|
Signomial
A signomial is an algebraic function of one or more independent variables. It is perhaps most easily thought of as an algebraic extension of multivariable polynomials—an extension that permits exponents to be arbitrary real numbers (rather than just non-negative integers) while requiring the independent variables to be strictly positive (so that division by zero and other inappropriate algebraic operations are not encountered). Formally, a signomial is a function with domain \mathbb_^n which takes values : f(x_1, x_2, \dots, x_n) = \sum_^M \left(c_i \prod_^n x_j^\right) where the coefficients c_i and the exponents a_ are real numbers. Signomials are closed under addition, subtraction, multiplication, and scaling. If we restrict all c_i to be positive, then the function f is a posynomial. Consequently, each signomial is either a posynomial, the negative of a posynomial, or the difference of two posynomials. If, in addition, all exponents a_ are non-negative integers, then the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geometric Programming
A geometric program (GP) is an optimization problem of the form : \begin \mbox & f_0(x) \\ \mbox & f_i(x) \leq 1, \quad i=1, \ldots, m\\ & g_i(x) = 1, \quad i=1, \ldots, p, \end where f_0,\dots,f_m are posynomials and g_1,\dots,g_p are monomials. In the context of geometric programming (unlike standard mathematics), a monomial is a function from \mathbb_^n to \mathbb defined as :x \mapsto c x_1^ x_2^ \cdots x_n^ where c > 0 \ and a_i \in \mathbb . A posynomial is any sum of monomials.S. Boyd, S. J. Kim, L. Vandenberghe, and A. Hassibi. A Tutorial on Geometric Programming'' Retrieved 20 October 2019. Geometric programming is closely related to convex optimization: any GP can be made convex by means of a change of variables. GPs have numerous applications, including component sizing in IC design, aircraft design, maximum likelihood estimation for logistic regression in statistics, and parameter tuning of positive linear systems in control theory. Convex form Geometric programs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Function (mathematics)
In mathematics, a function from a set to a set assigns to each element of exactly one element of .; the words map, mapping, transformation, correspondence, and operator are often used synonymously. The set is called the domain of the function and the set is called the codomain of the function.Codomain ''Encyclopedia of Mathematics'Codomain. ''Encyclopedia of Mathematics''/ref> The earliest known approach to the notion of function can be traced back to works of Persian mathematicians Al-Biruni and Sharaf al-Din al-Tusi. Functions were originally the idealization of how a varying quantity depends on another quantity. For example, the position of a planet is a ''function'' of time. Historically, the concept was elaborated with the infinitesimal calculus at the end of the 17th century, and, until the 19th century, the functions that were considered were differentiable (that is, they had a high degree of regularity). The concept of a function was formalized at the end of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polynomial
In mathematics, a polynomial is an expression consisting of indeterminates (also called variables) and coefficients, that involves only the operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication, and positive-integer powers of variables. An example of a polynomial of a single indeterminate is . An example with three indeterminates is . Polynomials appear in many areas of mathematics and science. For example, they are used to form polynomial equations, which encode a wide range of problems, from elementary word problems to complicated scientific problems; they are used to define polynomial functions, which appear in settings ranging from basic chemistry and physics to economics and social science; they are used in calculus and numerical analysis to approximate other functions. In advanced mathematics, polynomials are used to construct polynomial rings and algebraic varieties, which are central concepts in algebra and algebraic geometry. Etymology The word ''polynomial'' join ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Closure (mathematics)
In mathematics, a subset of a given set is closed under an operation of the larger set if performing that operation on members of the subset always produces a member of that subset. For example, the natural numbers are closed under addition, but not under subtraction: is not a natural number, although both 1 and 2 are. Similarly, a subset is said to be closed under a ''collection'' of operations if it is closed under each of the operations individually. The closure of a subset is the result of a closure operator applied to the subset. The ''closure'' of a subset under some operations is the smallest subset that is closed under these operations. It is often called the ''span'' (for example linear span) or the ''generated set''. Definitions Let be a set equipped with one or several methods for producing elements of from other elements of . Operations and (partial) multivariate function are examples of such methods. If is a topological space, the limit of a sequence of element ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Posynomial
A posynomial, also known as a posinomial in some literature, is a function of the form : f(x_1, x_2, \dots, x_n) = \sum_^K c_k x_1^ \cdots x_n^ where all the coordinates x_i and coefficients c_k are positive real numbers, and the exponents a_ are real numbers. Posynomials are closed under addition, multiplication, and nonnegative scaling. For example, : f(x_1, x_2, x_3) = 2.7 x_1^2x_2^x_3^ + 2x_1^x_3^ is a posynomial. Posynomials are not the same as polynomials in several independent variables. A polynomial's exponents must be non-negative integers, but its independent variables and coefficients can be arbitrary real numbers; on the other hand, a posynomial's exponents can be arbitrary real numbers, but its independent variables and coefficients must be positive real numbers. This terminology was introduced by Richard J. Duffin, Elmor L. Peterson, and Clarence Zener in their seminal book on geometric programming. Posynomials are a special case of signomial A signomial is an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthant
In geometry, an orthant or hyperoctant is the analogue in ''n''-dimensional Euclidean space of a quadrant in the plane or an octant in three dimensions. In general an orthant in ''n''-dimensions can be considered the intersection of ''n'' mutually orthogonal half-spaces. By independent selections of half-space signs, there are 2''n'' orthants in ''n''-dimensional space. More specifically, a closed orthant in R''n'' is a subset defined by constraining each Cartesian coordinate to be nonnegative or nonpositive. Such a subset is defined by a system of inequalities: :ε1''x''1 ≥ 0 ε2''x''2 ≥ 0 · · · ε''n''''x''''n'' ≥ 0, where each ε''i'' is +1 or −1. Similarly, an open orthant in R''n'' is a subset defined by a system of strict inequalities :ε1''x''1 > 0 ε2''x''2 > 0 · ·&nb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optimization Problem
In mathematics, computer science and economics, an optimization problem is the problem of finding the ''best'' solution from all feasible solutions. Optimization problems can be divided into two categories, depending on whether the variables are continuous or discrete: * An optimization problem with discrete variables is known as a ''discrete optimization'', in which an object such as an integer, permutation or graph must be found from a countable set. * A problem with continuous variables is known as a ''continuous optimization'', in which an optimal value from a continuous function must be found. They can include constrained problems and multimodal problems. Continuous optimization problem The '' standard form'' of a continuous optimization problem is \begin &\underset& & f(x) \\ &\operatorname & &g_i(x) \leq 0, \quad i = 1,\dots,m \\ &&&h_j(x) = 0, \quad j = 1, \dots,p \end where * is the objective function to be minimized over the -variable vector , * are called ine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nonlinear Optimization
In mathematics, nonlinear programming (NLP) is the process of solving an optimization problem where some of the constraints or the objective function are nonlinear. An optimization problem is one of calculation of the extrema (maxima, minima or stationary points) of an objective function over a set of unknown real variables and conditional to the satisfaction of a system of equalities and inequalities, collectively termed constraints. It is the sub-field of mathematical optimization that deals with problems that are not linear. Applicability A typical non-convex problem is that of optimizing transportation costs by selection from a set of transportation methods, one or more of which exhibit economies of scale, with various connectivities and capacity constraints. An example would be petroleum product transport given a selection or combination of pipeline, rail tanker, road tanker, river barge, or coastal tankship. Owing to economic batch size the cost functions may have discontin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constrained Optimization
In mathematical optimization, constrained optimization (in some contexts called constraint optimization) is the process of optimizing an objective function with respect to some variables in the presence of constraints on those variables. The objective function is either a cost function or energy function, which is to be minimized, or a reward function or utility function, which is to be maximized. Constraints can be either hard constraints, which set conditions for the variables that are required to be satisfied, or soft constraints, which have some variable values that are penalized in the objective function if, and based on the extent that, the conditions on the variables are not satisfied. Relation to constraint-satisfaction problems The constrained-optimization problem (COP) is a significant generalization of the classic constraint-satisfaction problem (CSP) model. COP is a CSP that includes an ''objective function'' to be optimized. Many algorithms are used to handle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Objective Function
In mathematical optimization and decision theory, a loss function or cost function (sometimes also called an error function) is a function that maps an event or values of one or more variables onto a real number intuitively representing some "cost" associated with the event. An optimization problem seeks to minimize a loss function. An objective function is either a loss function or its opposite (in specific domains, variously called a reward function, a profit function, a utility function, a fitness function, etc.), in which case it is to be maximized. The loss function could include terms from several levels of the hierarchy. In statistics, typically a loss function is used for parameter estimation, and the event in question is some function of the difference between estimated and true values for an instance of data. The concept, as old as Laplace, was reintroduced in statistics by Abraham Wald in the middle of the 20th century. In the context of economics, for example, this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
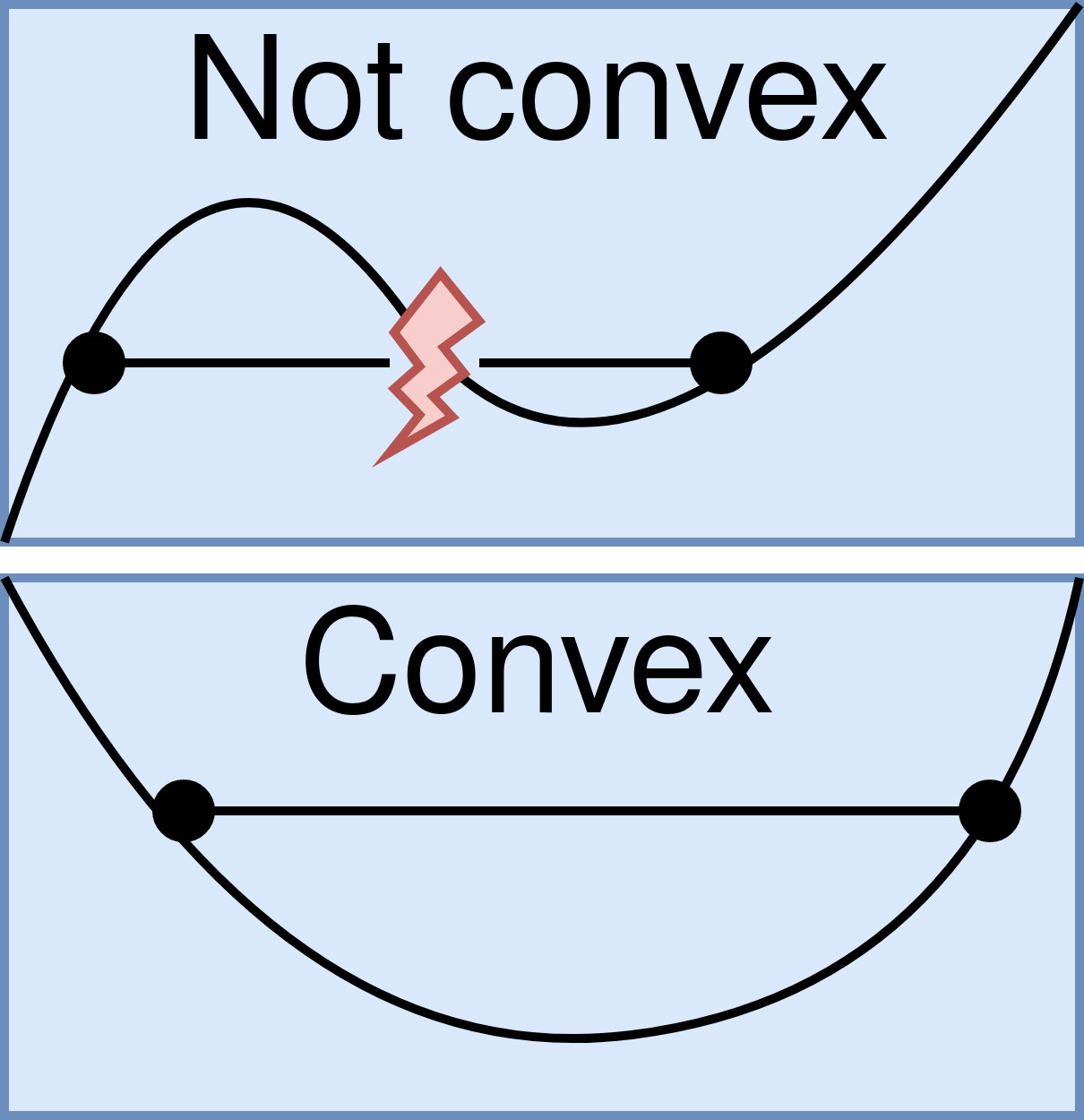
Convex Function
In mathematics, a real-valued function is called convex if the line segment between any two points on the graph of a function, graph of the function lies above the graph between the two points. Equivalently, a function is convex if its epigraph (mathematics), epigraph (the set of points on or above the graph of the function) is a convex set. A twice-differentiable function of a single variable is convex if and only if its second derivative is nonnegative on its entire domain. Well-known examples of convex functions of a single variable include the quadratic function x^2 and the exponential function e^x. In simple terms, a convex function refers to a function whose graph is shaped like a cup \cup, while a concave function's graph is shaped like a cap \cap. Convex functions play an important role in many areas of mathematics. They are especially important in the study of optimization problems where they are distinguished by a number of convenient properties. For instance, a st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Posynomial
A posynomial, also known as a posinomial in some literature, is a function of the form : f(x_1, x_2, \dots, x_n) = \sum_^K c_k x_1^ \cdots x_n^ where all the coordinates x_i and coefficients c_k are positive real numbers, and the exponents a_ are real numbers. Posynomials are closed under addition, multiplication, and nonnegative scaling. For example, : f(x_1, x_2, x_3) = 2.7 x_1^2x_2^x_3^ + 2x_1^x_3^ is a posynomial. Posynomials are not the same as polynomials in several independent variables. A polynomial's exponents must be non-negative integers, but its independent variables and coefficients can be arbitrary real numbers; on the other hand, a posynomial's exponents can be arbitrary real numbers, but its independent variables and coefficients must be positive real numbers. This terminology was introduced by Richard J. Duffin, Elmor L. Peterson, and Clarence Zener in their seminal book on geometric programming. Posynomials are a special case of signomial A signomial is an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |