|
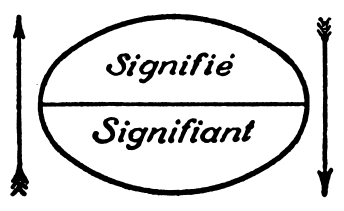
Signified
In semiotics, signified and signifier ( French: ''signifié'' and ''signifiant'') stand for the two main components of a sign, where ''signified'' pertains to the "plane of content", while ''signifier'' is the "plane of expression". The idea was first proposed in the work of Swiss linguist Ferdinand de Saussure, one of the two founders of semiotics. Concept of signs The concept of signs has been around for a long time, having been studied by many classic philosophers such as Plato, Aristotle, Augustine, William of Ockham, and Francis Bacon, among others. The term ''semiotics'' derives from the Greek root ''seme'', as in ''semeiotikos'' (an 'interpreter of signs'). Berger, Arthur Asa. 2012. ''Media Analysis Techniques''. Beverly Hills: Sage Publications. It was not until the early part of the 20th century, however, that Saussure and American philosopher Charles Sanders Peirce brought the term into more common use. While both Saussure and Peirce contributed greatly to the concept ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperreality
Described by Jean Baudrillard, the concept of hyperreality captures the inability to distinguish "The Real" (a term borrowed from Jacques Lacan) from the signifier of it. This is more prominent in technologically advanced societies. Hyperreality is seen as a condition in which what is real and what is fiction are seamlessly blended together so that there is no clear distinction between where one ends and the other begins. It allows the merging of physical reality with virtual reality (VR) or augmented reality (AR), and human intelligence with artificial intelligence (AI). Jean Baudrillard is a French cultural theorist, sociologist and philosopher. His most notable work consists of establishing the concept of hyperreality and the simulacra. Some of Baudrillard's most influential theorists consist of Karl Marx, Freud, Levi Strauss, Nietzsche, etc. Baudrillard's work stems around his interest in the theories of post-structuralism and post-modernism. Some famous theorists who contribu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean Baudrillard
Jean Baudrillard ( , , ; 27 July 1929 – 6 March 2007) was a French sociologist, philosopher and poet with interest in cultural studies. He is best known for his analyses of media, contemporary culture, and technological communication, as well as his formulation of concepts such as simulation and hyperreality. Baudrillard wrote about diverse subjects, including consumerism, gender relations, critique of economy, economics, social history, art, Western foreign policy, and popular culture. Among his best known works are ''Seduction'' (1978), ''Simulacra and Simulation'' (1981), ''America'' (1986), and '' The Gulf War Did Not Take Place'' (1991). His work is frequently associated with postmodernism and specifically post-structuralism. Baudrillard: "I have nothing to do with postmodernism."MLA Brennan, Eugene. Review of Pourquoi la guerre aujourd’hui?, by Jean Baudrillard, Jacques Derrida. French Studies: A Quarterly Review, vol. 71 no. 3, 2017, p. 449-449. Project MUSE mus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferdinand De Saussure
Ferdinand de Saussure (; ; 26 November 1857 – 22 February 1913) was a Swiss linguist, semiotician and philosopher. His ideas laid a foundation for many significant developments in both linguistics and semiotics in the 20th century. He is widely considered one of the founders of 20th-century linguistics and one of two major founders (together with Charles Sanders Peirce) of semiotics, or ''semiology'', as Saussure called it. One of his translators, Roy Harris, summarized Saussure's contribution to linguistics and the study of "the whole range of human sciences. It is particularly marked in linguistics, philosophy, psychoanalysis, psychology, sociology and anthropology." Although they have undergone extension and critique over time, the dimensions of organization introduced by Saussure continue to inform contemporary approaches to the phenomenon of language. As Leonard Bloomfield stated after reviewing the ''Cours'': "he has given us the theoretical basis for a science of human s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saussure Signifie-Signifiant
Saussure or de Saussure may refer to: * Saussure (crater), a lunar crater * 13580 de Saussure, an asteroid Surname People of the surname Saussure or de Saussure include * Horace-Bénédict de Saussure (1740–1799), Genevan physicist and Alpine traveller ** Nicolas-Théodore de Saussure (1767–1845), chemist, son of Horace-Bénédict, and brother of Albertine ** Albertine Necker de Saussure (1766–1841), Swiss writer, educationalist, and advocate of education for women, daughter of Horace-Bénédict, and sister of Nicolas-Théodore * Henri Louis Frédéric de Saussure (1829–1905), Swiss mineralogist and entomologist (taxonomist), and father of Ferdinand, Léopold and René. ** Ferdinand de Saussure (1857–1913), Swiss linguist, brother of Léopold and René ** Léopold de Saussure (1866–1925), sinologist, astronomer, French Naval Officer, brother of Ferdinand and René *** (1901–1984), female sailing pioneer and scholar, specialist of Jean-Jacques Rousseau, daughter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacques Lacan
Jacques Marie Émile Lacan (, , ; 13 April 1901 – 9 September 1981) was a French psychoanalyst and psychiatrist. Described as "the most controversial psycho-analyst since Freud", Lacan gave yearly seminars in Paris from 1953 to 1981, and published papers that were later collected in the book ''Écrits''. His work made a significant impact on continental philosophy and cultural theory in areas such as post-structuralism, critical theory, feminist theory and film theory, as well as on the practice of psychoanalysis itself. Lacan took up and discussed the whole range of Freudian concepts, emphasizing the philosophical dimension of Freud's thought and applying concepts derived from structuralism in linguistics and anthropology to its development in his own work, which he would further augment by employing formulae from predicate logic and topology. Taking this new direction, and introducing controversial innovations in clinical practice, led to expulsion for Lacan and his foll ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Society (journal)
''Society'' is a journal that publishes discussions and research findings in the social sciences and public policy. It was founded as ''Transaction: Social Science and Modern SOCIETY'' by Irving Louis Horowitz in 1962. It was published by Transaction Publishers for decades before being purchased by Springer. Its chief editors are Daniel Gordon (UMass Amherst) and Andreas Hess (UCD). Abstracting and indexing ''Society'' is abstracted and indexed in the Social Sciences Citation Index. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2017 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given journal, as i ... of 0.529. References External links ''Society''— official journal homepage at Springer site Sociology journals Publications established in 1962 Springer Sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis Hjelmslev
Louis Trolle Hjelmslev (; 3 October 189930 May 1965) was a Danish linguist whose ideas formed the basis of the Copenhagen School of linguistics. Born into an academic family (his father was the mathematician Johannes Hjelmslev), Hjelmslev studied comparative linguistics in Copenhagen, Prague and Paris (with Antoine Meillet and Joseph Vendryes, among others). In 1931, he founded the Cercle Linguistique de Copenhague. Together with Hans Jørgen Uldall he developed a structuralist theory of language which he called glossematics, which further developed the semiotic theory of Ferdinand de Saussure. Glossematics as a theory of language is characterized by a high degree of formalism. It is interested in describing the formal and semantic characteristics of language in separation from sociology, psychology or neurobiology, and has a high degree of logical rigour. Hjelmslev regarded linguistics – or glossematics – as a formal science. He was the inventor of formal linguistics. Hjelmsl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daniel Chandler
Daniel Chandler (born 1952) is a British visual semiotician based since 2001 at the Department of Theatre, Film and Television Studies at Aberystwyth University, where he has taught since 1989. His best-known publication is ''Semiotics: The Basics'' (Routledge: 1st edn 2002, 2nd edn 2007), which is frequently used as a basis for university courses in semiotics, and the online version ''Semiotics for Beginners'' (online since 1995). He has a particular interest in the visual semiotics of gender and advertising. Early career Chandler trained as a schoolteacher at Magdalene College, Cambridge, and began his career teaching English in middle and secondary schools in the 1970s and 1980s. He adopted a progressive, constructivist philosophy of education at a time when microcomputers were first introduced into the classroom. Resisting the hyped image of computing in education as a boon to instructional productivity, Chandler recognized the computer as a tool for learning, but he rejec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unconscious Mind
The unconscious mind (or the unconscious) consists of the processes in the mind which occur automatically and are not available to introspection and include thought processes, memories, interests, and motivations. Even though these processes exist well under the surface of conscious awareness, they are theorized to exert an effect on behavior. The term was coined by the German Romantic philosopher Friedrich Schelling and later introduced into English by the poet and essayist Samuel Taylor Coleridge.Christopher John Murray, ''Encyclopedia of the Romantic Era, 1760-1850'' (Taylor & Francis, 2004: ), pp. 1001–1002. Empirical evidence suggests that unconscious phenomena include repressed feelings, automatic skills, subliminal perceptions, and automatic reactions, and possibly also Complex (psychology), complexes, hidden phobias, and desires. The concept was popularized by the Austrian neurologist and Psychoanalysis, psychoanalyst Sigmund Freud. In psychoanalytic theory#The uncon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Repression (psychoanalysis)
Repression is a key concept of psychoanalysis, where it is understood as a defence mechanism that "ensures that what is unacceptable to the conscious mind, and would if recalled arouse anxiety, is prevented from entering into it." According to psychoanalytic theory, repression plays a major role in many mental illnesses, and in the psyche of the average person.Laplanche pp. 390, 392 There has been debate as to whether (or how often) memory repression really occurs and mainstream psychology holds that true memory repression occurs infrequently. American psychologists began to attempt to study repression in the experimental laboratory around 1930. However, psychoanalysts were at first uninterested in attempts to study repression in laboratory settings, and later came to reject them. Most psychoanalysts concluded that such attempts misrepresented the psychoanalytic concept of repression. Sigmund Freud's theory As Sigmund Freud moved away from hypnosis, and towards urging his patient ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Denotation
In linguistics and philosophy, the denotation of an expression is its literal meaning. For instance, the English word "warm" denotes the property of being warm. Denotation is contrasted with other aspects of meaning including connotation. For instance, the word "warm" may evoke calmness or cosiness, but these associations are not part of the word's denotation. Similarly, an expression's denotation is separate from pragmatic inferences it may trigger. For instance, describing something as "warm" often implicates that it is not hot, but this is once again not part of the word's denotation. Denotation plays a major role in several fields. Within philosophy of language, denotation is studied as an important aspect of meaning. In mathematics and computer science, assignments of denotations are assigned to expressions are a crucial step in defining interpreted formal languages. The main task of formal semantics is to reverse engineer the computational system which assigns denotations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Other (philosophy)
In phenomenology, the terms the Other and the Constitutive Other identify the other human being, in their differences from the Self, as being a cumulative, constituting factor in the self-image of a person; as acknowledgement of being real; hence, the Other is dissimilar to and the opposite of the Self, of Us, and of the Same.''The Oxford Companion to Philosophy'' (1995) p. 637. The Constitutive Other is the relation between the personality (essential nature) and the person (body) of a human being; the relation of essential and superficial characteristics of personal identity that corresponds to the relationship between opposite, but correlative, characteristics of the Self, because the difference is inner-difference, within the Self. The condition and quality of Otherness (the characteristics of the Other) is the state of being different from and alien to the social identity of a person and to the identity of the Self. In the discourse of philosophy, the term Otherness iden ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |