|
Statue Of Israel Putnam
''General Israel Putnam'' is a monumental statue in Hartford, Connecticut, United States. Located in the city's Bushnell Park, the statue was designed by sculptor John Quincy Adams Ward and honors Israel Putnam, a military officer in the Continental Army during the American Revolutionary War. The statue was largely paid for by a donation from judge Joseph P. Allyn and was dedicated in a large ceremony in 1874. It was one of the first statues to be erected in the park, which nowadays houses several other monuments to famous Connecticut residents. From an artistic standpoint, the statue has received mixed reviews from critics. History Israel Putnam was a military officer who served as a major general in the Continental Army during the American Revolutionary War. Born in Salem, Massachusetts in 1718, he moved to Connecticut in 1739 and died there in 1790, having become a folk hero in the state. In 1869, Joseph P. Allyn, a judge from the state capital of Hartford, Connecticu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bushnell Park
Bushnell Park in Hartford, Connecticut is the oldest publicly funded park in the United States. It was conceived by the Reverend Horace Bushnell in the mid-1850s at a time when the need for open public spaces was just starting to be recognized. Today the park comprises of green space, and is visited by over one million people each year. Paths through the park contribute to the East Coast Greenway. History Hartford in the 1850s was a rapidly growing river town, doubling in population from 1850 to 1860. The city's economy was booming, driven by industries such as publishing, insurance, banking, munitions, manufacturing and river shipping. Like many American cities of the time, Hartford was enjoying the benefits of the Industrial Revolution. But along with this growth came some growing pains, including crime, crowded tenements, poverty, poor sanitation, polluted water and air. It was in this context that Bushnell presented an idea that had not been suggested in any other American ci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the List of United States cities by population, most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the List of United States cities by population density, most densely populated major city in the United States, and is more than twice as populous as second-place Los Angeles. New York City lies at the southern tip of New York (state), New York State, and constitutes the geographical and demographic center of both the Northeast megalopolis and the New York metropolitan area, the largest metropolitan area in the world by urban area, urban landmass. With over 20.1 million people in its metropolitan statistical area and 23.5 million in its combined statistical area as of 2020, New York is one of the world's most populous Megacity, megacities, and over 58 million people live within of the city. New York City is a global city, global Culture of New ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cravat (early)
The cravat () is a neckband, the forerunner of the modern tailored necktie and bow tie, originating from a style worn by members of the 17th century military unit known as the Croats. The modern British "cravat" is called an "ascot" in American English. From the end of the sixteenth century, the term ''band'' applied to any long-strip neckcloth that was not a ruff. The ruff, a starched, pleated white linen strip, originated earlier in the sixteenth century as a neckcloth (readily changeable, to minimize the soiling of a doublet), as a bib, or as a napkin. A band could be either a plain, attached shirt collar, or a detachable "falling band" that draped over the doublet collar. It is possible that initially, cravats were worn to hide soil on shirts. History According to 1828 encyclopedic ''The art of tying the cravat: demonstrated in sixteen lessons'', the Romans were the first to wear knotted kerchiefs around their neck, but the modern version of the cravat (French: ''la crav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frock Coat
A frock coat is a formal men's coat characterised by a knee-length skirt cut all around the base just above the knee, popular during the Victorian and Edwardian periods (1830s–1910s). It is a fitted, long-sleeved coat with a centre vent at the back and some features unusual in post-Victorian dress. These include the reverse collar and lapels, where the outer edge of the lapel is often cut from a separate piece of cloth from the main body and also a high degree of waist suppression around the waistcoat, where the coat's diameter round the waist is less than round the chest. This is achieved by a high horizontal waist seam with side bodies, which are extra panels of fabric above the waist used to pull in the naturally cylindrical drape. As was usual with all coats in the 19th century, shoulder padding was rare or minimal. In the Age of Revolution around the end of the 18th century, men abandoned the justaucorps with tricorne hats for the directoire style: dress coat with bre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Granite
Granite () is a coarse-grained (phaneritic) intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly cools and solidifies underground. It is common in the continental crust of Earth, where it is found in igneous intrusions. These range in size from dikes only a few centimeters across to batholiths exposed over hundreds of square kilometers. Granite is typical of a larger family of ''granitic rocks'', or ''granitoids'', that are composed mostly of coarse-grained quartz and feldspars in varying proportions. These rocks are classified by the relative percentages of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase (the QAPF classification), with true granite representing granitic rocks rich in quartz and alkali feldspar. Most granitic rocks also contain mica or amphibole minerals, though a few (known as leucogranites) contain almost no dark minerals. Granite is nearly alway ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bronze
Bronze is an alloy consisting primarily of copper, commonly with about 12–12.5% tin and often with the addition of other metals (including aluminium, manganese, nickel, or zinc) and sometimes non-metals, such as phosphorus, or metalloids such as arsenic or silicon. These additions produce a range of alloys that may be harder than copper alone, or have other useful properties, such as ultimate tensile strength, strength, ductility, or machinability. The three-age system, archaeological period in which bronze was the hardest metal in widespread use is known as the Bronze Age. The beginning of the Bronze Age in western Eurasia and India is conventionally dated to the mid-4th millennium BCE (~3500 BCE), and to the early 2nd millennium BCE in China; elsewhere it gradually spread across regions. The Bronze Age was followed by the Iron Age starting from about 1300 BCE and reaching most of Eurasia by about 500 BCE, although bronze continued to be much more widely used than it is in mod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Israel Putnam Statue - Bushnell Park, Hartford, CT
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southeastern shore of the Mediterranean Sea and the northern shore of the Red Sea, and shares borders with Lebanon to the north, Syria to the northeast, Jordan to the east, and Egypt to the southwest. Israel also is bordered by the Palestinian territories of the West Bank and the Gaza Strip to the east and west, respectively. Tel Aviv is the economic and technological center of the country, while its seat of government is in its proclaimed capital of Jerusalem, although Israeli sovereignty over East Jerusalem is unrecognized internationally. The land held by present-day Israel witnessed some of the earliest human occupations outside Africa and was among the earliest known sites of agriculture. It was inhabited by the Canaanites ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Save Outdoor Sculpture!
Save Outdoor Sculpture! (SOS!) was a community-based effort to identify, document, and conserve outdoor sculpture in the United States. The program was initiated in 1989 and ended in 1999. History Save Outdoor Sculpture! was initiated by Heritage Preservation: The National Institute of Conservation in 1989. As of 1998, volunteers had cataloged and assessed the condition of over 30,000 outdoor statues and monuments. The Smithsonian Museum of American Art became an active partner in the SOS! project, making SOS! material available online as part of the Inventory of American Sculpture at the Smithsonian American Art Museum. "Some of the most-requested materials" are available via the Foundation for Advancement in Conservation. Other records and resources for SOS!, including the Heritage Preservation website, including the public art guidance "Designing Outdoor Sculpture Today for Tomorrow", and "Mural Creation Best Practices", were accessioned by and are made accessible by the Sm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Church Brownell
Thomas Church Brownell (October 19, 1779 – January 13, 1865) was founder of Trinity College (Connecticut), Trinity College in Hartford, Connecticut, and Presiding Bishop of the Episcopal Church in the United States of America, Episcopal Church from 1852 to 1865. Biography Brownell was born in Westport, Massachusetts on October 19, 1779. He was a descendant on his mother's side from Benjamin Church (ranger), Colonel Benjamin Church, an early settler in Little Compton, Rhode Island and the father of United States Army Rangers, American ranging. He studied at Union College, Schenectady, New York, receiving his degree in 1804. Brownell was ordained to the diaconate and priesthood by Bishop John Henry Hobart. He was consecrated Bishop of Connecticut in New Haven on October 27, 1819. Brownell's extensive writings include diocesan charges, liturgical material, scriptural commentaries and other works. He founded Washington College (now known as Trinity College (Connecticut), Trini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by states that had seceded. The central cause of the war was the dispute over whether slavery would be permitted to expand into the western territories, leading to more slave states, or be prevented from doing so, which was widely believed would place slavery on a course of ultimate extinction. Decades of political controversy over slavery were brought to a head by the victory in the 1860 U.S. presidential election of Abraham Lincoln, who opposed slavery's expansion into the west. An initial seven southern slave states responded to Lincoln's victory by seceding from the United States and, in 1861, forming the Confederacy. The Confederacy seized U.S. forts and other federal assets within their borders. Led by Confederate President Jefferson Davis, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
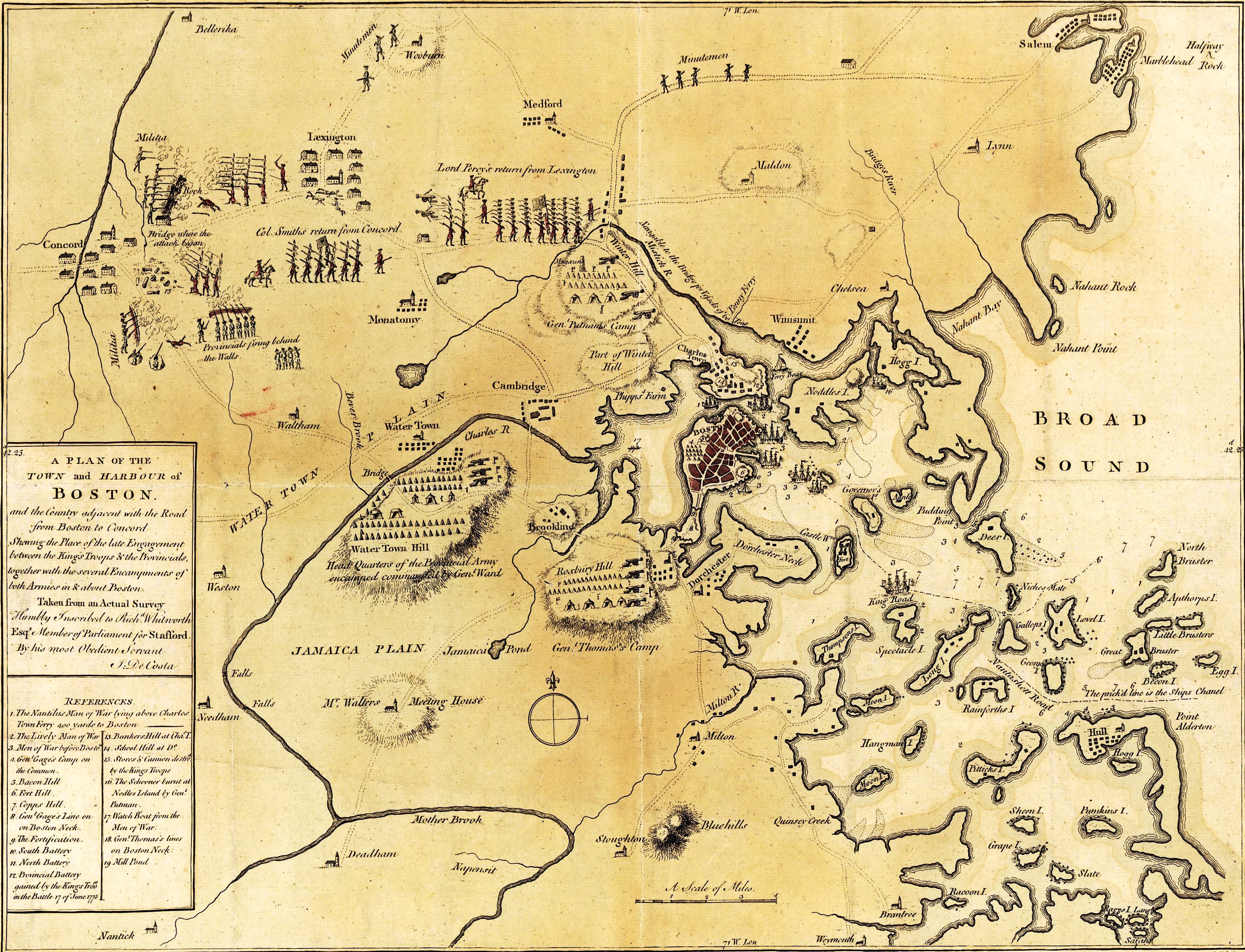
Battle Of Bunker Hill
The Battle of Bunker Hill was fought on June 17, 1775, during the Siege of Boston in the first stage of the American Revolutionary War. The battle is named after Bunker Hill in Charlestown, Massachusetts, which was peripherally involved in the battle. It was the original objective of both the colonial and British troops, though the majority of combat took place on the adjacent hill which later became known as Breed's Hill. On June 13, 1775, the leaders of the colonial forces besieging Boston learned that the British were planning to send troops out from the city to fortify the unoccupied hills surrounding the city, which would give them control of Boston Harbor. In response, 1,200 colonial troops under the command of William Prescott stealthily occupied Bunker Hill and Breed's Hill. During the night, the colonists constructed a strong redoubt on Breed's Hill, as well as smaller fortified lines across the Charlestown Peninsula. By daybreak of June 17, the British became a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philadelphia
Philadelphia, often called Philly, is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, the sixth-largest city in the U.S., the second-largest city in both the Northeast megalopolis and Mid-Atlantic regions after New York City. Since 1854, the city has been coextensive with Philadelphia County, the most populous county in Pennsylvania and the urban core of the Delaware Valley, the nation's seventh-largest and one of world's largest metropolitan regions, with 6.245 million residents . The city's population at the 2020 census was 1,603,797, and over 56 million people live within of Philadelphia. Philadelphia was founded in 1682 by William Penn, an English Quaker. The city served as capital of the Pennsylvania Colony during the British colonial era and went on to play a historic and vital role as the central meeting place for the nation's founding fathers whose plans and actions in Philadelphia ultimately inspired the American Revolution and the nation's inde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)