|
Spectrogram
A spectrogram is a visual representation of the spectrum of frequencies of a signal as it varies with time. When applied to an audio signal, spectrograms are sometimes called sonographs, voiceprints, or voicegrams. When the data are represented in a 3D plot they may be called '' waterfall displays''. Spectrograms are used extensively in the fields of music, linguistics, sonar, radar, speech processing, seismology, and others. Spectrograms of audio can be used to identify spoken words phonetically, and to analyse the various calls of animals. A spectrogram can be generated by an optical spectrometer, a bank of band-pass filters, by Fourier transform or by a wavelet transform (in which case it is also known as a scaleogram or scalogram). A spectrogram is usually depicted as a heat map, i.e., as an image with the intensity shown by varying the colour or brightness. Format A common format is a graph with two geometric dimensions: one axis represents time, and the other a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spectral Density
The power spectrum S_(f) of a time series x(t) describes the distribution of power into frequency components composing that signal. According to Fourier analysis, any physical signal can be decomposed into a number of discrete frequencies, or a spectrum of frequencies over a continuous range. The statistical average of a certain signal or sort of signal (including noise) as analyzed in terms of its frequency content, is called its spectrum. When the energy of the signal is concentrated around a finite time interval, especially if its total energy is finite, one may compute the energy spectral density. More commonly used is the power spectral density (or simply power spectrum), which applies to signals existing over ''all'' time, or over a time period large enough (especially in relation to the duration of a measurement) that it could as well have been over an infinite time interval. The power spectral density (PSD) then refers to the spectral energy distribution that would ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Spectrometer
An optical spectrometer (spectrophotometer, spectrograph or spectroscope) is an instrument used to measure properties of light over a specific portion of the electromagnetic spectrum, typically used in spectroscopic analysis to identify materials. The variable measured is most often the light's intensity but could also, for instance, be the polarization state. The independent variable is usually the wavelength of the light or a unit directly proportional to the photon energy, such as reciprocal centimeters or electron volts, which has a reciprocal relationship to wavelength. A spectrometer is used in spectroscopy for producing spectral lines and measuring their wavelengths and intensities. Spectrometers may operate over a wide range of non-optical wavelengths, from gamma rays and X-rays into the far infrared. If the instrument is designed to measure the spectrum on an absolute scale rather than a relative one, then it is typically called a spectrophotometer. The majority o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
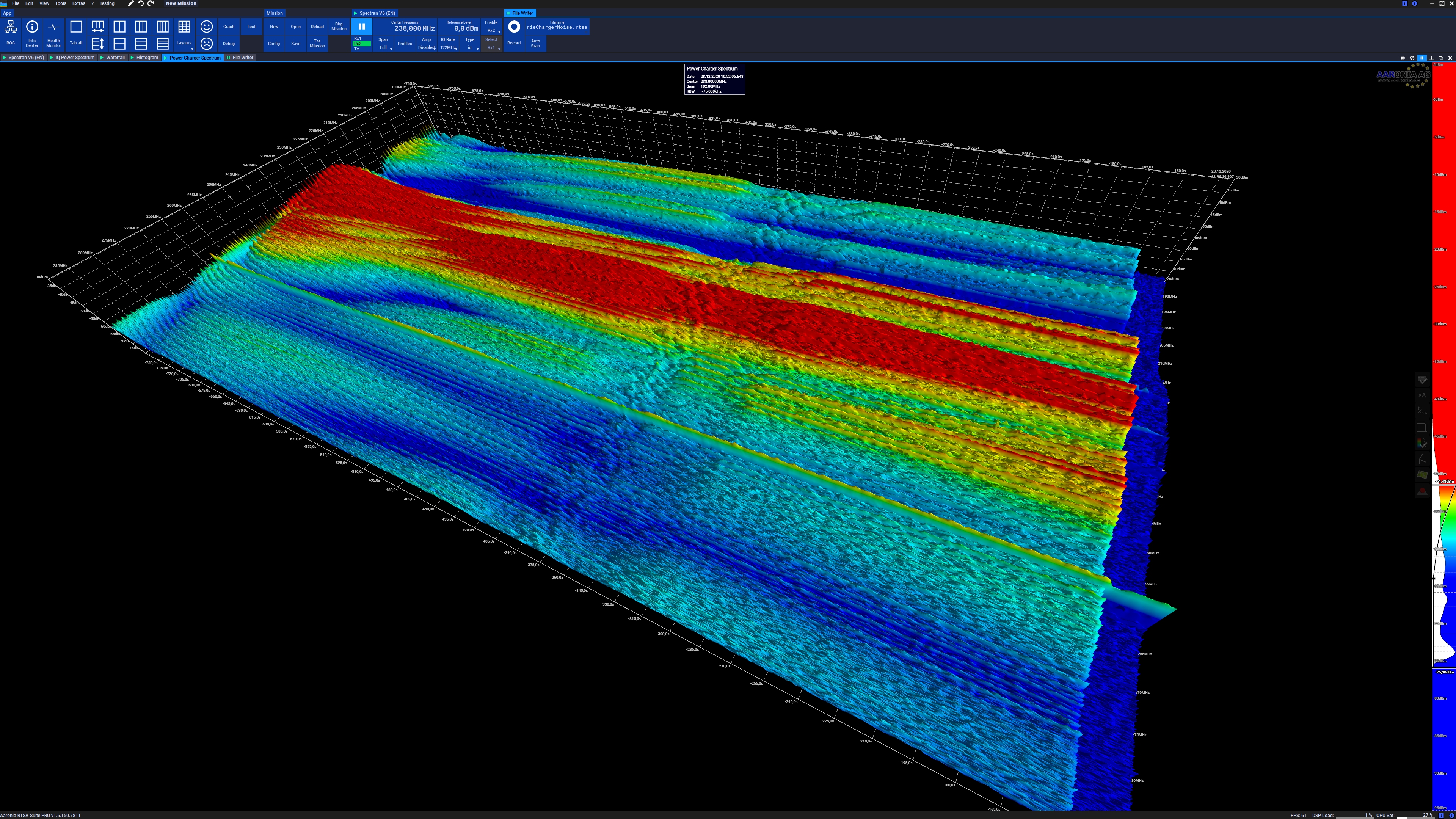
Waterfall Plot
Waterfall plots are often used to show how two-dimensional phenomena change over time. A three-dimensional ''spectral waterfall plot'' is a plot in which multiple curves of data, typically spectra, are displayed simultaneously. Typically the curves are staggered both across the screen and vertically, with "nearer" curves masking the ones behind. The result is a series of "mountain" shapes that appear to be side by side. The waterfall plot is often used to show how two-dimensional information changes over time or some other variable such as rotational speed. Waterfall plots are also often used to depict ''spectrograms'' or ''cumulative spectral decay'' (CSD). Uses * The results of spectral density estimation, showing the spectrum of the signal at successive intervals of time. * The delayed response from a loudspeaker or listening room produced by impulse response testing or MLSSA. * Spectra at different engine speeds when testing engines. See also * Loudspeaker acoustics * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Music
Music is generally defined as the The arts, art of arranging sound to create some combination of Musical form, form, harmony, melody, rhythm or otherwise Musical expression, expressive content. Exact definition of music, definitions of music vary considerably around the world, though it is an aspect of all human societies, a cultural universal. While scholars agree that music is defined by a elements of music, few specific elements, there is Elements of music#Selection of elements, no consensus on their precise definitions. The creation of music is commonly divided into musical composition, musical improvisation, and musical performance, though the topic itself extends into #Academic study, academic disciplines, Music journalism, criticism, Philosophy of music, philosophy, and Music psychology, psychology. Music may be performed or improvised using a vast range of musical instrument, instruments, including the human voice. In some musical contexts, a performance or composi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. It is also occasionally referred to as ''temporal frequency'' for clarity, and is distinct from '' angular frequency''. Frequency is measured in hertz (Hz) which is equal to one event per second. The period is the interval of time between events, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency. For example, if a heart beats at a frequency of 120 times a minute (2 hertz), the period, —the interval at which the beats repeat—is half a second (60 seconds divided by 120 beats). Frequency is an important parameter used in science and engineering to specify the rate of oscillatory and vibratory phenomena, such as mechanical vibrations, audio signals ( sound), radio waves, and light. Definitions and units For cyclical phenomena such as oscillations, waves, or for examples of simple harmonic motion, the term ''frequency'' is defined as the number of cycles or vibrations per unit of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colour
Color (American English) or colour (British English) is the visual perceptual property deriving from the spectrum of light interacting with the photoreceptor cells of the eyes. Color categories and physical specifications of color are associated with objects or materials based on their physical properties such as light absorption, reflection, or emission spectra. By defining a color space, colors can be identified numerically by their coordinates. Because perception of color stems from the varying spectral sensitivity of different types of cone cells in the retina to different parts of the spectrum, colors may be defined and quantified by the degree to which they stimulate these cells. These physical or physiological quantifications of color, however, do not fully explain the psychophysical perception of color appearance. Color science includes the perception of color by the eye and brain, the origin of color in materials, color theory in art, and the physics of elec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brightness
Brightness is an attribute of visual perception in which a source appears to be radiating or reflecting light. In other words, brightness is the perception elicited by the luminance of a visual target. The perception is not linear to luminance, and relies on the context of the viewing environment (for example, see White's illusion). Brightness is a subjective sensation of an object being observed and one of the color appearance parameters of many color appearance models, typically denoted as Q. Brightness refers to how much light ''appears to shine'' from something. This is a different perception than lightness, which is how light something appears ''compared to'' a similarly lit white object. The adjective ''bright'' derives from an Old English ''beorht'' with the same meaning via metathesis giving Middle English ''briht''. The word is from a Common Germanic ', ultimately from a PIE root with a closely related meaning, *' "white, bright". "Brightness" was formerly used as a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Time
Time is the continued sequence of existence and events that occurs in an apparently irreversible succession from the past, through the present, into the future. It is a component quantity of various measurements used to sequence events, to compare the duration of events or the intervals between them, and to quantify rates of change of quantities in material reality or in the conscious experience. Time is often referred to as a fourth dimension, along with three spatial dimensions. Time has long been an important subject of study in religion, philosophy, and science, but defining it in a manner applicable to all fields without circularity has consistently eluded scholars. Nevertheless, diverse fields such as business, industry, sports, the sciences, and the performing arts all incorporate some notion of time into their respective measuring systems. 108 pages. Time in physics is operationally defined as "what a clock reads". The physical nature of time is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amplitude
The amplitude of a periodic variable is a measure of its change in a single period (such as time or spatial period). The amplitude of a non-periodic signal is its magnitude compared with a reference value. There are various definitions of amplitude (see below), which are all functions of the magnitude of the differences between the variable's extreme values. In older texts, the phase of a periodic function is sometimes called the amplitude. Definitions Peak amplitude & semi-amplitude For symmetric periodic waves, like sine wave A sine wave, sinusoidal wave, or just sinusoid is a curve, mathematical curve defined in terms of the ''sine'' trigonometric function, of which it is the graph of a function, graph. It is a type of continuous wave and also a Smoothness, smooth p ...s, square waves or triangle waves ''peak amplitude'' and ''semi amplitude'' are the same. Peak amplitude In audio system measurements, telecommunications and others where the wikt:measurand, measu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |