|
Rubidgeines
Rubidgeinae is an extinct subfamily of gorgonopsid therapsids known only from Africa. They were among the largest gorgonopsians, and their fossils are common in the Cistecephalus and Daptocephalus assemblage zones of the Karoo Basin. They lived during the Late Permian, and became extinct at the end of the Permian. Description Rubidgeines were large, quadrupedal carnivores of the family Gorgonopsidae. Their largest teeth are their upper canines, which were blade-like and had well-developed serrations. Their postcanine teeth were small and conical, but were also frequently serrated. Tooth replacement was rapid relative to basal therocephalians. Rubidgeines can be distinguished from other gorgonopsians by the absence of a blade-like parasphenoid bone and reduced or absent preparietal bone. The jugal bone, while narrow in most gorgonopsians, was often broadly expanded in rubidgeines. The largest rubidgeins were '' Dinogorgon'' and '' Rubidgea''. Paleobiology Rubidgeines were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gorgonopsid
Gorgonopsia (from the Greek Gorgon, a mythological beast, and 'aspect') is an extinct clade of sabre-toothed therapsids from the Middle to Upper Permian roughly 265 to 252 million years ago. They are characterised by a long and narrow skull, as well as elongated upper and sometimes lower canine teeth and incisors which were likely used as slashing and stabbing weapons. Postcanine teeth are generally reduced or absent. For hunting large prey, they possibly used a bite-and-retreat tactic, ambushing and taking a debilitating bite out of the target, and following it at a safe distance before its injuries exhausted it, whereupon the gorgonopsian would grapple the animal and deliver a killing bite. They would have had an exorbitant gape, possibly in excess of 90°, without having to unhinge the jaw. They markedly increased in size as time went on, growing from small skull lengths of in the Middle Permian to bear-like proportions of up to in the Upper Permian. The latest gorgono ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gorgonopsidae
Gorgonopsia (from the Greek Gorgon, a mythological beast, and 'aspect') is an extinct clade of sabre-toothed therapsids from the Middle to Upper Permian roughly 265 to 252 million years ago. They are characterised by a long and narrow skull, as well as elongated upper and sometimes lower canine teeth and incisors which were likely used as slashing and stabbing weapons. Postcanine teeth are generally reduced or absent. For hunting large prey, they possibly used a bite-and-retreat tactic, ambushing and taking a debilitating bite out of the target, and following it at a safe distance before its injuries exhausted it, whereupon the gorgonopsian would grapple the animal and deliver a killing bite. They would have had an exorbitant gape, possibly in excess of 90°, without having to unhinge the jaw. They markedly increased in size as time went on, growing from small skull lengths of in the Middle Permian to bear-like proportions of up to in the Upper Permian. The latest gorgonop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rubidgeini
Rubidgeinae is an extinct subfamily of gorgonopsid therapsids known only from Africa. They were among the largest gorgonopsians, and their fossils are common in the Cistecephalus and Daptocephalus assemblage zones of the Karoo Basin. They lived during the Late Permian, and became extinct at the end of the Permian. Description Rubidgeines were large, quadrupedal carnivores of the family Gorgonopsidae. Their largest teeth are their upper canines, which were blade-like and had well-developed serrations. Their postcanine teeth were small and conical, but were also frequently serrated. Tooth replacement was rapid relative to basal therocephalians. Rubidgeines can be distinguished from other gorgonopsians by the absence of a blade-like parasphenoid bone and reduced or absent preparietal bone. The jugal bone, while narrow in most gorgonopsians, was often broadly expanded in rubidgeines. The largest rubidgeins were ''Dinogorgon'' and ''Rubidgea''. Paleobiology Rubidgeines were among ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinogorgon Rubidgei
''Dinogorgon'' is a genus of gorgonopsid from the Late Permian of South Africa and Tanzania. The generic name ''Dinogorgon'' is derived from Greek, meaning "terrible gorgon", while its species name ''rubidgei'' is taken from the surname of renowned Karoo paleontologist, Professor Bruce Rubidge, who has contributed to much of the research conducted on therapsids of the Karoo Basin. The type species of the genus is ''D. rubidgei''. ''Dinogorgon'' is part of the gorgonopsian subfamily Rubidgeinae, a derived group of large-bodied gorgonopsians restricted to the Late Permian (Lopingian). The Rubidgeinae subfamily first appeared in the ''Tropidostoma'' Assemblage Zone, and reached their highest diversity in the ''Cistecephalus'' and ''Daptocephalus'' assemblage zones of the Beaufort Group in South Africa. History of discovery The type species of ''Dinogorgon rubidgei'' was discovered on Wellwood farm, a farm owned by the grandfather of Bruce Rubidge, Sidney H. Rubidge, outside of G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smilesaurus Ferox
''Smilesaurus'' is an extinct genus of gorgonopsian known from Africa. It lived during the Late Permian. It contains the single species ''S. ferox''. Description ''Smilesaurus'' was a large gorgonopsian, with a skull length of up to 31 centimeters. It is characterized by extremely long canine teeth, and has the proportionally longest canines of any gorgonopsian. Unlike other gorgonopsians, which probably hunted similarly to predatory reptiles, ''Smilesaurus'' probably was a true saber-toothed predator which hunted using similar tactics to saber-toothed cats. It can be distinguished by other rubidgeines by its lack of cranial pachyostosis and rugosoties, and by its relatively small orbits. Classification The classification of ''Smilesaurus'' has been disputed. It has often been included in Rubidgeinae, but it differs from other members of the clade considerably. Instead, it may be more closely related to '' Arctops'', a position supported by a phylogenetic analysis in 2018. Bel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clelandina
''Clelandina'' is an extinct genus of rubidgeine gorgonopsian from the Late Permian of ''Cistecephalus'' Assemblage Zone of South Africa. It was first named by Broom in 1948. The type and only species is ''C. rubidgei''. It is relatively rare, with only four known specimens. Description ''Clelandina rubidgei'' has an extraordinarily small sclerotic ring relative to the size of its orbit, which implies that it was diurnal. It is the only rubidgeine with a preserved sclerotic ring, so it is unknown whether this trait was shared by other members of the subfamily. Like all rubidgeines, it was relatively large, with a skull up to 36 cm long. It had reduced dentition, with the teeth posterior to the canines being absent and replaced with a bony ridge. The skull has heavily pachyostosed, with massive rugose bosses. Classification ''Clelandina'' shares many characteristics with the contemporary ''Rubidgea'', and is currently recognized as the sister taxon of this genus. Toge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinogorgon
''Dinogorgon'' is a genus of gorgonopsid from the Late Permian of South Africa and Tanzania. The generic name ''Dinogorgon'' is derived from Greek, meaning "terrible gorgon", while its species name ''rubidgei'' is taken from the surname of renowned Karoo paleontologist, Professor Bruce Rubidge, who has contributed to much of the research conducted on therapsids of the Karoo Basin. The type species of the genus is ''D. rubidgei''. ''Dinogorgon'' is part of the gorgonopsian subfamily Rubidgeinae, a derived group of large-bodied gorgonopsians restricted to the Late Permian (Lopingian). The Rubidgeinae subfamily first appeared in the ''Tropidostoma'' Assemblage Zone, and reached their highest diversity in the ''Cistecephalus'' and ''Daptocephalus'' assemblage zones of the Beaufort Group in South Africa. History of discovery The type species of ''Dinogorgon rubidgei'' was discovered on Wellwood farm, a farm owned by the grandfather of Bruce Rubidge, Sidney H. Rubidge, outside of G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Predation
Predation is a biological interaction where one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey. It is one of a family of common feeding behaviours that includes parasitism and micropredation (which usually do not kill the host) and parasitoidism (which always does, eventually). It is distinct from scavenging on dead prey, though many predators also scavenge; it overlaps with herbivory, as seed predators and destructive frugivores are predators. Predators may actively search for or pursue prey or wait for it, often concealed. When prey is detected, the predator assesses whether to attack it. This may involve ambush or pursuit predation, sometimes after stalking the prey. If the attack is successful, the predator kills the prey, removes any inedible parts like the shell or spines, and eats it. Predators are adapted and often highly specialized for hunting, with acute senses such as vision, hearing, or smell. Many predatory animals, both vertebrate and inv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theropod
Theropoda (; ), whose members are known as theropods, is a dinosaur clade that is characterized by hollow bones and three toes and claws on each limb. Theropods are generally classed as a group of saurischian dinosaurs. They were ancestrally carnivorous, although a number of theropod groups evolved to become herbivores and omnivores. Theropods first appeared during the Carnian age of the late Triassic period 231.4 million years ago ( Ma) and included all the large terrestrial carnivores from the Early Jurassic until at least the close of the Cretaceous, about 66 Ma. In the Jurassic, birds evolved from small specialized coelurosaurian theropods, and are today represented by about 10,500 living species. Biology Diet and teeth Theropods exhibit a wide range of diets, from insectivores to herbivores and carnivores. Strict carnivory has always been considered the ancestral diet for theropods as a group, and a wider variety of diets was historically considered a characteri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinosaurs
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the evolution of dinosaurs is the subject of active research. They became the dominant terrestrial vertebrates after the Triassic–Jurassic extinction event 201.3 mya; their dominance continued throughout the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods. The fossil record shows that birds are feathered dinosaurs, having evolved from earlier theropods during the Late Jurassic epoch, and are the only dinosaur lineage known to have survived the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event approximately 66 mya. Dinosaurs can therefore be divided into avian dinosaurs—birds—and the extinct non-avian dinosaurs, which are all dinosaurs other than birds. Dinosaurs are varied from taxonomic, morphological and ecological standpoints. Birds, at over 10,700 living species, are among ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ruhuhucerberus Haughtoni
''Ruhuhucerberus'' is a genus of very large, extinct Extinction is the termination of a kind of organism or of a group of kinds (taxon), usually a species. The moment of extinction is generally considered to be the death of the last individual of the species, although the capacity to breed and ... gorgonopsian therapsids which existed in Tanzania during the Late Permian. Its fossils are found in the Penman Kawinga Formation of the Ruhuhu Basin. It existed sympatrically with the even larger '' Rubidgea''. References Gorgonopsia Prehistoric therapsid genera Lopingian synapsids of Africa Lopingian genus first appearances Lopingian genus extinctions {{paleo-therapsid-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
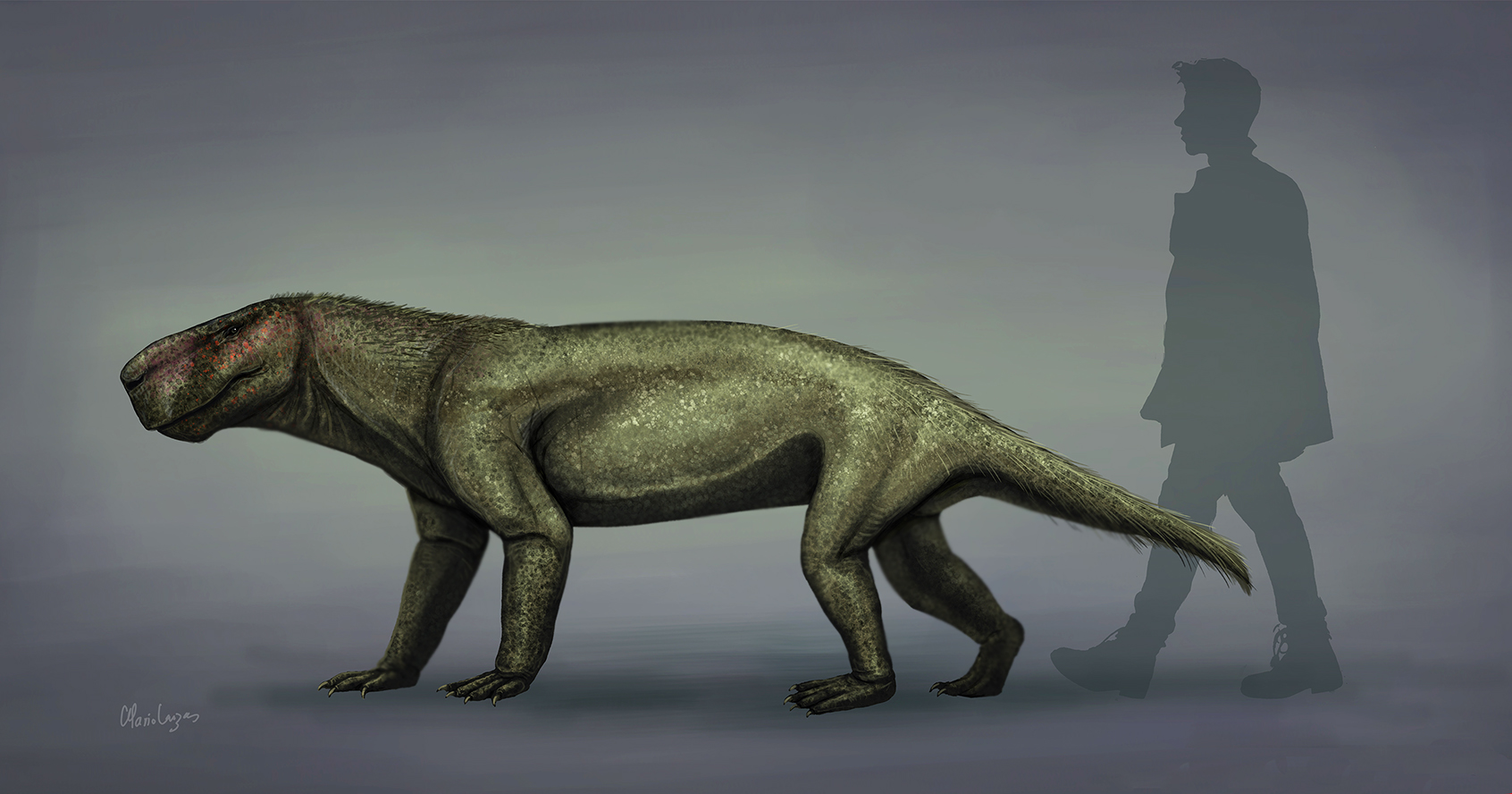





_with_its_prey.jpg)

