|
Singular Perturbation
In mathematics, a singular perturbation problem is a problem containing a small parameter that cannot be approximated by setting the parameter value to zero. More precisely, the solution cannot be uniformly approximated by an asymptotic expansion :\varphi(x) \approx \sum_^N \delta_n(\varepsilon) \psi_n(x) \, as \varepsilon \to 0. Here \varepsilon is the small parameter of the problem and \delta_n(\varepsilon) are a sequence of functions of \varepsilon of increasing order, such as \delta_n(\varepsilon) = \varepsilon^n. This is in contrast to regular perturbation problems, for which a uniform approximation of this form can be obtained. Singularly perturbed problems are generally characterized by dynamics operating on multiple scales. Several classes of singular perturbations are outlined below. The term "singular perturbation" was coined in the 1940s by Kurt Otto Friedrichs and Wolfgang R. Wasow. Methods of analysis A perturbed problem whose solution can be approximated on the wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics with the major subdisciplines of number theory, algebra, geometry, and analysis, respectively. There is no general consensus among mathematicians about a common definition for their academic discipline. Most mathematical activity involves the discovery of properties of abstract objects and the use of pure reason to prove them. These objects consist of either abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicsentities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. A ''proof'' consists of a succession of applications of deductive rules to already established results. These results include previously proved theorems, axioms, andin case of abstraction from naturesome basic properties that are considered true starting poin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matching (perturbation)
Matching may refer to: * Matching, Essex, England ** Matching Green ** Matching Tye * Matching (graph theory), in graph theory, a set of edges without common vertices * Graph matching, detection of similarity between graphs * Matching (statistics), a technique for reducing bias when analyzing data from observational studies * Matching funds, funds set to be paid in equal amount to funds available from other sources * Matching principle, an accounting method * Matching theory (economics), the assigning of job candidates to vacancies * Matching law, in behaviorism and learning, the matching law suggests that an animal's response rate to a scenario will be proportionate to the amount/duration of reinforcement delivered * National Resident Matching Program, the process of allocating medical graduates to internship programs * Matchmaking, the process of introducing people for the purpose of marriage * Impedance matching, in electronics, attempting to make the output impedance of a sour ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Differential Equations
In mathematics, a differential equation is an equation that relates one or more unknown functions and their derivatives. In applications, the functions generally represent physical quantities, the derivatives represent their rates of change, and the differential equation defines a relationship between the two. Such relations are common; therefore, differential equations play a prominent role in many disciplines including engineering, physics, economics, and biology. Mainly the study of differential equations consists of the study of their solutions (the set of functions that satisfy each equation), and of the properties of their solutions. Only the simplest differential equations are solvable by explicit formulas; however, many properties of solutions of a given differential equation may be determined without computing them exactly. Often when a closed-form expression for the solutions is not available, solutions may be approximated numerically using computers. The theor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quadratic Function
In mathematics, a quadratic polynomial is a polynomial of degree two in one or more variables. A quadratic function is the polynomial function defined by a quadratic polynomial. Before 20th century, the distinction was unclear between a polynomial and its associated polynomial function; so "quadratic polynomial" and "quadratic function" were almost synonymous. This is still the case in many elementary courses, where both terms are often abbreviated as "quadratic". For example, a univariate (single-variable) quadratic function has the form :f(x)=ax^2+bx+c,\quad a \ne 0, where is its variable. The graph of a univariate quadratic function is a parabola, a curve that has an axis of symmetry parallel to the -axis. If a quadratic function is equated with zero, then the result is a quadratic equation. The solutions of a quadratic equation are the zeros of the corresponding quadratic function. The bivariate case in terms of variables and has the form : f(x,y) = a x^2 + bx ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cubic Function
In mathematics, a cubic function is a function of the form f(x)=ax^3+bx^2+cx+d where the coefficients , , , and are complex numbers, and the variable takes real values, and a\neq 0. In other words, it is both a polynomial function of degree three, and a real function. In particular, the domain and the codomain are the set of the real numbers. Setting produces a cubic equation of the form :ax^3+bx^2+cx+d=0, whose solutions are called roots of the function. A cubic function has either one or three real roots (which may not be distinct); all odd-degree polynomials have at least one real root. The graph of a cubic function always has a single inflection point. It may have two critical points, a local minimum and a local maximum. Otherwise, a cubic function is monotonic. The graph of a cubic function is symmetric with respect to its inflection point; that is, it is invariant under a rotation of a half turn around this point. Up to an affine transformation, there are o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Root Of A Function
In mathematics, a zero (also sometimes called a root) of a real-, complex-, or generally vector-valued function f, is a member x of the domain of f such that f(x) ''vanishes'' at x; that is, the function f attains the value of 0 at x, or equivalently, x is the solution to the equation f(x) = 0. A "zero" of a function is thus an input value that produces an output of 0. A root of a polynomial is a zero of the corresponding polynomial function. The fundamental theorem of algebra shows that any non-zero polynomial has a number of roots at most equal to its degree, and that the number of roots and the degree are equal when one considers the complex roots (or more generally, the roots in an algebraically closed extension) counted with their multiplicities. For example, the polynomial f of degree two, defined by f(x)=x^2-5x+6 has the two roots (or zeros) that are 2 and 3. f(2)=2^2-5\times 2+6= 0\textf(3)=3^2-5\times 3+6=0. If the function maps real numbers to real numbers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecology
Ecology () is the study of the relationships between living organisms, including humans, and their physical environment. Ecology considers organisms at the individual, population, community, ecosystem, and biosphere level. Ecology overlaps with the closely related sciences of biogeography, evolutionary biology, genetics, ethology, and natural history. Ecology is a branch of biology, and it is not synonymous with environmentalism. Among other things, ecology is the study of: * The abundance, biomass, and distribution of organisms in the context of the environment * Life processes, antifragility, interactions, and adaptations * The movement of materials and energy through living communities * The successional development of ecosystems * Cooperation, competition, and predation within and between species * Patterns of biodiversity and its effect on ecosystem processes Ecology has practical applications in conservation biology, wetland management, natural resour ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
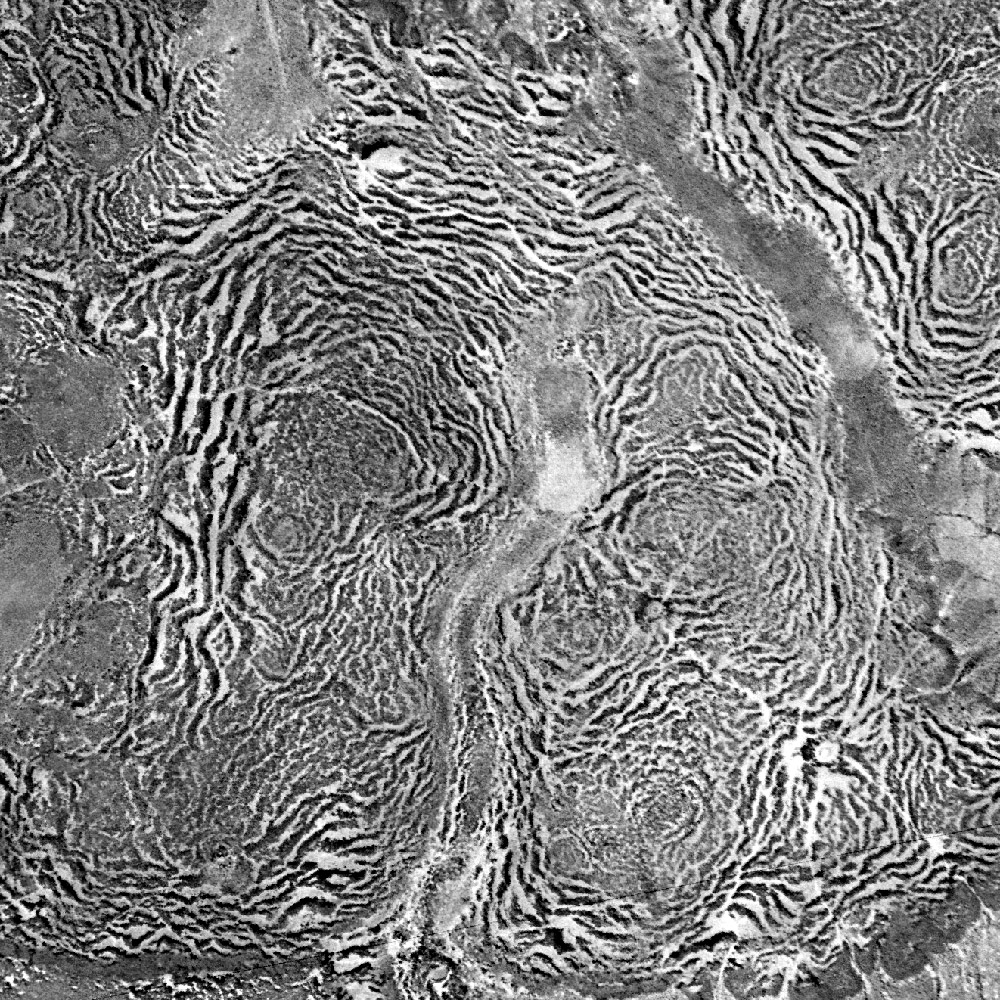
Pattern Formation
The science of pattern formation deals with the visible, (statistically) orderly outcomes of self-organization and the common principles behind similar patterns in nature. In developmental biology, pattern formation refers to the generation of complex organizations of cell fates in space and time. The role of genes in pattern formation is an aspect of morphogenesis, the creation of diverse anatomies from similar genes, now being explored in the science of evolutionary developmental biology or evo-devo. The mechanisms involved are well seen in the anterior-posterior patterning of embryos from the model organism ''Drosophila melanogaster'' (a fruit fly), one of the first organisms to have its morphogenesis studied, and in the eyespots of butterflies, whose development is a variant of the standard (fruit fly) mechanism. Patterns in nature Examples of pattern formation can be found in biology, physics, and science, and can readily be simulated with computer graphics, as desc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reaction–diffusion System
Reaction–diffusion systems are mathematical models which correspond to several physical phenomena. The most common is the change in space and time of the concentration of one or more chemical substances: local chemical reactions in which the substances are transformed into each other, and diffusion which causes the substances to spread out over a surface in space. Reaction–diffusion systems are naturally applied in chemistry. However, the system can also describe dynamical processes of non-chemical nature. Examples are found in biology, geology and physics (neutron diffusion theory) and ecology. Mathematically, reaction–diffusion systems take the form of semi-linear parabolic partial differential equations. They can be represented in the general form :\partial_t \boldsymbol = \underline \,\nabla^2 \boldsymbol + \boldsymbol(\boldsymbol), where represents the unknown vector function, is a diagonal matrix of diffusion coefficients, and accounts for all local reactions. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boundary Layer
In physics and fluid mechanics, a boundary layer is the thin layer of fluid in the immediate vicinity of a bounding surface formed by the fluid flowing along the surface. The fluid's interaction with the wall induces a no-slip boundary condition (zero velocity at the wall). The flow velocity then monotonically increases above the surface until it returns to the bulk flow velocity. The thin layer consisting of fluid whose velocity has not yet returned to the bulk flow velocity is called the velocity boundary layer. The air next to a human is heated resulting in gravity-induced convective airflow, airflow which results in both a velocity and thermal boundary layer. A breeze disrupts the boundary layer, and hair and clothing protect it, making the human feel cooler or warmer. On an aircraft wing, the velocity boundary layer is the part of the flow close to the wing, where viscous forces distort the surrounding non-viscous flow. In the Earth's atmosphere, the atmospheric b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluid Mechanics
Fluid mechanics is the branch of physics concerned with the mechanics of fluids (liquids, gases, and plasmas) and the forces on them. It has applications in a wide range of disciplines, including mechanical, aerospace, civil, chemical and biomedical engineering, geophysics, oceanography, meteorology, astrophysics, and biology. It can be divided into fluid statics, the study of fluids at rest; and fluid dynamics, the study of the effect of forces on fluid motion. It is a branch of continuum mechanics, a subject which models matter without using the information that it is made out of atoms; that is, it models matter from a ''macroscopic'' viewpoint rather than from ''microscopic''. Fluid mechanics, especially fluid dynamics, is an active field of research, typically mathematically complex. Many problems are partly or wholly unsolved and are best addressed by numerical methods, typically using computers. A modern discipline, called computational fluid dynamics (CFD), i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrey Nikolayevich Tikhonov
Andrey Nikolayevich Tikhonov (russian: Андре́й Никола́евич Ти́хонов; October 17, 1906 – October 7, 1993) was a leading Soviet Russian mathematician and geophysicist known for important contributions to topology, functional analysis, mathematical physics, and ill-posed problems. He was also one of the inventors of the magnetotellurics method in geophysics. Other transliterations of his surname include "Tychonoff", "Tychonov", "Tihonov", "Tichonov." Biography Born in Gzhatsk, he studied at the Moscow State University where he received a Ph.D. in 1927 under the direction of Pavel Sergeevich Alexandrov. In 1933 he was appointed as a professor at Moscow State University. He became a corresponding member of the USSR Academy of Sciences on 29 January 1939 and a full member of the USSR Academy of Sciences on 1 July 1966. Research work Tikhonov worked in a number of different fields in mathematics. He made important contributions to topology, functi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)