrete the proteins that contain the enzyme lysozyme, which degrades the cell walls of bacteria. In this way, lysozyme confers antimicrobial activity to mucus. The serous demilune is an artifact from traditional methods of preparing samples. Samples are traditionally preserved and fixed in formaldehyde. When samples were preserved by quick-freezing in liquid nitrogen and then fixed with osmium tetraoxide in acetone, no demilunes were found. Examination showed that the serous cells and mucosal cells were aligned in the acinus. The traditional preparation caused mucous cells to swell during fixation which results in the serous cells being popped out of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Submaxillary Gland
The paired submandibular glands (historically known as submaxillary glands) are major salivary glands located beneath the floor of the mouth. They each weigh about 15 grams and contribute some 60–67% of unstimulated saliva secretion; on stimulation their contribution decreases in proportion as the parotid secretion rises to 50%. The average length of the normal human submandibular salivary gland is approximately 27mm, while the average width is approximately 14.3mm. Structure Lying superior to the digastric muscles, each submandibular gland is divided into superficial and deep lobes, which are separated by the mylohyoid muscle: * The superficial lobe comprises most of the gland, with the mylohyoid muscle runs under it * The deep lobe is the smaller part Secretions are delivered into the submandibular duct on the deep portion after which they hook around the posterior edge of the mylohyoid muscle and proceed on the superior surface laterally. The excretory ducts are then crosse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salivary Glands
The salivary glands in mammals are exocrine glands that produce saliva through a system of ducts. Humans have three paired major salivary glands ( parotid, submandibular, and sublingual), as well as hundreds of minor salivary glands. Salivary glands can be classified as serous, mucous, or seromucous (mixed). In serous secretions, the main type of protein secreted is alpha-amylase, an enzyme that breaks down starch into maltose and glucose, whereas in mucous secretions, the main protein secreted is mucin, which acts as a lubricant. In humans, 1200 to 1500 ml of saliva are produced every day. The secretion of saliva (salivation) is mediated by parasympathetic stimulation; acetylcholine is the active neurotransmitter and binds to muscarinic receptors in the glands, leading to increased salivation. The fourth pair of salivary glands, the tubarial glands discovered in 2020, are named for their location, being positioned in front and over the torus tubarius. However, this fin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serous
In physiology, serous fluid or serosal fluid (originating from the Medieval Latin word ''serosus'', from Latin ''serum'') is any of various body fluids resembling serum, that are typically pale yellow or transparent and of a benign nature. The fluid fills the inside of body cavities. Serous fluid originates from serous glands, with secretions enriched with proteins and water. Serous fluid may also originate from mixed glands, which contain both mucous and serous cells. A common trait of serous fluids is their role in assisting digestion, excretion, and respiration. In medical fields, especially cytopathology, serous fluid is a synonym for effusion fluids from various body cavities. Examples of effusion fluid are pleural effusion and pericardial effusion. There are many causes of effusions which include involvement of the cavity by cancer. Cancer in a serous cavity is called a serous carcinoma. Cytopathology evaluation is recommended to evaluate the causes of effusions in these ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lysozyme
Lysozyme (EC 3.2.1.17, muramidase, ''N''-acetylmuramide glycanhydrolase; systematic name peptidoglycan ''N''-acetylmuramoylhydrolase) is an antimicrobial enzyme produced by animals that forms part of the innate immune system. It is a glycoside hydrolase that catalyzes the following process: : Hydrolysis of (1→4)-β-linkages between ''N''-acetylmuramic acid and ''N''-acetyl-D-glucosamine residues in a peptidoglycan and between ''N''-acetyl-D-glucosamine residues in chitodextrins Peptidoglycan is the major component of gram-positive bacterial cell wall. This hydrolysis in turn compromises the integrity of bacterial cell walls causing lysis of the bacteria. Lysozyme is abundant in secretions including tears, saliva, human milk, and mucus. It is also present in cytoplasmic granules of the macrophages and the polymorphonuclear neutrophils (PMNs). Large amounts of lysozyme can be found in egg white. C-type lysozymes are closely related to α-lactalbumin in sequence and struc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit soil, water, Hot spring, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep biosphere of Earth's crust. Bacteria are vital in many stages of the nutrient cycle by recycling nutrients such as the nitrogen fixation, fixation of nitrogen from the Earth's atmosphere, atmosphere. The nutrient cycle includes the decomposition of cadaver, dead bodies; bacteria are responsible for the putrefaction stage in this process. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, extremophile bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, such as hydrogen sulp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mucus
Mucus ( ) is a slippery aqueous secretion produced by, and covering, mucous membranes. It is typically produced from cells found in mucous glands, although it may also originate from mixed glands, which contain both serous and mucous cells. It is a viscous colloid containing inorganic salts, antimicrobial enzymes (such as lysozymes), immunoglobulins (especially IgA), and glycoproteins such as lactoferrin and mucins, which are produced by goblet cells in the mucous membranes and submucosal glands. Mucus serves to protect epithelial cells in the linings of the respiratory, digestive, and urogenital systems, and structures in the visual and auditory systems from pathogenic fungi, bacteria and viruses. Most of the mucus in the body is produced in the gastrointestinal tract. Amphibians, fish, snails, slugs, and some other invertebrates also produce external mucus from their epidermis as protection against pathogens, and to help in movement and is also produced in fish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formaldehyde
Formaldehyde ( , ) (systematic name methanal) is a naturally occurring organic compound with the formula and structure . The pure compound is a pungent, colourless gas that polymerises spontaneously into paraformaldehyde (refer to section Forms below), hence it is stored as an aqueous solution (formalin), which is also used to store animal specimens. It is the simplest of the aldehydes (). The common name of this substance comes from its similarity and relation to formic acid. Formaldehyde is an important precursor to many other materials and chemical compounds. In 1996, the installed capacity for the production of formaldehyde was estimated at 8.7 million tons per year. It is mainly used in the production of industrial resins, e.g., for particle board and coatings. Forms Formaldehyde is more complicated than many simple carbon compounds in that it adopts several diverse forms. These compounds can often be used interchangeably and can be interconverted. *Molecular forma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liquid Nitrogen
Liquid nitrogen—LN2—is nitrogen in a liquid state at low temperature. Liquid nitrogen has a boiling point of about . It is produced industrially by fractional distillation of liquid air. It is a colorless, low viscosity liquid that is widely used as a coolant. Physical properties The diatomic character of the N2 molecule is retained after liquefaction. The weak van der Waals interaction between the N2 molecules results in little interatomic interaction, manifested in its very low boiling point. The temperature of liquid nitrogen can readily be reduced to its freezing point by placing it in a vacuum chamber pumped by a vacuum pump. Liquid nitrogen's efficiency as a coolant is limited by the fact that it boils immediately on contact with a warmer object, enveloping the object in an insulating layer of nitrogen gas bubbles. This effect, known as the Leidenfrost effect, occurs when any liquid comes in contact with a surface which is significantly hotter than its boil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetone
Acetone (2-propanone or dimethyl ketone), is an organic compound with the formula . It is the simplest and smallest ketone (). It is a colorless, highly volatile and flammable liquid with a characteristic pungent odour. Acetone is miscible with water and serves as an important organic solvent in its own right, in industry, home, and laboratory. About 6.7 million tonnes were produced worldwide in 2010, mainly for use as a solvent and production of methyl methacrylate (and from that PMMA) as well as bisphenol A.Acetone World Petrochemicals report, January 2010Stylianos Sifniades, Alan B. Levy, "Acetone" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2005. It is a common building block in |
Acinus
An acinus (; plural, acini; adjective, acinar or acinous) refers to any cluster of cells that resembles a many-lobed "berry," such as a raspberry (''acinus'' is Latin for "berry"). The berry-shaped termination of an exocrine gland, where the secretion is produced, is acinar in form, as is the alveolar sac containing multiple alveoli in the lungs. Exocrine glands Acinar exocrine glands are found in many organs, including: * the stomach * the sebaceous gland of the scalp * the salivary glands of the tongue * the liver * the lacrimal glands * the mammary glands * the pancreas * the bulbourethral (Cowper's) glands The thyroid follicles can also be considered of acinar formation but in this case the follicles, being part of an ''endocrine'' gland, act as a hormonal deposit rather than to facilitate secretion. Mucous acini usually stain pale, while serous acini usually stain dark. Lungs The end of the terminal bronchioles in the lungs mark the beginning of a pulmonary a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secretions
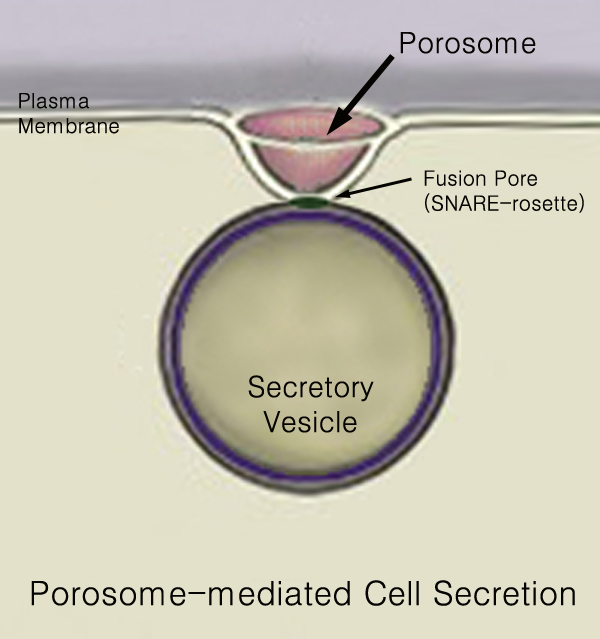
440px Secretion is the movement of material from one point to another, such as a secreted chemical substance from a cell or gland. In contrast, excretion is the removal of certain substances or waste products from a cell or organism. The classical mechanism of cell secretion is via secretory portals at the plasma membrane called porosomes. Porosomes are permanent cup-shaped lipoprotein structures embedded in the cell membrane, where secretory vesicles transiently dock and fuse to release intra-vesicular contents from the cell. Secretion in bacterial species means the transport or translocation of effector molecules for example: proteins, enzymes or toxins (such as cholera toxin in pathogenic bacteria e.g. ''Vibrio cholerae'') from across the interior (cytoplasm or cytosol) of a bacterial cell to its exterior. Secretion is a very important mechanism in bacterial functioning and operation in their natural surrounding environment for adaptation and survival. In eukaryotic cells M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giuseppe Oronzo Giannuzzi
Giuseppe Oronzo Giannuzzi (March 16, 1838, Altamura, Italy – March 8, 1876, Siena, Italy) was an Italian physiologist. His most important discovery is one of the serous demilunes, or crescents: cellular formations that are on some submaxillary salivary glands. After graduating in medicine in Pisa in 1861,Libro Dottorati dall'anno 1835 all'anno 1860 (ASP) Sez. D. II. 10, N. 3483 he studied at Claude Bernard's laboratory in Paris. In 1864 he moved to Berlin in the school of Rudolf Virchow under the leadership of Wilhelm Kühne. He was also at Carl Ludwig's laboratory in Leipzig. In 1867 he became professor of Physiology at the University of Siena The University of Siena ( it, Università degli Studi di Siena, abbreviation: UNISI) in Siena, Tuscany, is one of the oldest and first publicly funded universities in Italy. Originally called ''Studium Senese'', the institution was founded in 1240 ... where he carried out original research. He founded the "Rivista Scientifica" and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |