|
Signalling Protocol
A signaling protocol is a type of communications protocol for encapsulating the signaling between communication endpoints and switching systems to establish or terminate a connection and to identify the state of connection. The following is a list of signaling protocols: * ALOHA * Digital Subscriber System No. 1 (EDSS1) * Dual-tone multi-frequency signaling * H.248 * H.323 * H.225.0 * Jingle * Media Gateway Control Protocol (MGCP) * Megaco * Regional System R1 * NBAP (Node B Application Part) * Signalling System R2 * Session Initiation Protocol * Signaling System No. 5 * Signaling System No. 6 * Signaling System No. 7 * Skinny Client Control Protocol (SCCP, ''Skinny'') * Q.931 * QSIG QSIG is an ISDN based signaling protocol for signaling between private branch exchanges (PBXs) in a private integrated services network (PISN). It makes use of the connection-level Q.931 protocol and the application-level ROSE protocol. ISDN "prop ... Network protocols Telephony signal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Encapsulation (networking)
In computer networking, encapsulation is a method of designing modular communication protocols in which logically separate functions in the network are abstracted from their underlying structures by inclusion or information hiding within higher-level objects. In other words, encapsulation "takes information from a higher layer and adds a header to it, treating the higher layer information as data". The physical layer is responsible for physical transmission of the data, link encapsulation allows local area networking, IP provides global addressing of individual computers, and TCP selects the process or application (i.e., the TCP or UDP port) that specifies the service such as a Web or TFTP server. During encapsulation, each layer builds a protocol data unit (PDU) by adding a header and optionally a trailer, both of which contain control information to the PDU from the layer above. For example, in the IP suite, the contents of a web page are encapsulated with an HTTP h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Signalling (telecommunications)
In telecommunication, signaling is the use of signals for controlling communications. This may constitute an information exchange concerning the establishment and control of a telecommunication circuit and the management of the network. Classification Signaling systems may be classified based on several principal characteristics. In-band and out-of-band signaling In the public switched telephone network (PSTN), in-band signaling is the exchange of call control information within the same physical channel, or within the same frequency band, that the telephone call itself is using. An example is dual-tone multi-frequency signaling (DTMF), which is used on most telephone lines to customer premises. Out-of-band signaling is telecommunication signaling on a dedicated channel separate from that used for the telephone call. Out-of-band signaling has been used since Signaling System No. 6 (SS6) was introduced in the 1970s, and also in Signalling System No. 7 (SS7) in 1980 which b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ALOHAnet
ALOHAnet, also known as the ALOHA System, or simply ALOHA, was a pioneering computer networking system developed at the University of Hawaii. ALOHAnet became operational in June 1971, providing the first public demonstration of a wireless packet data network. ALOHA originally stood for Additive Links On-line Hawaii Area. The ALOHAnet used a new method of medium access, called ''ALOHA random access'', and experimental ultra high frequency (UHF) for its operation. In the 1970s ALOHA random access was employed in the nascent Ethernet cable based network and then in the Marisat (now Inmarsat) satellite network. In the early 1980s frequencies for mobile networks became available, and in 1985 frequencies suitable for what became known as Wi-Fi were allocated in the US. These regulatory developments made it possible to use the ALOHA random-access techniques in both Wi-Fi and in mobile telephone networks. ALOHA channels were used in a limited way in the 1980s in 1G mobile phones fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Subscriber System No
Digital usually refers to something using discrete digits, often binary digits. Technology and computing Hardware *Digital electronics, electronic circuits which operate using digital signals **Digital camera, which captures and stores digital images ***Digital versus film photography **Digital computer, a computer that handles information represented by discrete values **Digital recording, information recorded using a digital signal Socioeconomic phenomena *Digital culture, the anthropological dimension of the digital social changes * Digital divide, a form of economic and social inequality in access to or use of information and communication technologies * Digital economy, an economy based on computing and telecommunications resources Other uses in technology and computing * Digital data, discrete data, usually represented using binary numbers *Digital marketing, search engine & social media presence booster, usually represented using online visibility. * Digital media, media ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
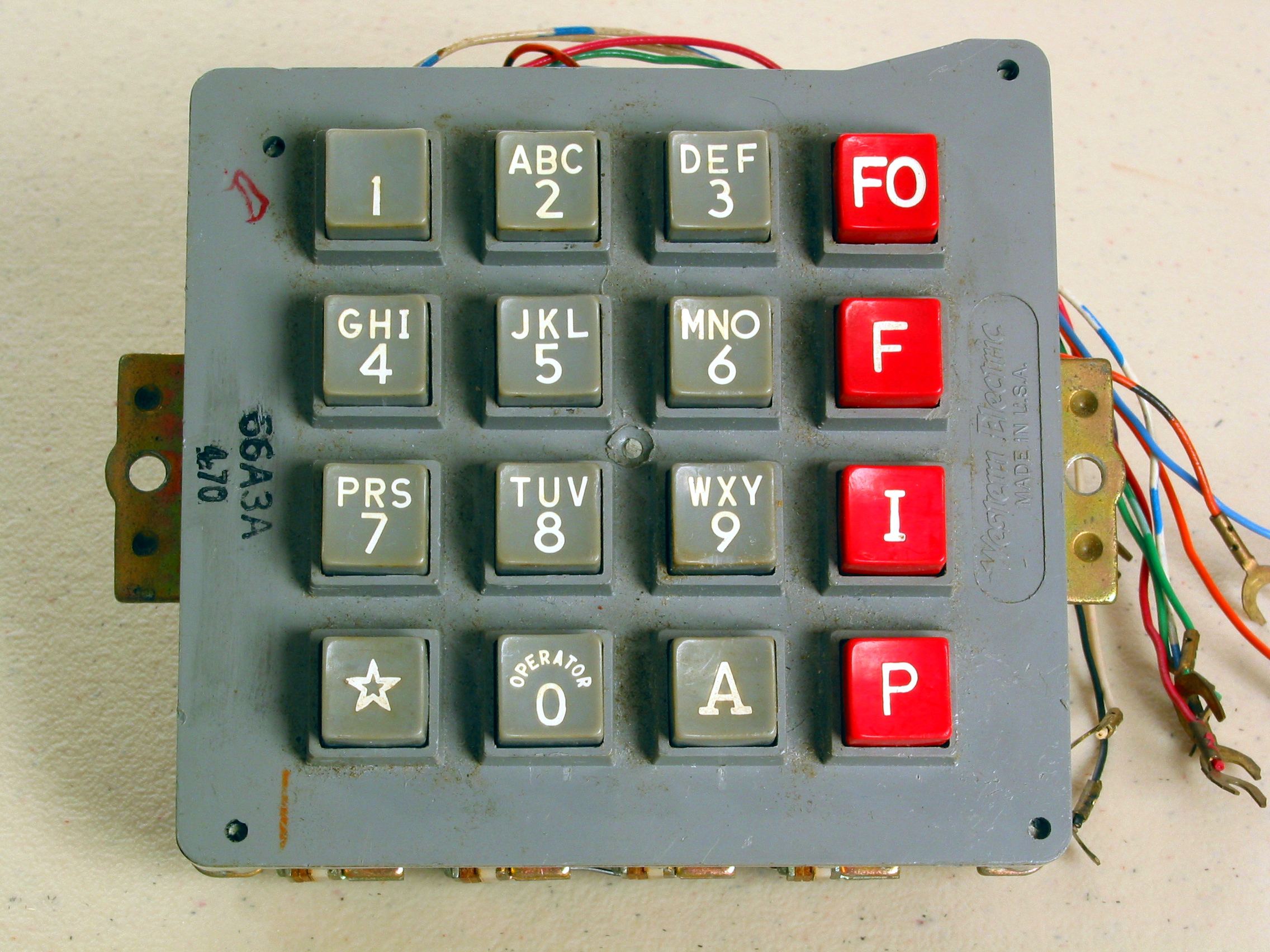
Dual-tone Multi-frequency Signaling
Dual-tone multi-frequency signaling (DTMF) is a telecommunication signaling system using the voice-frequency band over telephone lines between telephone equipment and other communications devices and switching centers. DTMF was first developed in the Bell System in the United States, and became known under the trademark Touch-Tone for use in push-button telephones supplied to telephone customers, starting in 1963. DTMF is standardized as ITU-T Recommendation Q.23. It is also known in the UK as ''MF4''. The Touch-Tone system using a telephone keypad gradually replaced the use of rotary dial and has become the industry standard for landline and mobile service. Other multi-frequency systems are used for internal signaling within the telephone network. Multifrequency signaling Before the development of DTMF, telephone numbers were dialed by users with a loop-disconnect (LD) signaling, more commonly known as pulse dialing (dial pulse, DP) in the United States. It functions by i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jingle (protocol)
Jingle is an extension to XMPP (Extensible Messaging and Presence Protocol) which adds peer-to-peer (P2P) session control (signaling) for multimedia interactions such as in Voice over IP (VoIP) or videoconferencing communications. It was designed by Google and the XMPP Standards Foundation. The multimedia streams are delivered using the Real-time Transport Protocol (RTP). If needed, NAT traversal is assisted using Interactive Connectivity Establishment (ICE). , the proposed Jingle specification had not yet been approved by the XMPP Standards Foundation, but is now a Draft Standard, meaning: "''Implementations are encouraged and the protocol is appropriate for deployment in production systems, but some changes to the protocol are possible before it becomes a Final Standard.''" The libjingle library, used by Google Talk to implement Jingle, has been released to the public under a BSD license. It implements both the current standard protocol and the older, pre-standard versio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Media Gateway Control Protocol
The Media Gateway Control Protocol (MGCP) is a signaling and call control communication protocol used in voice over IP (VoIP) telecommunication systems. It implements the media gateway control protocol architecture for controlling media gateways connected to the public switched telephone network (PSTN).RFC 2805, Media Gateway Control Protocol Architecture and Requirements, N. Greene, M. Ramalho, B. Rosen, IETF, April 2000 The media gateways provide conversion of traditional electronic media to the Internet Protocol (IP) network. The protocol is a successor to the Simple Gateway Control Protocol (SGCP), which was developed by Bellcore and Cisco, and the Internet Protocol Device Control (IPDC). The methodology of MGCP reflects the structure of the PSTN with the power of the network residing in a call control center softswitch which is analogous to the central office in the telephone network. The endpoints are low-intelligence devices, mostly executing control commands from a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megaco
The Gateway Control Protocol (Megaco, H.248) is an implementation of the media gateway control protocol architecture for providing telecommunication services across a converged internetwork consisting of the traditional public switched telephone network (PSTN) and modern packet networks, such as the Internet. ''H.248'' is the designation of the recommendations developed by the ITU Telecommunication Standardization Sector (ITU-T) and ''Megaco'' is a contraction of ''media gateway control protocol'' used by the earliest specifications by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). The standard published in March 2013 by ITU-T is entitled ''H.248.1: Gateway control protocol: Version 3''. Megaco/H.248 follows the guidelines published in RFC 2805 in April 2000, entitled ''Media Gateway Control Protocol Architecture and Requirements''. The protocol performs the same functions as the Media Gateway Control Protocol (MGCP), is however a formal standard while MGCP has only informational ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multi-frequency
In telephony, multi-frequency signaling (MF) is a type of signaling that was introduced by the Bell System after World War II. It uses a combination of audible tones for address (telephone number) transport and supervision signaling on trunk lines between central offices. The signaling is sent '' in-band'' over the same channel as the bearer channel used for voice traffic. Multi-frequency signaling defines electronic signals that consist of a combination of two audible frequencies, usually selected from a set of six frequencies. Over several decades, various types of MF signaling were developed, including national and international varieties. The CCITT standardization process specified the American Bell System version as ''Regional Standard No. 1'', or Signalling System R1, and a corresponding European standard as Signalling System R2. Both were largely replaced by digital systems, such as Signalling System 7, which operate out-of-band on a separate data network. Because of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NBAP
The Radio Network Controller (RNC) is a governing element in the UMTS radio access network ( UTRAN) and is responsible for controlling the Node Bs that are connected to it. The RNC carries out radio resource management, some of the mobility management functions and is the point where encryption is done before user data is sent to and from the mobile. The RNC connects to the Circuit Switched Core Network through Media Gateway ( MGW) and to the SGSN (Serving GPRS Support Node) in the Packet Switched Core Network. Interfaces The logical connections between the network elements are known as interfaces. The interface between the RNC and the Circuit Switched Core Network (CS-CN) is called Iu-CS and between the RNC and the Packet Switched Core Network is called Iu-PS. Other interfaces include Iub (between the RNC and the Node B) and Iur (between RNCs in the same network). Iu interfaces carry user traffic (such as voice or data) as well as control information (see ), and Iur interface ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Signalling System R2
Signalling System R2 is a signalling protocol for telecommunications that was in use from the 1960s mostly in Europe, and later also in Latin America, Asia, and Australia, to convey exchange information between two telephone switching systems for establishing a telephone call via a telephone trunk.ITU-T Recommendation Q.400-Q.490 - Specifications of Signalling System R2 It is suitable for signaling on analog as well as digital circuits. R2 signaling specifications were first published by the International Telegraph and Telephone Consultative Committee (CCITT) in ITU White Book Volume VI of 1969,IVth Plenary Assembly (Mar Del Plata, 23 September-25 October 1968), White Book Volume VI, ''Telephone Signaling and Switching'', Recommendations Series Q, ITU 1969. and are maintained by the [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Session Initiation Protocol
The Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) is a signaling protocol used for initiating, maintaining, and terminating communication sessions that include voice, video and messaging applications. SIP is used in Internet telephony, in private IP telephone systems, as well as mobile phone calling over LTE (VoLTE). The protocol defines the specific format of messages exchanged and the sequence of communications for cooperation of the participants. SIP is a text-based protocol, incorporating many elements of the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) and the Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP). A call established with SIP may consist of multiple media streams, but no separate streams are required for applications, such as text messaging, that exchange data as payload in the SIP message. SIP works in conjunction with several other protocols that specify and carry the session media. Most commonly, media type and parameter negotiation and media setup are performed with the Session Descripti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |