|
Social Communication Disorder
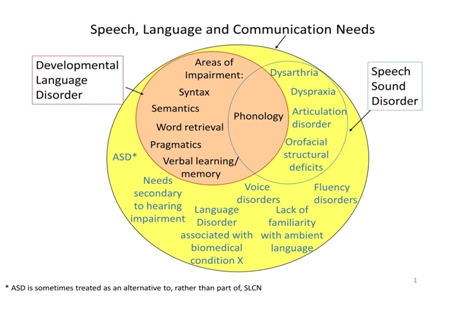
Social (pragmatic) communication disorder (SPCD) - previously called semantic-pragmatic disorder (SPD) or pragmatic language impairment (PLI) - is a disorder in understanding pragmatic aspects of language. People with SPCD have special challenges with the semantic aspect of language (the meaning of what is being said) and the pragmatics of language (using language appropriately in social situations). Individuals have difficulties with verbal and nonverbal social communication. Relates to Pragmatic Language Impairment and Autism Spectrum Disorder. It has only been since 2013 that SPCD has become its own category in the DSM-5. In creating this new category it allowed individuals to be considered with a form of communication disorder ''distinct'' from PLI and ASD. As well, SPCD lacks behaviors associated with restrictions and repetition which are seen in ASD. Presentation # Issues with communication for social purposes # Unable to adapt communication to context # Struggles to follow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Speech–language Pathology
Speech-language pathology (or speech and language pathology) is a healthcare field of expertise practiced globally. Speech-language pathology (SLP) specializes in the evaluation, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of communication disorders ( speech and language impairments), cognitive-communication disorders, voice disorders, and swallowing disorder across the lifespan. It is an independent profession that is sometimes considered a "related health profession" or allied health profession by professional bodies like thAmerican Speech-Language-Hearing Association (ASHA)anSpeech Pathology Australia Allied health professions include audiology, optometry, occupational therapy, rehabilitation psychology, physical therapy and others. The field of speech-language pathology is practiced by a clinician known as a speech-language pathologist (SLP) or a speech and language therapist (SLT), and sometimes as a speech therapist. An SLP is a university-trained individual who provides pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autism Spectrum
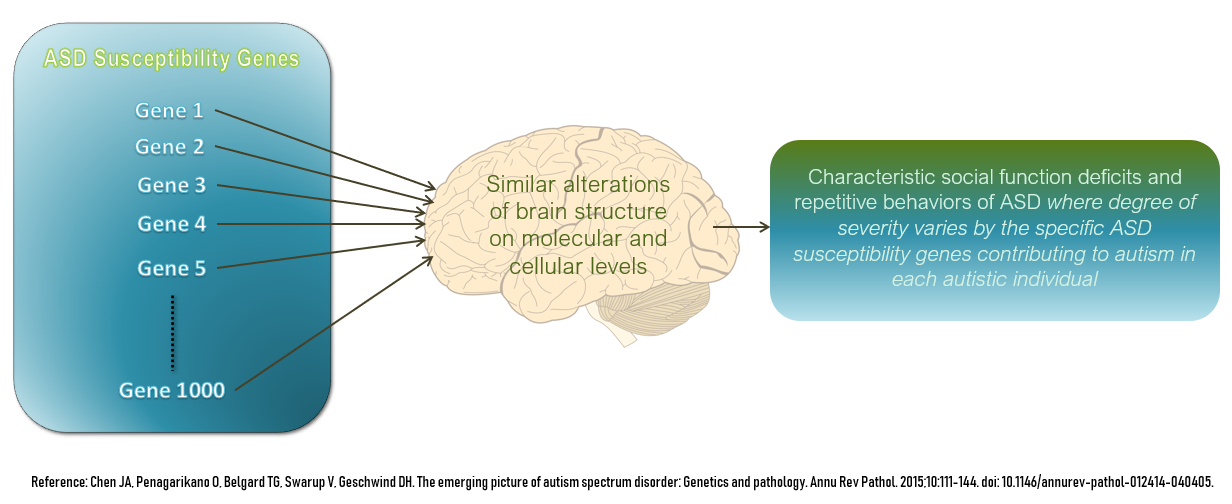
The autism spectrum, often referred to as just autism or in the context of a professional diagnosis autism spectrum disorder (ASD) or autism spectrum condition (ASC), is a neurodevelopmental condition (or conditions) characterized by difficulties in social interaction, verbal and nonverbal communication, and the presence of repetitive behavior and restricted interests. Other common signs include unusual responses to sensory stimuli. Autism is generally understood as a ''spectrum disorder'', which means that it can manifest differently in each person: any given autistic individual is likely to show some, but not all, of the characteristics associated with it, and the person may exhibit them to varying degrees. Some autistic people remain nonspeaking over the course of their lifespan, while others have relatively unimpaired spoken language. There is large variation in the level of support people require, and the same person may present differently at varying times. Historically, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High-functioning Autism
High-functioning autism (HFA) is an autism classification where a person exhibits no intellectual disability, but may exhibit deficits in communication, emotion recognition and expression, and social interaction. HFA is not included in either the American Psychological Association's DSM-5 or the World Health Organization's ICD-10, neither of which subdivides autism based on intellectual capabilities. Characterization High-functioning autism is characterized by features similar to those of Asperger syndrome. The defining characteristic recognized by psychologists is a significant delay in the development of early speech and language skills, before the age of three years. The diagnostic criteria of Asperger syndrome ''exclude'' a general language delay. Further differences in features of people with high-functioning autism from those with Asperger syndrome include the following: * Lower verbal reasoning ability * Better visual/spatial skills (higher performance IQ) * Less devi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autism
The autism spectrum, often referred to as just autism or in the context of a professional diagnosis autism spectrum disorder (ASD) or autism spectrum condition (ASC), is a neurodevelopmental condition (or conditions) characterized by difficulties in social interaction, verbal and nonverbal communication, and the presence of repetitive behavior and restricted interests. Other common signs include unusual responses to sensory stimuli. Autism is generally understood as a ''spectrum disorder'', which means that it can manifest differently in each person: any given autistic individual is likely to show some, but not all, of the characteristics associated with it, and the person may exhibit them to varying degrees. Some autistic people remain nonspeaking over the course of their lifespan, while others have relatively unimpaired spoken language. There is large variation in the level of support people require, and the same person may present differently at varying times. Historically ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterised by excessive amounts of inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity that are pervasive, impairing in multiple contexts, and otherwise age-inappropriate. ADHD symptoms arise from executive dysfunction, and emotional dysregulation is often considered a core symptom. In children, problems paying attention may result in poor school performance. ADHD is associated with other neurodevelopmental and mental disorders as well as some non-psychiatric disorders, which can cause additional impairment, especially in modern society. Although people with ADHD struggle to focus on tasks they are not particularly interested in completing, they are often able to maintain an unusually prolonged and intense level of attention for tasks they do find interesting or rewarding; this is known as hyperfocus. The precise causes of ADHD are unknown in the majority of cases. Genetic factors play an impor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asperger Syndrome
Asperger syndrome (AS), also known as Asperger's, is a former neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by significant difficulties in Interpersonal relationship, social interaction and nonverbal communication, along with restricted and repetitive patterns of behaviour and interests. The syndrome is no longer recognised as a diagnosis in itself, having been merged with other disorders into Autism spectrum, autism spectrum disorder (ASD). It was considered to differ from other diagnoses that were merged into ASD by relatively unimpaired language development, spoken language and cognitive development, intelligence. The syndrome was named after the Austrian Pediatrics, pediatrician Hans Asperger, who, in 1944, described children in his care who struggled to form friendships, did not understand others' Nonverbal communication, gestures or Empathy#Cognitive empathy, feelings, engaged in one-sided conversations about their favourite interests, and were clumsy. In 1994, the diagno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexithymia
Alexithymia is a personality trait characterized by the inability to identify and describe emotions experienced by oneself. The core characteristic of alexithymia is marked dysfunction in emotional awareness, social attachment, and interpersonal relation. Furthermore, people with high levels of alexithymia can have difficulty distinguishing and appreciating the emotions of others, which is thought to lead to unempathic and ineffective emotional responses. High levels of alexithymia occur in approximately 10% of the population and can occur with a number of psychiatric conditions as well as any neurodevelopmental disorder. Difficulty with recognizing and talking about their emotions appears at subclinical levels in men who conform to cultural notions of masculinity (such as thinking that sadness is a feminine emotion). This is called normative male alexithymia by some researchers. However, both alexithymia itself and its association with traditionally masculine norms occur in b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Specific Language Impairment
Specific language impairment (SLI) (the term developmental language disorder is preferred by some) is diagnosed when a child's language does not develop normally and the difficulties cannot be accounted for by generally slow development, physical abnormality of the speech apparatus, autism spectrum disorder, apraxia, acquired brain damage or hearing loss. Twin studies have shown that it is under genetic influence. Although language impairment can result from a single-gene mutation, this is unusual. More commonly SLI results from the combined influence of multiple genetic variants, each of which is found in the general population, as well as environmental influences. Classification Specific language impairment (SLI) is diagnosed when a child has delayed or disordered language development for no apparent reason. Usually the first indication of SLI is that the child is later than usual in starting to speak and subsequently is delayed in putting words together to form sentences. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Developmental Language Disorder
Developmental language disorder (DLD) is identified when a child has problems with language development that continue into school age and beyond. The language problems have a significant impact on everyday social interactions or educational progress, and occur in the absence of autism spectrum disorder, intellectual disability or a known biomedical condition. The most obvious problems are difficulties in using words and sentences to express meanings, but for many children, understanding of language (receptive language) is also a challenge. This may not be evident unless the child is given a formal assessment. Classification Terminology The term developmental language disorder (DLD) was endorsed in a consensus study involving a panel of experts (CATALISE Consortium) in 2017. The study was conducted in response to concerns that a wide range of terminology was used in this area, with the consequence that there was poor communication, lack of public recognition, and in some cases childr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High-functioning Autism
High-functioning autism (HFA) is an autism classification where a person exhibits no intellectual disability, but may exhibit deficits in communication, emotion recognition and expression, and social interaction. HFA is not included in either the American Psychological Association's DSM-5 or the World Health Organization's ICD-10, neither of which subdivides autism based on intellectual capabilities. Characterization High-functioning autism is characterized by features similar to those of Asperger syndrome. The defining characteristic recognized by psychologists is a significant delay in the development of early speech and language skills, before the age of three years. The diagnostic criteria of Asperger syndrome ''exclude'' a general language delay. Further differences in features of people with high-functioning autism from those with Asperger syndrome include the following: * Lower verbal reasoning ability * Better visual/spatial skills (higher performance IQ) * Less devi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Encephalopathies
Encephalopathy (; from grc, ἐνκέφαλος "brain" + πάθος "suffering") means any disorder or disease of the brain, especially chronic degenerative conditions. In modern usage, encephalopathy does not refer to a single disease, but rather to a syndrome of overall brain dysfunction; this syndrome has many possible organic and inorganic causes. Signs and symptoms The hallmark of encephalopathy is an altered mental state or delirium. Characteristic of the altered mental state is impairment of the cognition, attention, orientation, sleep–wake cycle and consciousness. An altered state of consciousness may range from failure of selective attention to drowsiness. Hypervigilance may be present; with or without: cognitive deficits, headache, epileptic seizures, myoclonus (involuntary twitching of a muscle or group of muscles) or asterixis ("flapping tremor" of the hand when wrist is extended). Depending on the type and severity of encephalopathy, common neurological sympt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuropathies
Peripheral neuropathy, often shortened to neuropathy, is a general term describing disease affecting the peripheral nerves, meaning nerves beyond the brain and spinal cord. Damage to peripheral nerves may impair sensation, movement, gland, or organ function depending on which nerves are affected; in other words, neuropathy affecting motor, sensory, or autonomic nerves result in different symptoms. More than one type of nerve may be affected simultaneously. Peripheral neuropathy may be acute (with sudden onset, rapid progress) or chronic (symptoms begin subtly and progress slowly), and may be reversible or permanent. Common causes include systemic diseases (such as diabetes or leprosy), hyperglycemia-induced glycation, vitamin deficiency, medication (e.g., chemotherapy, or commonly prescribed antibiotics including metronidazole and the fluoroquinolone class of antibiotics (such as ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin, moxifloxacin)), traumatic injury, ischemia, radiation therapy, excessiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |